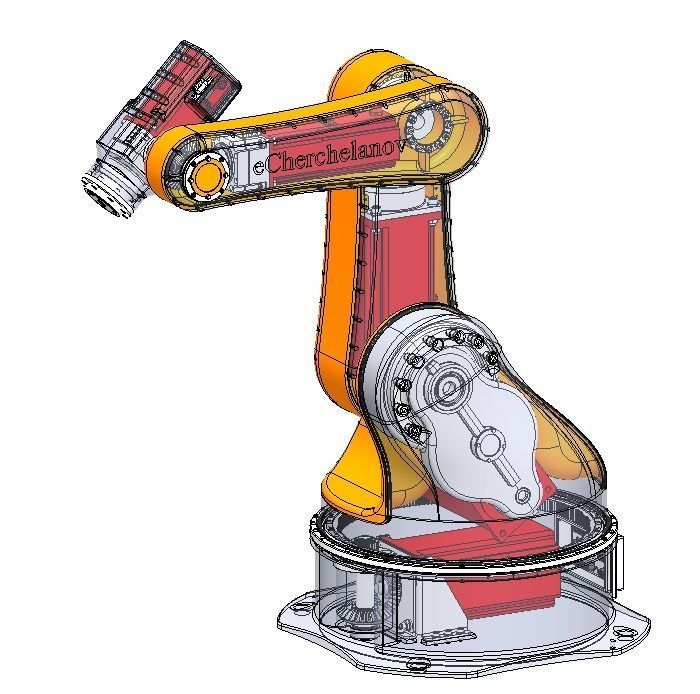
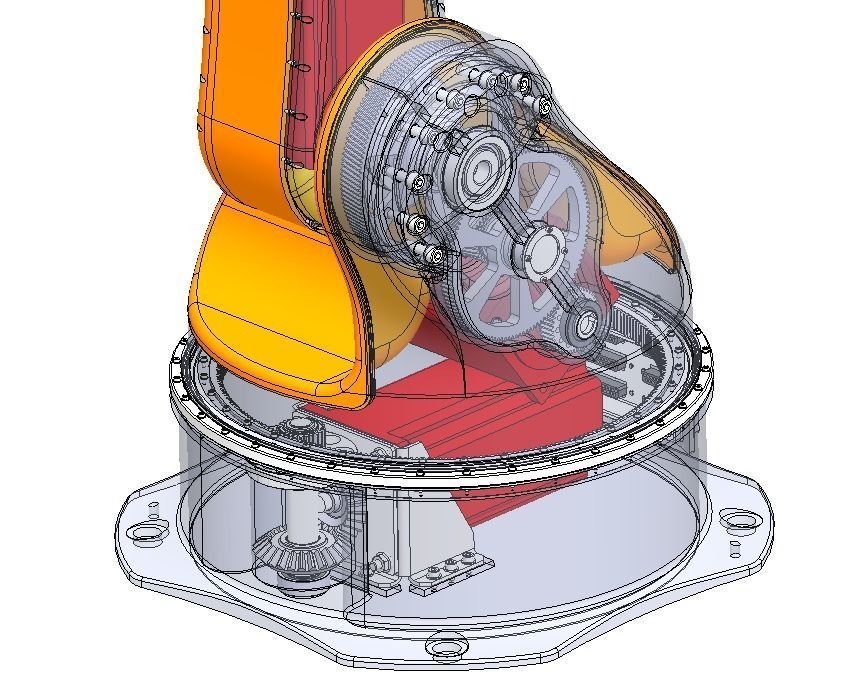
5 axis industrial robot 3D model
The industrial five-axis robot is an advanced automation device equipped with a multi-axis motion control system used to perform high-precision and complex industrial tasks. It typically consists of mechanical structure, electrical control, and software systems.
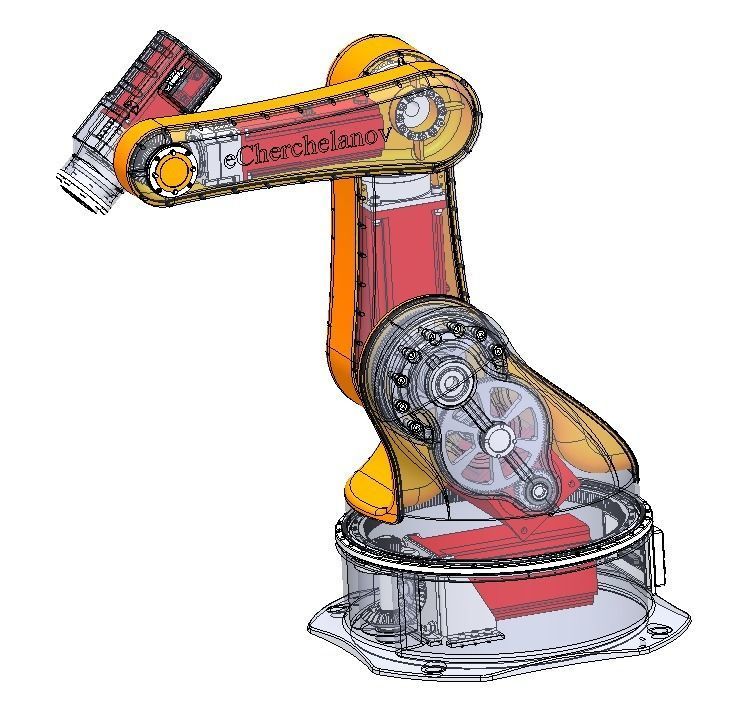
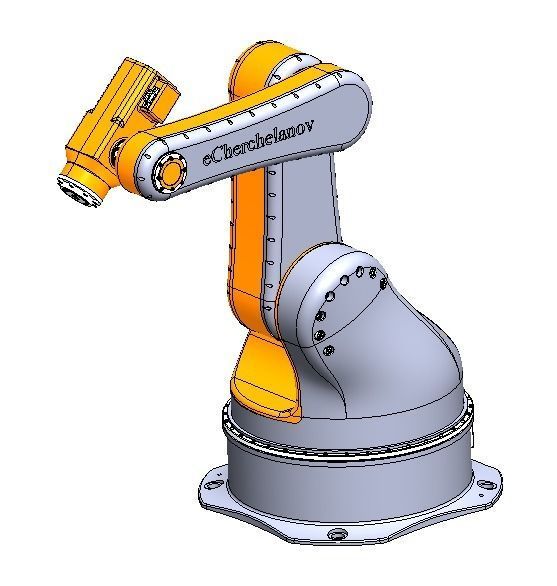
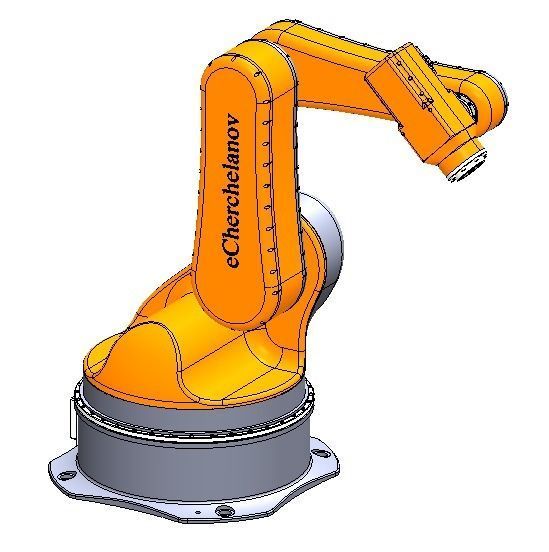
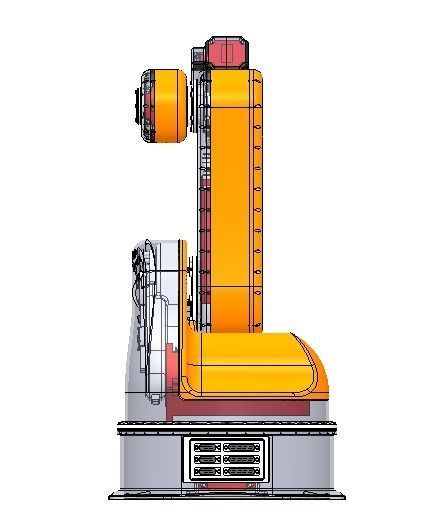
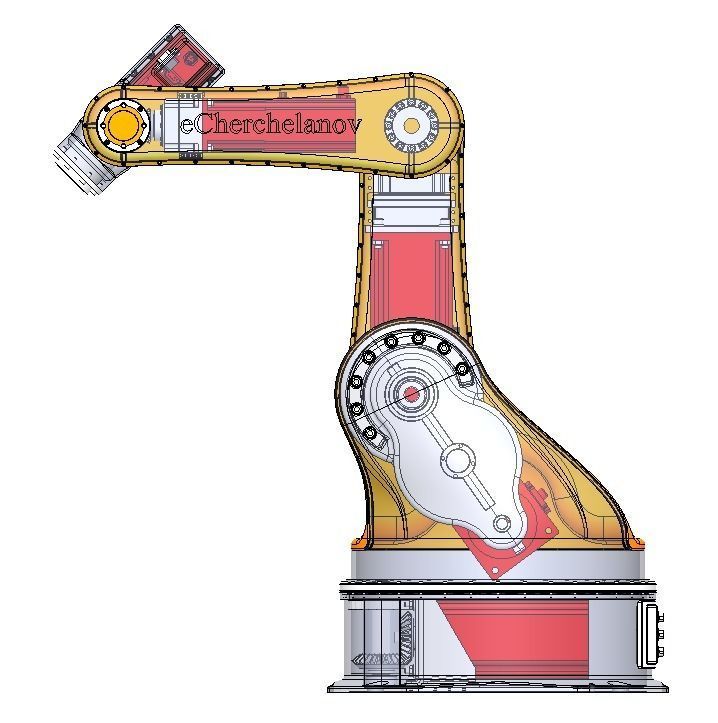
The mechanical structure of the robot includes a base, an arm, joints, and actuators. The base provides a stable foundation for the robot. The arm is the main supporting component that connects the base and the end effector, possessing high strength and rigidity to withstand the workload. Joints connect different parts of the arm and allow the robot to move in multiple axes. The actuator is the mechanical hand at the end of the robot, which can be equipped with various types of tools for gripping, handling, assembly, and other operations.
The electrical control system serves as the brain of the robot, comprising sensors, controllers, and electric motors. Sensors are used to perceive the environment and work objects, such as vision sensors, force sensors, and position sensors. The controller is the central control unit of the robot, receiving sensor signals and guiding the robot's motion based on preset programs and algorithms. Electric motors drive the movement of the mechanical structure through control signals, enabling precise position and velocity control.
The software system is the intelligent core of the robot, including motion planning, path planning, and task scheduling algorithms. The motion planning algorithm determines the trajectory of the robot's joints to achieve the desired target position and orientation. The path planning algorithm determines the optimal path for the robot in the workspace, avoiding obstacles and maximizing efficiency. The task scheduling algorithm arranges the robot's work sequence and resource allocation based on job requirements and priorities.
Industrial five-axis robots are widely used in manufacturing industries for tasks such as welding, handling, assembly, cutting, and precision machining. Their high precision, efficiency, and programmability make them essential tools for improving production efficiency and quality.