1/5
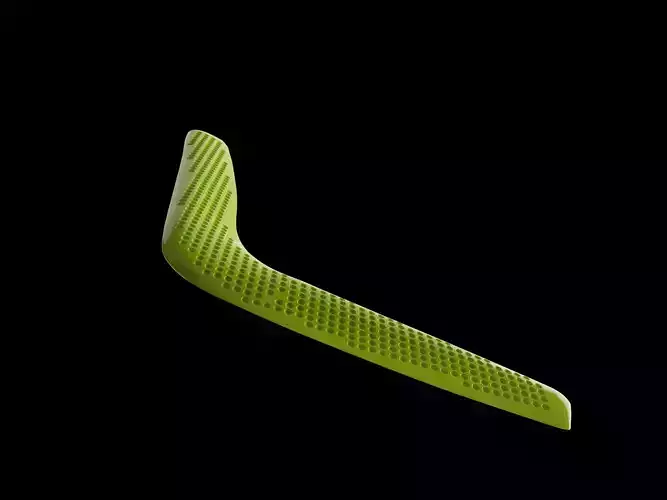
Printable right- handed boomerang. You can use any material, i used abs but i think it is better to use more flexible material. It's quite large, no big deal if you scale it. It will be better to use more percentage of infill - the more weight the better. Throw it with tilt 15-45° and try to make it spin faster as possible. You need open area 50/50m. Good luck)
Aerodynamics:
A returning boomerang is a rotating wing. It consists of two or more arms, or wings, connected at an angle; each wing is shaped as an airfoil section. Although it is not a requirement that a boomerang be in its traditional shape, it is usually flat.Boomerangs can be made for right- or left-handed throwers. The difference between right and left is subtle, the planform is the same but the leading edges of the aerofoil sections are reversed. A right-handed boomerang makes a counter-clockwise, circular flight to the left while a left-handed boomerang flies clockwise to the right. Most sport boomerangs weigh between 70 and 110 grams (2.5 and 3.9 oz), have a 250–350 millimetres (9.8–13.8 in) wingspan and a 20–40 m (22–44 yd) range.A falling boomerang starts spinning, and most then fall in a spiral. When the boomerang is thrown with high spin, a boomerang flies in a curved rather than a straight line. When thrown correctly, a boomerang returns to its starting point. As the wing rotates and the boomerang moves through the air, the airflow over the wings creates lift on both wings. However, during one-half of each blade's rotation, it sees a higher airspeed, because the rotation tip speed and the forward speed add, and when it is in the other half of the rotation, the tip speed subtracts from the forward speed. Thus if thrown nearly upright, each blade generates more lift at the top than the bottom. While it might be expected that this would cause the boomerang to tilt around the axis of travel, because the boomerang has significant angular momentum, the gyroscopic precession causes the plane of rotation to tilt about an axis that is 90 degrees to the direction of flight, causing it to turn. When thrown in the horizontal plane, as with a Frisbee, instead of in the vertical, the same gyroscopic precession will cause the boomerang to fly violently, straight up into the air and then crash.
Fast Catch boomerangs usually have three or more symmetrical wings (seen from above), whereas a Long Distance boomerang is most often shaped similar to a question mark. Maximum Time Aloft boomerangs mostly have one wing considerably longer than the other. This feature, along with carefully executed bends and twists in the wings help to set up an auto-rotation effect to maximise the boomerang's hover time in descending from the highest point in its flight.
Some boomerangs have turbulators — bumps or pits on the top surface that act to increase the lift as boundary layer transition activators (to keep attached turbulent flow instead of laminar separation).
REVIEWS & COMMENTS
accuracy, and usability.