1/8
4-CYLINDER OSCILLATING STEAM ENGINESOLIDWORK PART MODELLING AND ASSEMBLYSOLIDWORK MOTION STUDYFor more other 3d design engine or machines you can visit given below linkinstagram channel linkhttps://www.instagram.com/letsmakeitcad/youtube channel linkhttps://youtu.be/Bopuu4Y82jUdownload link for 3d file formathttps://www.cgtrader.com/lets-make-it-cad#solidworks#letsmakeitcad#steamengines
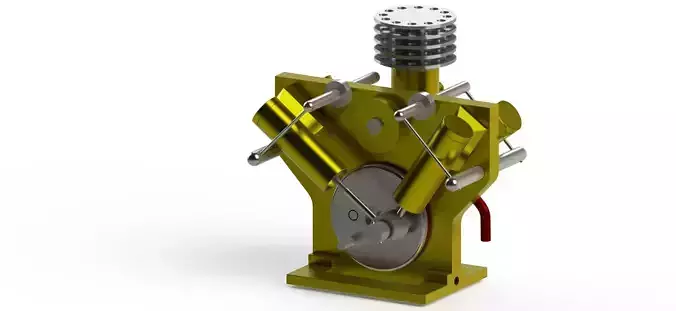
A 4-cylinder oscillating steam engine is a type of steam engine that features four cylinders arranged in a specific manner, and it operates using the oscillating motion of these cylinders. This design is often used in small-scale models, marine propulsion, and various industrial applications. Here's an overview of its components and operation:Certainly, let's delve into the components of a 4-cylinder oscillating steam engine in more detail:
Cylinders:The engine features four cylinders arranged in pairs on either side of the engine. Each cylinder houses a piston that moves back and forth due to the pressure of steam. The oscillating motion of the cylinders is a key characteristic of this engine design.
Pistons:Each cylinder contains a piston, which is a cylindrical object that fits inside the cylinder. The piston's movement is driven by the pressure of steam during the power stroke and the return stroke. The piston is connected to the central shaft through the oscillating mechanism.
Oscillating Mechanism:The oscillating mechanism allows the cylinders to pivot back and forth around a central point. This mechanism typically involves arms or trunnions connected to the cylinder assemblies. As steam pressure alternates between the cylinders, their oscillating motion is transferred to the central shaft.
Central Shaft:The central shaft is at the heart of the oscillating mechanism. It connects the cylinders' oscillating arms to the crankshaft. The oscillating motion of the cylinders is transmitted to the central shaft, which, in turn, drives the crankshaft's rotation.
Crankshaft:The crankshaft is connected to the central shaft. The oscillating motion of the central shaft is converted into rotary motion by the crankshaft. The crankshaft's rotation powers the flywheel and any connected machinery.
Flywheel:The flywheel is attached to the crankshaft and serves as a momentum reservoir. It stores kinetic energy during the power strokes of the cylinders and releases it during the return strokes, helping to maintain a smooth and continuous rotational output.
Valves:Valves control the entry and exit of steam in each cylinder. The timing of valve openings and closings is synchronized with the oscillating motion of the cylinders to ensure proper operation.
Valve Linkages:The valve linkages connect the valves to the engine's control mechanisms. These linkages are adjusted to control the timing of steam admission and exhaust in relation to the oscillating motion of the cylinders.
Steam Inlet and Exhaust Piping:Pipes deliver steam to the cylinders' steam inlets and carry away exhaust steam after it has done its work. These pipes are part of the engine's steam distribution system.
Support Structure:The engine's components are mounted on a sturdy framework or base that provides stability and support. This structure holds the oscillating mechanism, cylinders, crankshaft, and flywheel in place.
The 4-cylinder oscillating steam engine showcases a unique mechanism that converts linear reciprocating motion into rotary motion through oscillation. While this design is less common than other types of steam engines, it demonstrates the versatility and creativity that engineers have applied to various steam-powered systems.The working of a 4-cylinder oscillating steam engine involves a specific mechanism that converts the pressure of steam into mechanical motion through the oscillating motion of four cylinders. Here's a detailed explanation of how it works:
Steam Generation:Steam is generated in a separate boiler by heating water using a heat source such as coal, wood, or oil. The high-pressure steam produced is then directed towards the engine.
