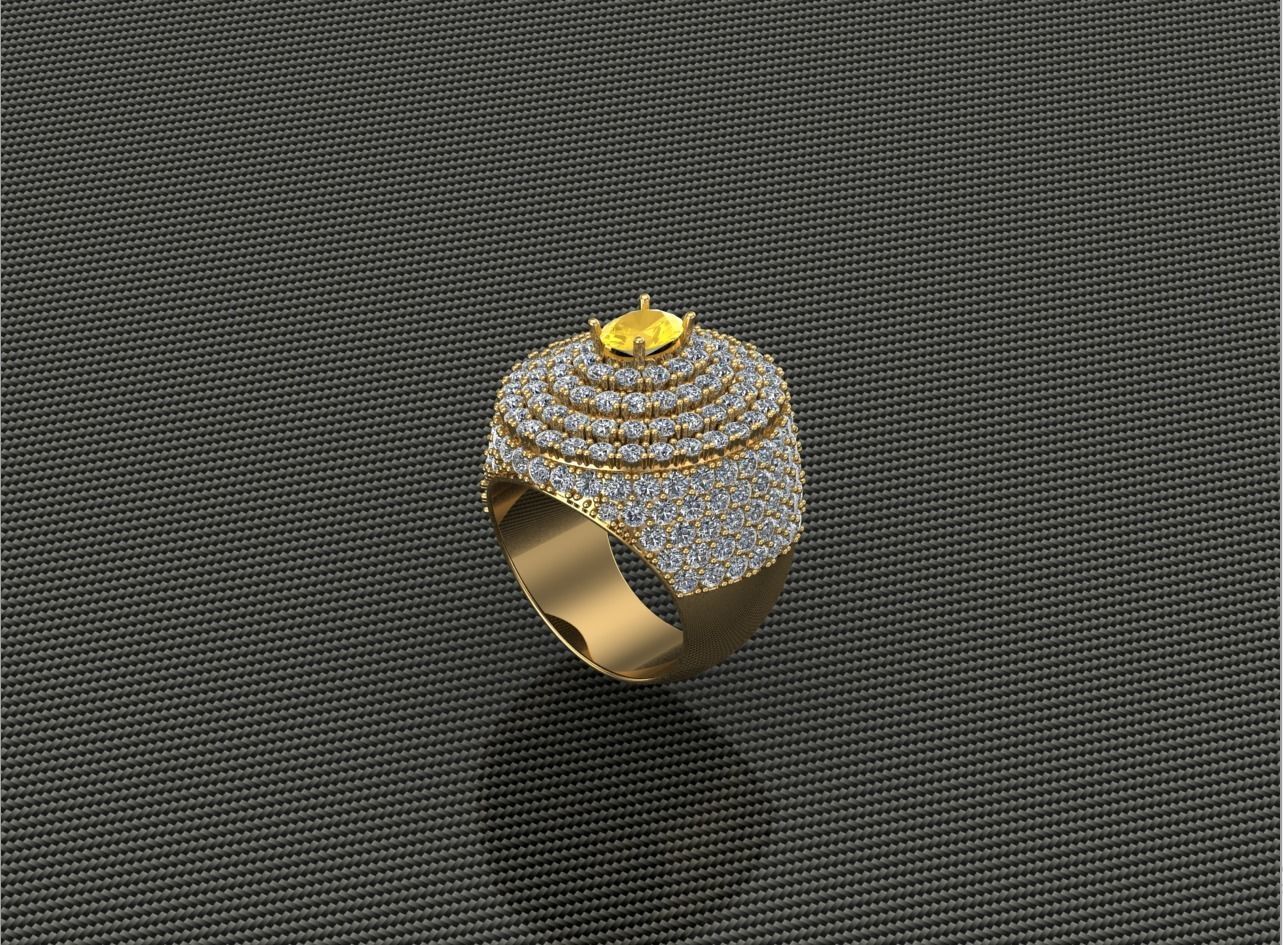
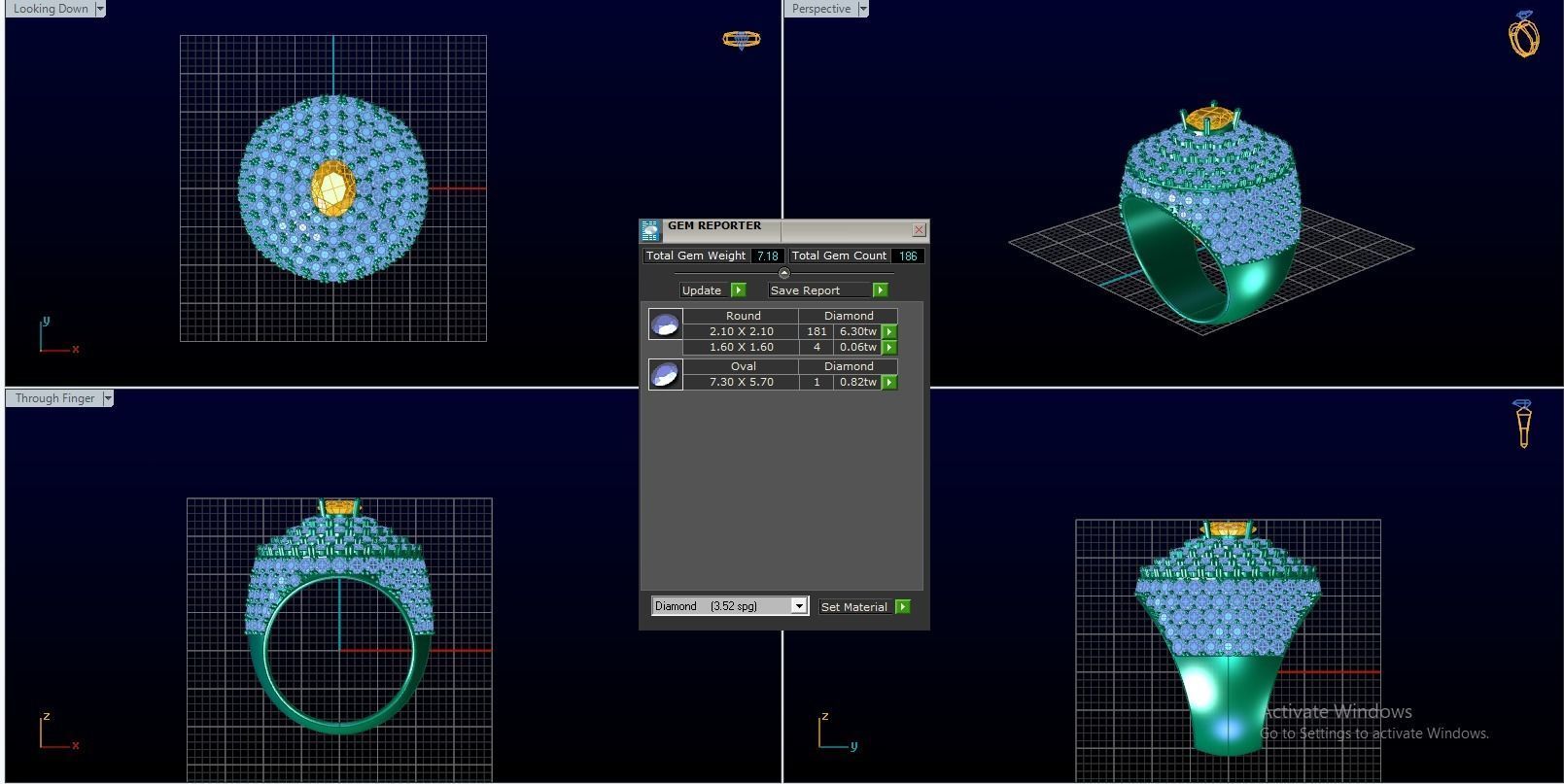
Diamond Ring 3D print model
This article is about the mineral. For the gemstone, see Diamond (gemstone). For other uses, see Diamond (disambiguation).DiamondA triangular prism-shaped diamondA naturally-cut diamond crystalGeneralCategory Native mineralsFormula(repeating unit) CIMA symbol Dia[1]Strunz classification 1.CB.10aDana classification 1.3.6.1Crystal system CubicCrystal class Hexoctahedral (m3m)H-M symbol: (4/m 3 2/m)Space group Fd3m (No. 227)StructureJmol (3D) Interactive imageIdentificationFormula mass 12.01 g/molColor Typically yellow, brown, or gray to colorless. Less often blue, green, black, translucent white, pink, violet, orange, purple, and red.Crystal habit OctahedralTwinning Spinel law common (yielding macle)Cleavage 111 (perfect in four directions)Fracture Irregular/UnevenMohs scale hardness 10 (defining mineral)Luster AdamantineStreak ColorlessDiaphaneity Transparent to subtransparent to translucentSpecific gravity 3.52±0.01Density 3.5–3.53 g/cm3 3500–3530 kg/m3Polish luster AdamantineOptical properties IsotropicRefractive index 2.418 (at 500 nm)Birefringence NonePleochroism NoneDispersion 0.044Melting point Pressure dependentReferences [2][3]
Main diamond producing countriesDiamond is a solid form of the element carbon with its atoms arranged in a crystal structure called diamond cubic. Another solid form of carbon known as graphite is the chemically stable form of carbon at room temperature and pressure, but diamond is metastable and converts to it at a negligible rate under those conditions. Diamond has the