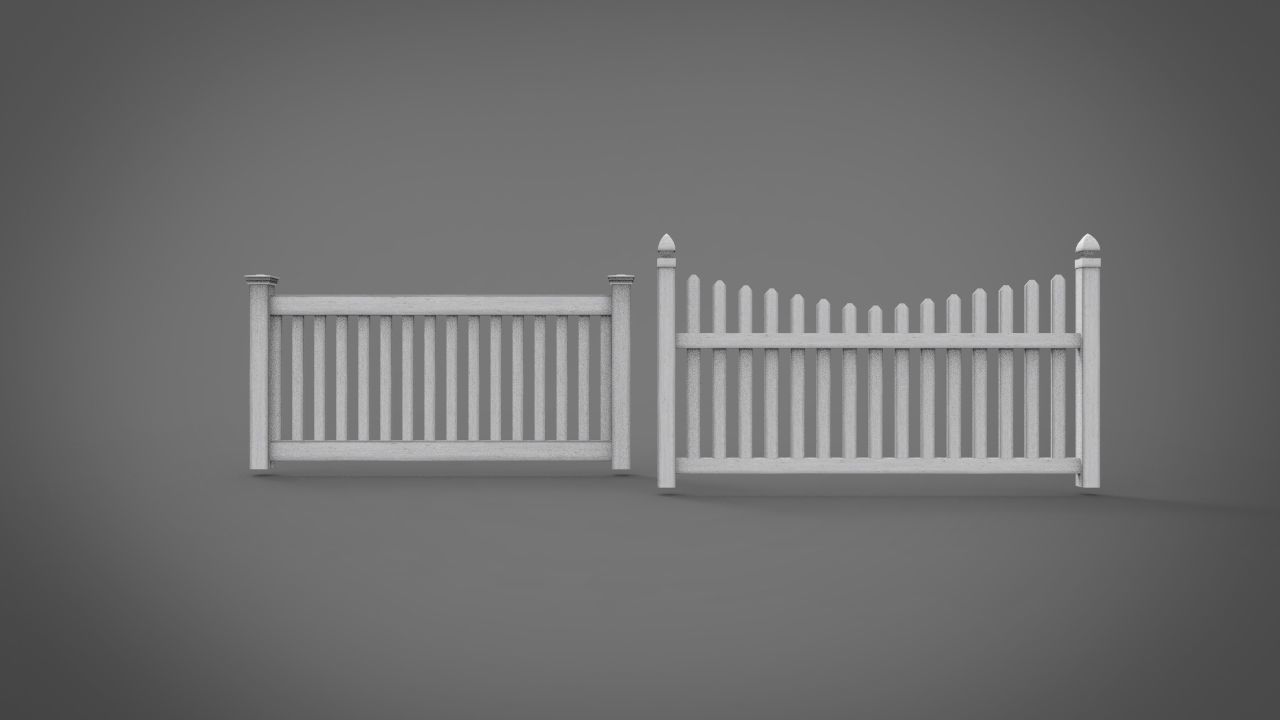
Pillar architecture 3D print model
Pillar architecture refers to the use and design of pillars (or columns) in building structures, which serve both structural and decorative functions. Pillars are vertical supports that transfer the weight of a structure from the roof or upper floors down to the foundation. Key aspects of pillar architecture include:
Structural Function: Pillars support beams or arches, helping to distribute the load of the building evenly and maintain stability. They are essential in many architectural styles and periods, providing strength and support.
Architectural Styles: Different architectural styles use pillars in various ways:
Classical Architecture: Includes styles like Doric, Ionic, and Corinthian columns from ancient Greek and Roman architecture, characterized by their specific proportions and decorative elements.Gothic Architecture: Features slender, elongated columns with intricate detailing that contribute to the verticality and lightness of the structures.Modern Architecture: Uses streamlined, minimalistic pillars that often emphasize functionality and simplicity.Decorative Elements: Pillars can be ornately designed with carvings, capitals (the top part of the pillar), and bases, adding to the aesthetic appeal of a building. They can also be used to create a sense of grandeur or formality.
Materials: Pillars can be constructed from various materials, including stone, concrete, steel, and wood, depending on the structural requirements and design preferences.
Pillar architecture plays a crucial role in both the functionality and aesthetic value of a building, offering a blend of structural integrity and artistic expression