Twin Turbo V12 Engine 3D model
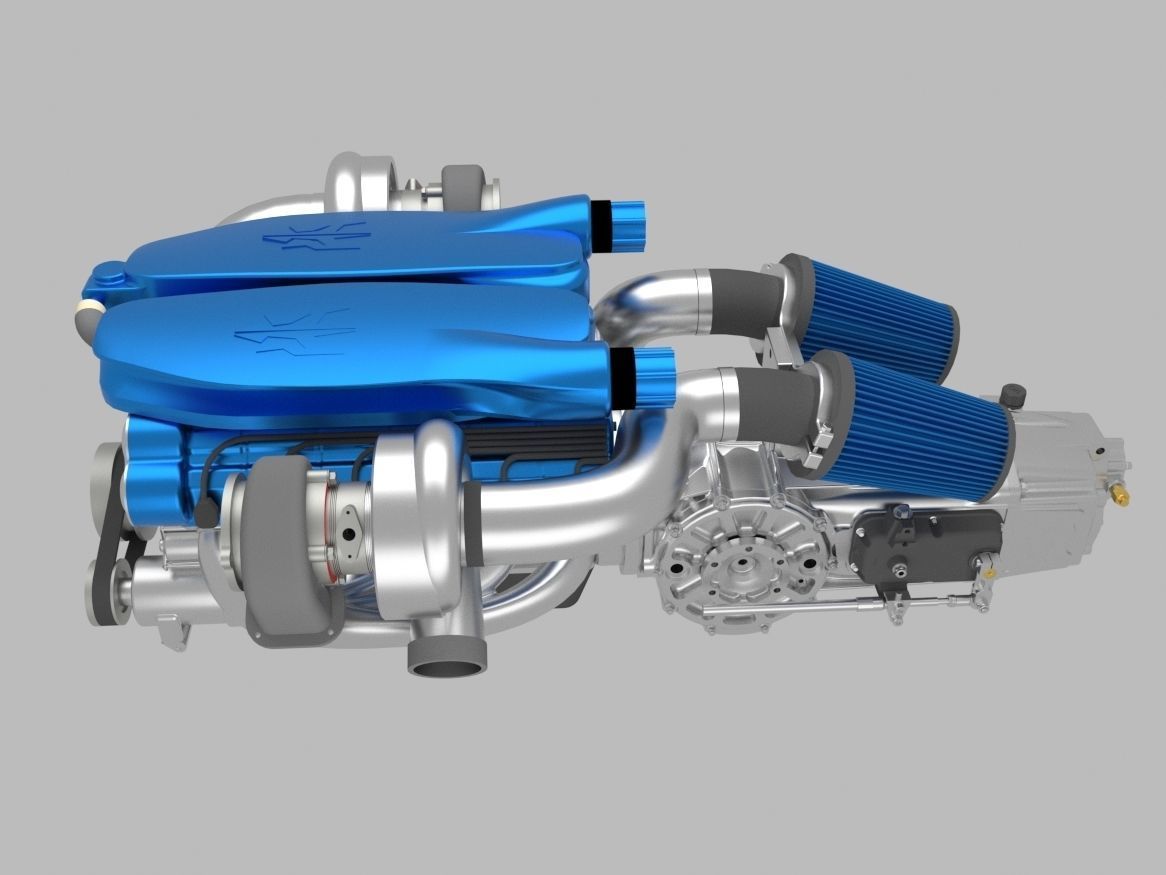
Twin Turbo V12 EngineTwin-turbo (not to be confused with a twincharger setup, which is a combination of a supercharger and a turbocharger) refers to an engine in which two turbochargers compress the intake fuel/air mixture (or intake air, in the case of a direct-injection engine). The most common layout features two identical or mirrored turbochargers in parallel, each processing half of a V engine's produced exhaust through independent piping. The two turbochargers can either be identical or different sizes (i.e. one large and one small).A parallel configuration refers to using two equally-sized turbochargers which each receive half of the exhaust gases.[2] Some designs combine the intake charge from each turbocharger into a single intake manifold, while others use a separate intake manifold for each turbocharger.
Parallel configurations are well suited to V6 and V8 engines since each turbocharger can be assigned to one cylinder bank, reducing the amount of exhaust piping needed. In this case, each turbocharger is fed exhaust gases by a separate exhaust manifold. For four-cylinder engines and straight-six engines, both turbochargers can be mounted to a single exhaust manifold.
The aim of using parallel twin-turbos is to reduce turbo lag by being able to use smaller turbochargers than if a single turbocharger was used for the engine. On engines with multiple cylinder banks (e.g. V engines and flat engines) use of parallel twin-turbos can also simplify the exhaust system.