1/6
China, officially the People's Republic of China, is a unitary sovereign state in East Asia and the world's most populous country, with a population of around 1.404 billion. Covering approximately 9,600,000 square kilometers (3,700,000 sq mi), it is the third- or fourth-largest country by total area, depending on the source consulted. China also has the most neighbor countries in the world. Governed by the Communist Party of China, it exercises jurisdiction over 22 provinces, five autonomous regions, four direct-controlled municipalities (Beijing, Tianjin, Shanghai, and Chongqing), and the special administrative regions of Hong Kong and Macau.
China emerged as one of the world's earliest civilizations, in the fertile basin of the Yellow River in the North China Plain. For millennia, China's political system was based on hereditary monarchies, or dynasties, beginning with the semi-legendary Xia dynasty in 21st century BCE. Since then, China has expanded, fractured, and re-unified numerous times. In the 3rd century BCE, the Qin unified core China and established the first Chinese dynasty. The succeeding Han dynasty saw some of the most advanced technology at that time, including papermaking and the compass, along with agricultural and medical improvements. The invention of gunpowder and printing in the Tang dynasty completed the Four Great Inventions. Tang culture spread widely in Asia, as the new maritime Silk Route brought traders to as far as Mesopotamia and Somalia. Dynastic rule ended in 1912 with the Xinhai Revolution, as a republic replaced the Qing dynasty. The Chinese Civil War led to the break up of the country in 1949, with the victorious Communist Party of China founding the People’s Republic of China on the mainland while the losing Kuomintang retreated to Taiwan, a dispute which is still unresolved.
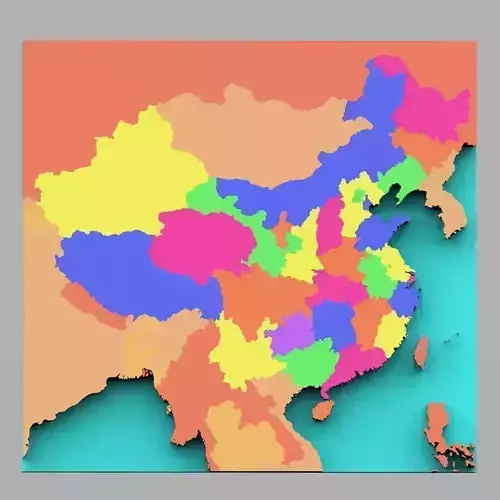
This is a digital model of the country of China with color-coded regions, as well as bordering countries such as Cambodia, India, Mongolia, Mynamar, Russia, Vietnam, and more.
Product Features:
- Approx 117471 polygons.
- Made with 3 and 4 point polygons.
- Includes different colors to separate the regions.
- Includes parts representing regions in the country.
- This version includes an mtl file, which your software program should read to colorize the model.
- The model has basic UV mapping and NO textures are included.
REVIEWS & COMMENTS
accuracy, and usability.