Useto navigate. Pressescto quit
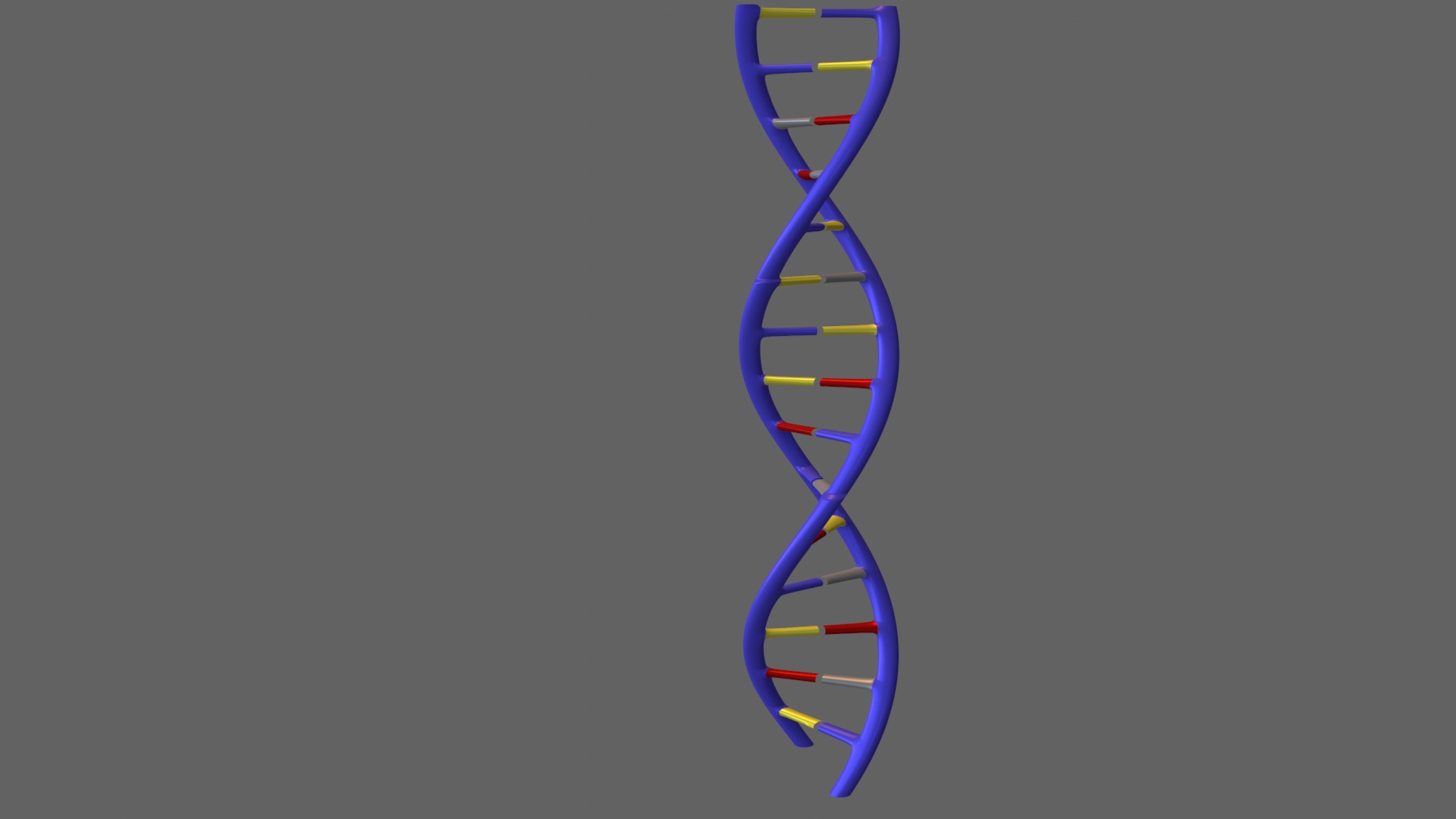
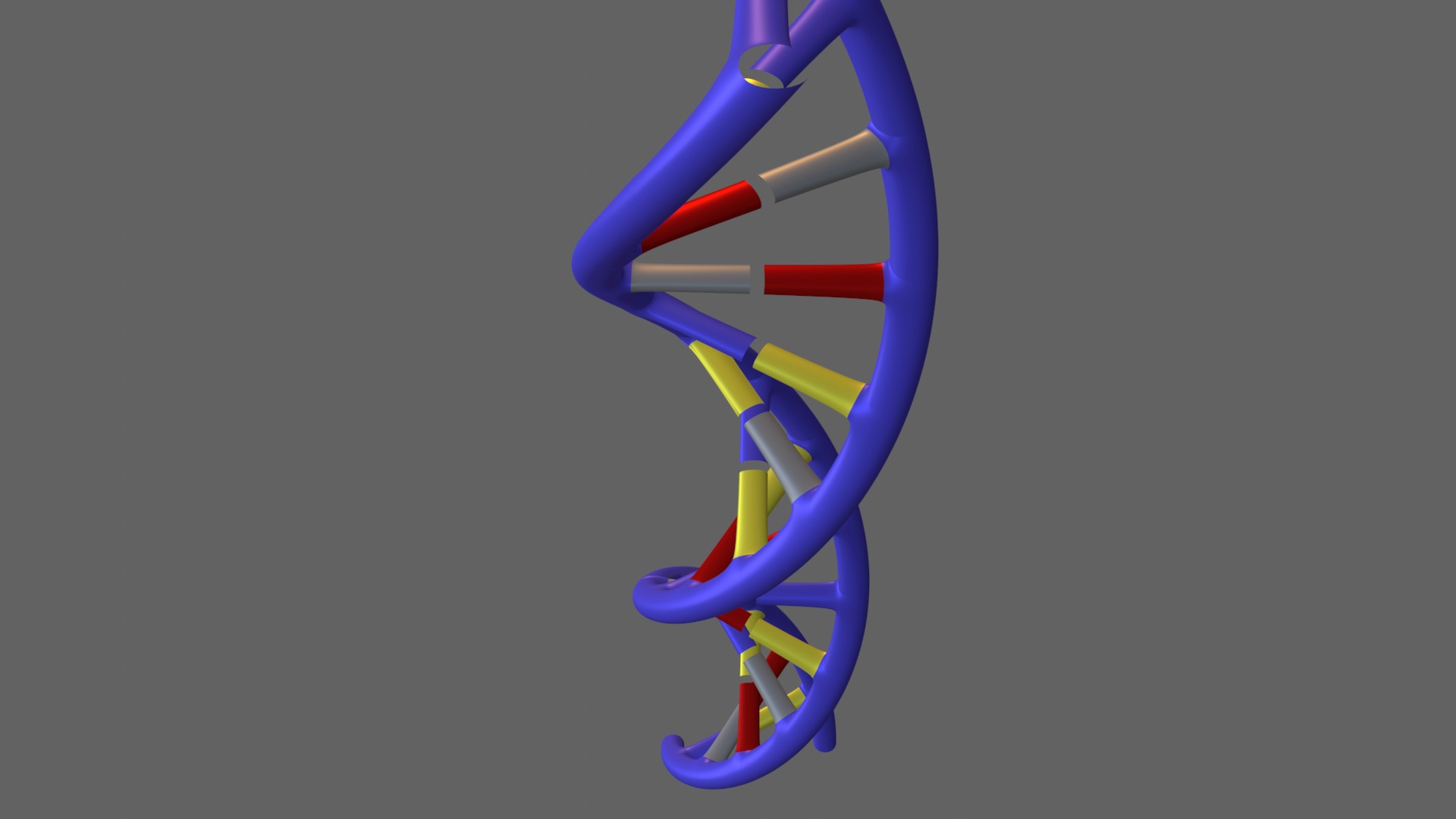
The DNA helix 3D model
Verification details of the FBX file
Files
Binary FBX
Scene
No unsupported objects
Geometry
No N-gonsNo faceted geometryManifold geometry
Textures and Materials
PBR texturesNo embed texturesSquare texturesPower of 2 texture sizesAssigned materials
UVs
No UV overlapsUV unwrapped model
Naming
Allowed characters
Description
The DNA helix is the structure that carries genetic information in our cells. Known as a double helix, the DNA structure consists of two strands that twist around each other, forming a spiral shape. Each strand is made up of small units called nucleotides. There are four basic types of nucleotides: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C). Adenine pairs with thymine, and guanine pairs with cytosine. These pairings help keep the strands together. The structure of DNA is crucial for encoding genetic information and copying this information during cell division. DNA forms the foundation of biological diversity and passes traits from one generation to the next.