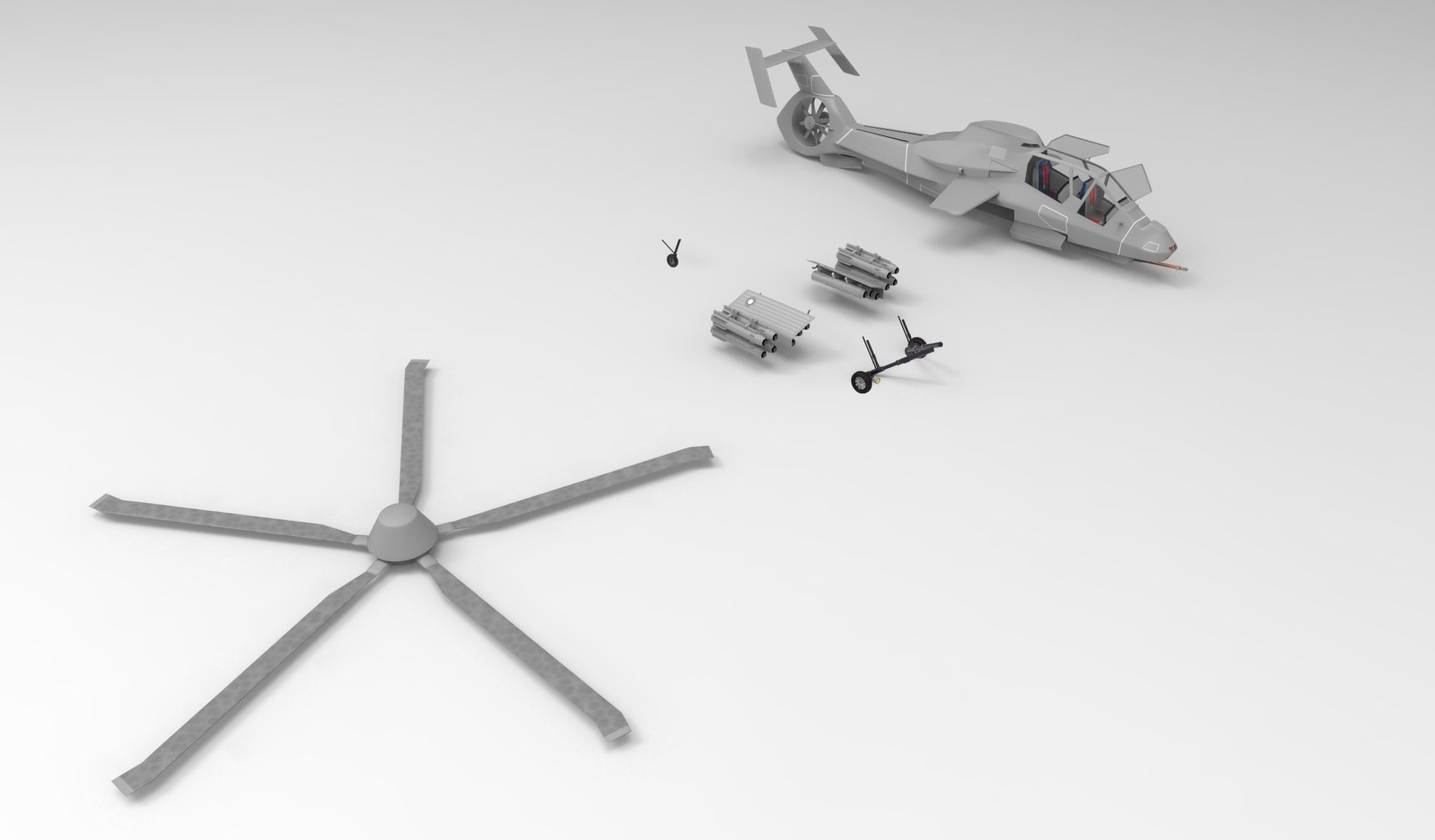
RAH 66 grey 3D Printed 3D print model
During the early 1980s, the US Army began to formulate requirements for replacement of the helicopters then in service, which resulted in the launch of the Light Helicopter Experimental (LHX) program. Nearly a decade later, after refinement of requirements, evaluation of submissions, and rebranding of the program as the Light Helicopter (LH) program, during April 1991, the Army announced the selection of the Boeing – Sikorsky design team as the winner of the contest, shortly after which the contract for the construction of the prototype was awarded. Comanche will incorporate some advanced elements, such as stealth technology, and a number of never-before-tested design features. Operationally, it uses advanced sensors in its reconnaissance role, where it is intended to set targets for the AH-64 Apache. It is also armed with a single rotary cannon and can carry missiles and rockets in the internal bay and optionally on the stub wing for light attack duty.
Two RAH-66 prototypes were built and underwent flight testing between 1996 and 2004. On June 1, 2000, the program entered a $3.1 billion engineering and manufacturing development (EMD) phase. However, during 2002, the Comanche program underwent a major restructuring; the number of Comanche to be purchased was cut to 650. At that time, the total projected cost for the full production of Comanche in that amount was $26.9 billion. Since the late 1990s, the Government Accountability Office (GAO) has reported that it has serious doubts about the program, The Boeing-Sikorsky RAH-66 Comanche is an American stealth armed reconnaissance and attack helicopter designed for the United States Army. After decades of development, during 2004, the RAH-66 program was canceled before mass production began, of which nearly US$7 billion was spent on the program.observing that Comanche will spent nearly two-thirds of the entire Aviation budget in Fiscal Year 2008. Several government agencies have acted to reduce the number of Comanches ordered, but, as a consequence of the massive reduction in the number to be purchased, unit costs have soared.
On February 23, 2004, the US Army announced the termination of the Comanche program, stating that it had determined that the RAH-66 would require major upgrades to survive on the battlefield and that the service would instead direct the majority of its rotary system funds toward renovating attack helicopters, utilities, and existing reconnaissance. The Army also announced new plans to accelerate development of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), which can also perform the reconnaissance role intended for the Comanche, but with less risk. Since the cancellation of the program, both prototypes have been placed on public screens.