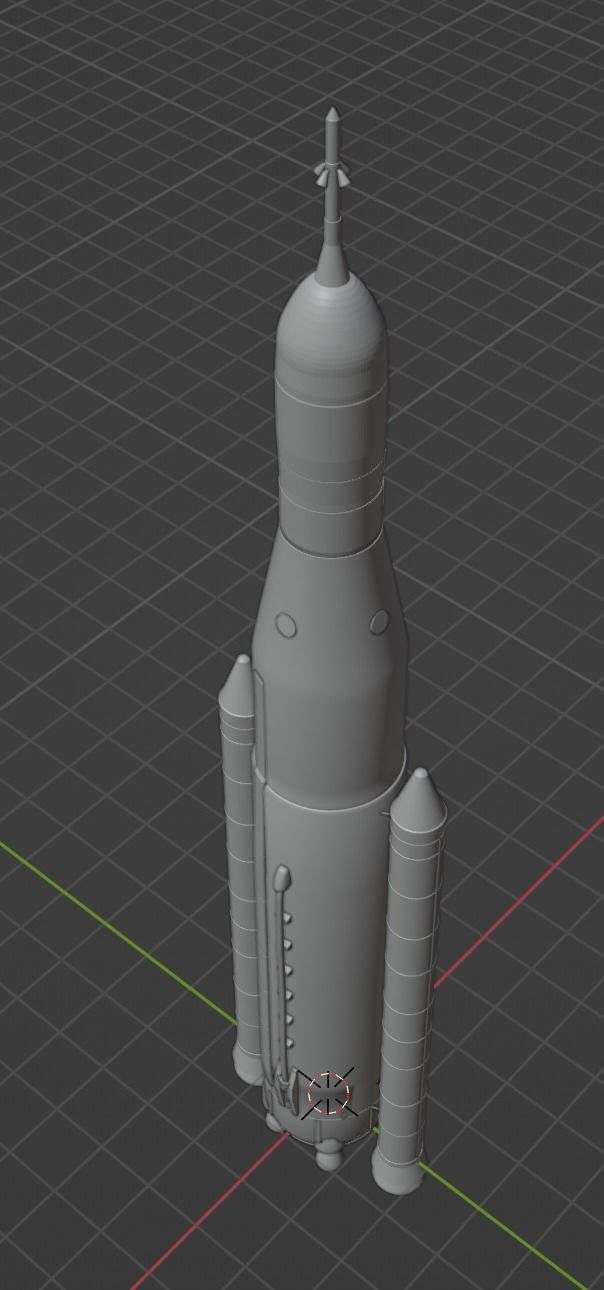
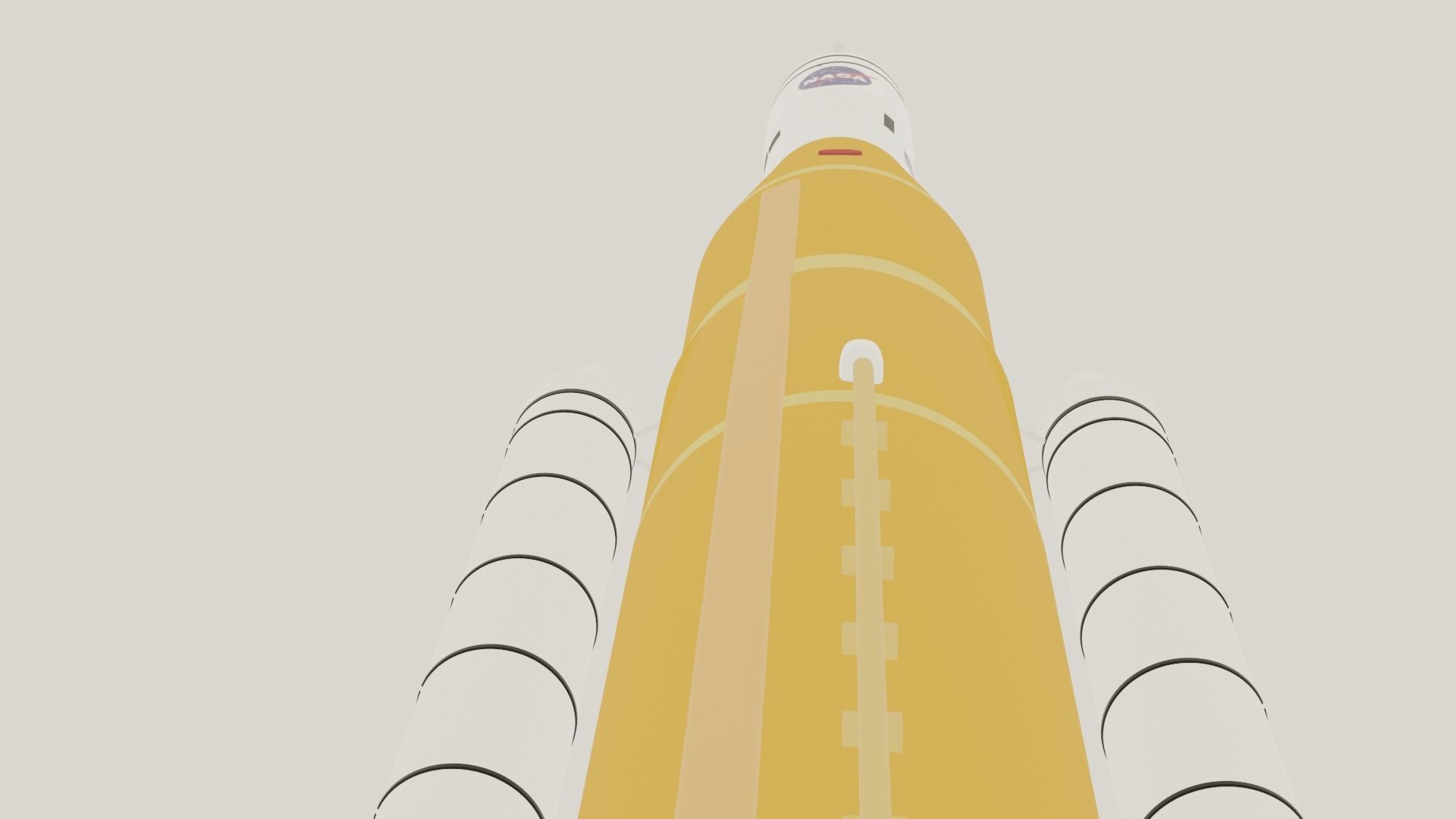
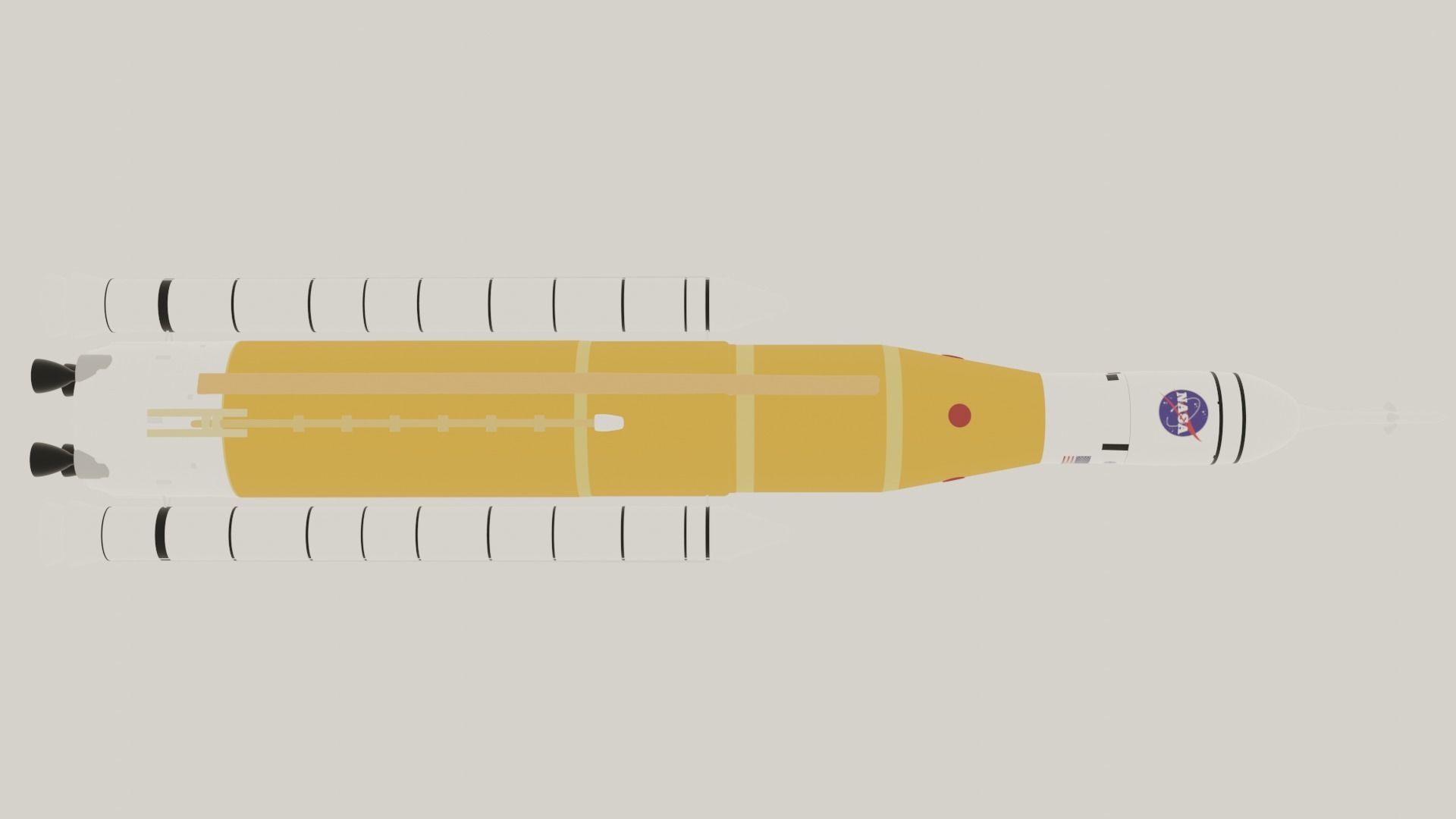
SLS space launch system Block 1 Low-poly 3D model
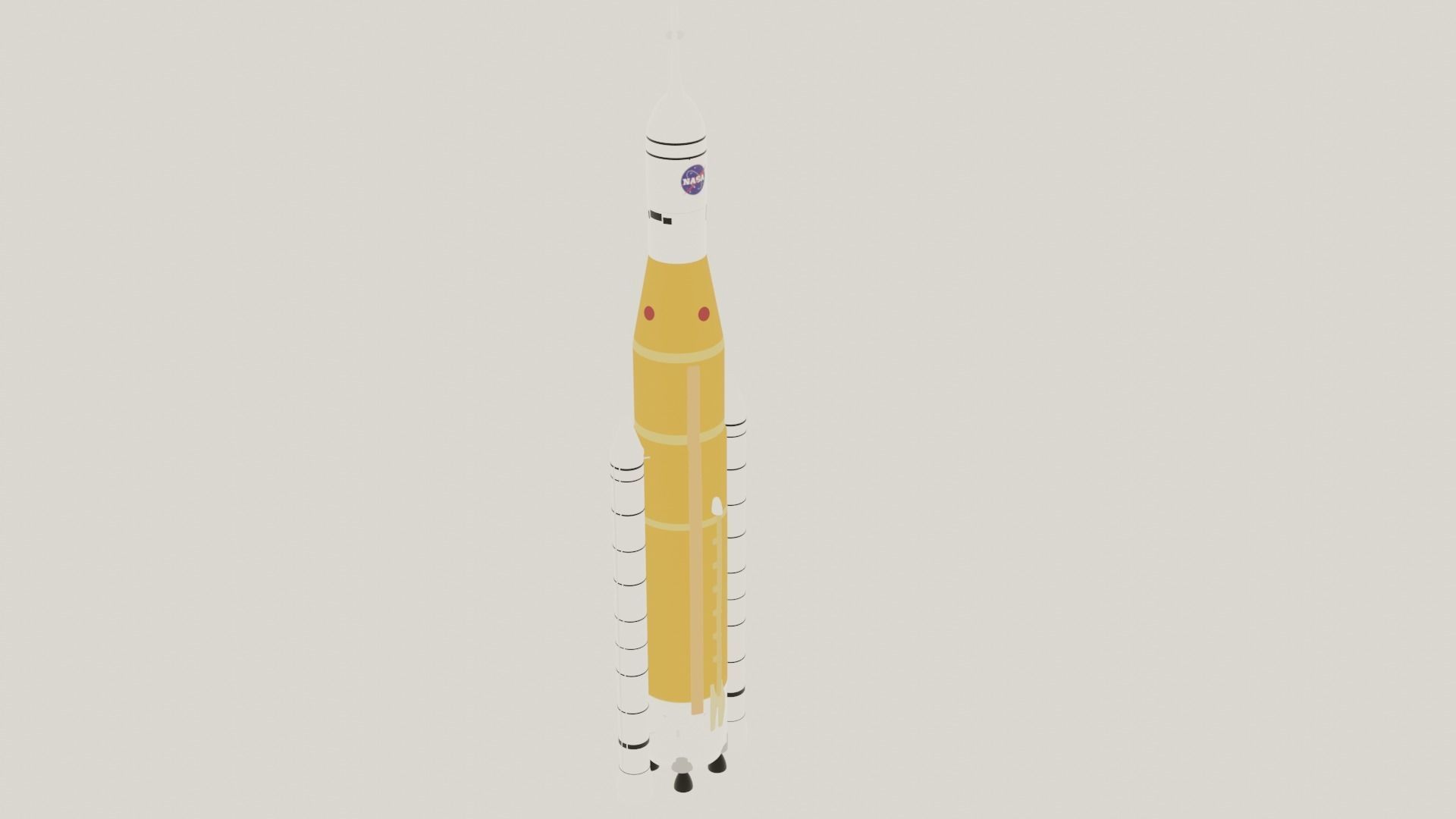
The Space Launch System (SLS) is an American super heavy-lift expendable launch vehicle developed by NASA. As of 2022, SLS has the highest payload capacity of any rocket in operational service, as well as the greatest liftoff thrust of any rocket in operation.[24][25][26] As the primary launch vehicle of the Artemis moon landing program, SLS is designed to launch the crewed Orion spacecraft on a trans-lunar trajectory. The first uncrewed launch, Artemis 1, took place on 16 November 2022. Although the SLS is only confirmed for use on the first few Artemis missions, many NASA mission concept studies for robotic missions planned to launch on the SLS, such as: Neptune Odyssey,[233][234] Europa Lander,[235][236][237] Enceladus Orbilander, Persephone,[238] HabEx,[117] Origins Space Telescope,[116] LUVOIR,[239] Lynx,[240] and Interstellar probe.[241] These concept studies were prepared for possible recommendation by the National Academy's Decadal surveys. The Astronomy and Astrophysics Decadal Survey in 2021 recommended a smaller, merged version of HabEx and LUVOIR preceded by a technology maturation program to reduce cost and schedule risk, although the eventual mission may or may not use SLS. In 2022 the Planetary Science Decadal Survey recommended Enceladus Orbilander as the third highest priority for flagship planetary missions in the 2020s. The Heliophysics Decadal Survey, due to be completed in 2024, is considering the Interstellar Probe mission concept.