Steam Inlet Valves:Each cylinder has its steam inlet valve. When the steam inlet valve opens, high-pressure steam enters the cylinder, pushing the piston inside.
Power Stroke:The entry of steam causes the piston to move away from the valve, creating the power stroke. As the piston moves, it's connected to an oscillating mechanism that allows it to pivot back and forth around a central point.
Oscillation and Central Shaft:The oscillating mechanism consists of arms or trunnions that connect each cylinder to a central shaft. As the piston moves back and forth due to steam pressure, the cylinder oscillates around the central point, causing the central shaft to move in an oscillating manner.
Crankshaft Connection:The central shaft is connected to the crankshaft. As the central shaft oscillates, it imparts an oscillating motion to the crankshaft.
Conversion to Rotary Motion:The oscillating motion of the crankshaft is converted into rotary motion. The crankshaft's rotation is what powers the flywheel and any machinery connected to it.
Exhaust Stroke and Valve Timing:After the power stroke, the steam inlet valve closes, and the exhaust valve opens. The used steam is released from the cylinder.
Return Stroke:As the exhaust valve opens, the piston is pushed back towards the valve end by the flywheel's momentum and the oscillating motion of the cylinder.
Steam Switch and Synchronization:While one pair of cylinders is going through the power and exhaust strokes, the other pair is going through the return stroke. This arrangement ensures a continuous and balanced rotational output.
Continuous Operation:The cycle repeats continuously as long as steam is supplied to the engine and the engine's mechanisms are properly synchronized.
The key feature of a 4-cylinder oscillating steam engine is the unique oscillating motion of the cylinders, which is harnessed to generate rotary motion for power. This type of engine is known for its smooth operation and is often used in models, small-scale industrial applications, and marine propulsion systems.A 4-cylinder oscillating steam engine offers several advantages that make it suitable for various applications, particularly in scenarios where compactness, simplicity, and balanced operation are desired. Here are some of the advantages of a 4-cylinder oscillating steam engine:
Compact Design:The arrangement of four cylinders in a compact layout allows for efficient use of space. This makes the engine well-suited for applications where space constraints are a concern, such as small-scale models or marine propulsion systems.
Balanced Operation:The design of the engine, with cylinders oscillating in pairs on either side, inherently balances out forces and vibrations. This results in smoother operation compared to engines with fewer cylinders.
Reduced Mechanical Complexity:The oscillating motion of the cylinders eliminates the need for complex crankshaft and connecting rod mechanisms. This simplifies the design and reduces the number of moving parts, potentially leading to easier maintenance and assembly.
Versatility:4-cylinder oscillating steam engines can be used in a range of applications, from small-scale models to marine propulsion and industrial machinery. Their compact size and balanced operation make them adaptable to various needs.
Smoother Power Output:The oscillating motion, combined with the flywheel's rotational energy storage, results in a relatively smoother power output compared to engines with more abrupt power strokes.
Reduced Vibrations:The balanced operation and oscillating motion contribute to reduced vibrations, which can be important in applications where steady and consistent power delivery is required.
Aesthetics and Educational Value:4-cylinder oscillating steam engines are often used as educational tools, providing a visual and functional demonstration of steam power principles. They can also be appreciated for their aesthetic appeal and historical significance.
Model and Hobby Use:Due to their unique design, 4-cylinder oscillating steam engines are popular choices for hobbyists and model enthusiasts. Their compact size and interesting motion make them intriguing projects for those interested in steam technology.
It's important to note that while 4-cylinder oscillating steam engines have these advantages, they also have limitations, such as limited power output compared to larger engines and potential challenges in designing and maintaining the oscillating mechanism. The choice of engine design depends on the specific application and requirements of the project.
REVIEWS & COMMENTS
accuracy, and usability.