highest hardness and thermal conductivity of any natural material, properties that are used in major industrial applications such as cutting and polishing tools. They are also the reason that diamond anvil cells can subject materials to pressures found deep in the Earth.
Because the arrangement of atoms in diamond is extremely rigid, few types of impurity can contaminate it (two exceptions are boron and nitrogen). Small numbers of defects or impurities (about one per million of lattice atoms) color diamond blue (boron), yellow (nitrogen), brown (defects), green (radiation exposure), purple, pink, orange, or red. Diamond also has a very high refractive index and a relatively high optical dispersion.
Most natural diamonds have ages between 1 billion and 3.5 billion years. Most were formed at depths between 150 and 250 kilometres (93 and 155 mi) in the Earth's mantle, although a few have come from as deep as 800 kilometres (500 mi). Under high pressure and temperature, carbon-containing fluids dissolved various minerals and replaced them with diamonds. Much more recently (hundreds to tens of million years ago), they were carried to the surface in volcanic eruptions and deposited in igneous rocks known as kimberlites and lamproites.
Synthetic diamonds can be grown from high-purity carbon under high pressures and temperatures or from hydrocarbon gases by chemical vapor deposition (CVD). Imitation diamonds can also be made out of materials such as cubic zirconia and silicon carbide. Natural, synthetic, and imitation diamonds are most commonly distinguished using optical techniques or thermal conductivity measurements.