1 CYLINDER HORIZONTAL STEAM ENGINE WITH SLIDE VALVE 3D model
1 CYLINDER HORIZONTAL STEAM ENGINE WITH SLIDE VALVESOLIDWORK PART MODELLING#SolidWorks#letsmakeitcadFor more other 3d design engine or machines you can visit given below linkinstagram channel linkhttps://www.instagram.com/letsmakeitcad/youtube channel linkhttps://www.youtube.com/channel/UCjqh...download link for 3d file formathttps://www.cgtrader.com/lets-make-it...#SolidWorks#letsmakeitcad#steamengines#mechanical#engineering
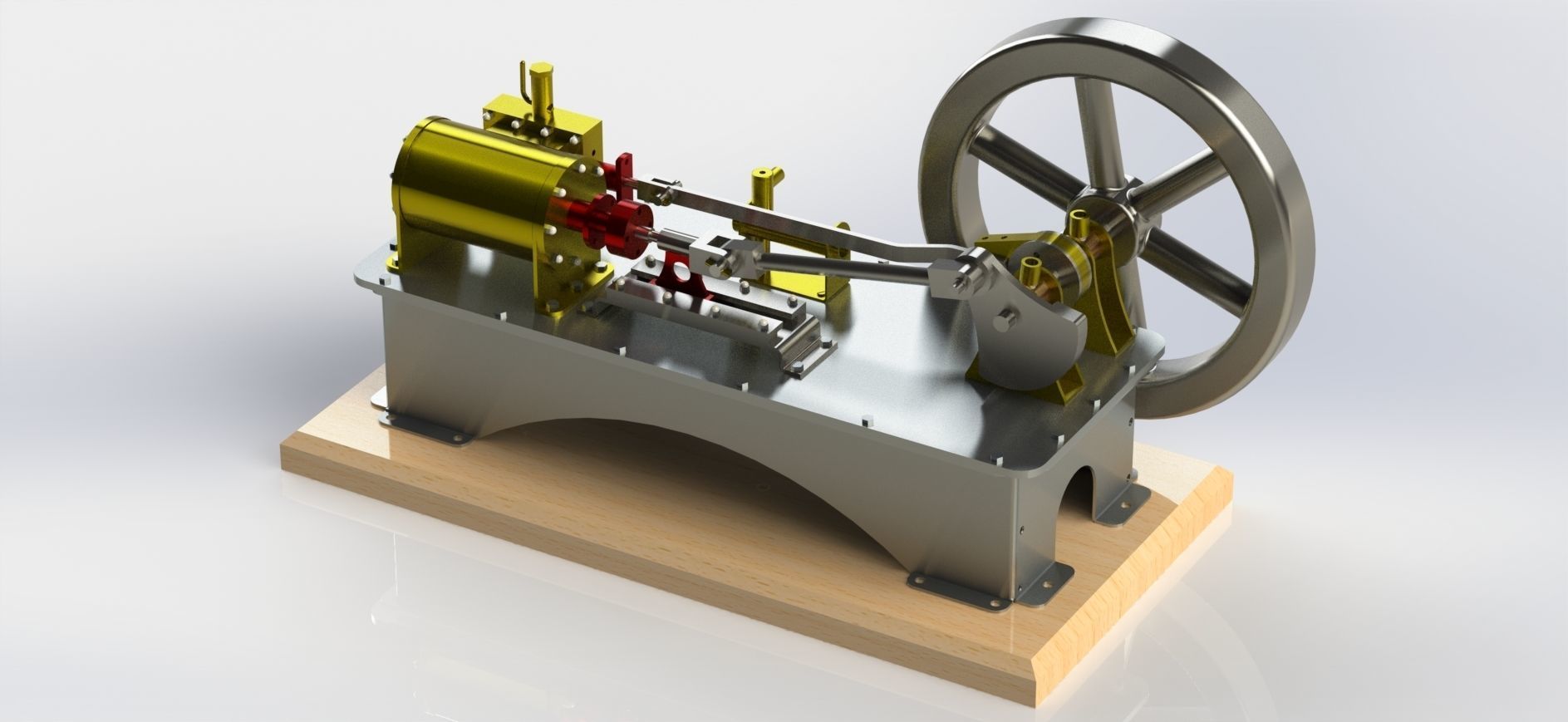
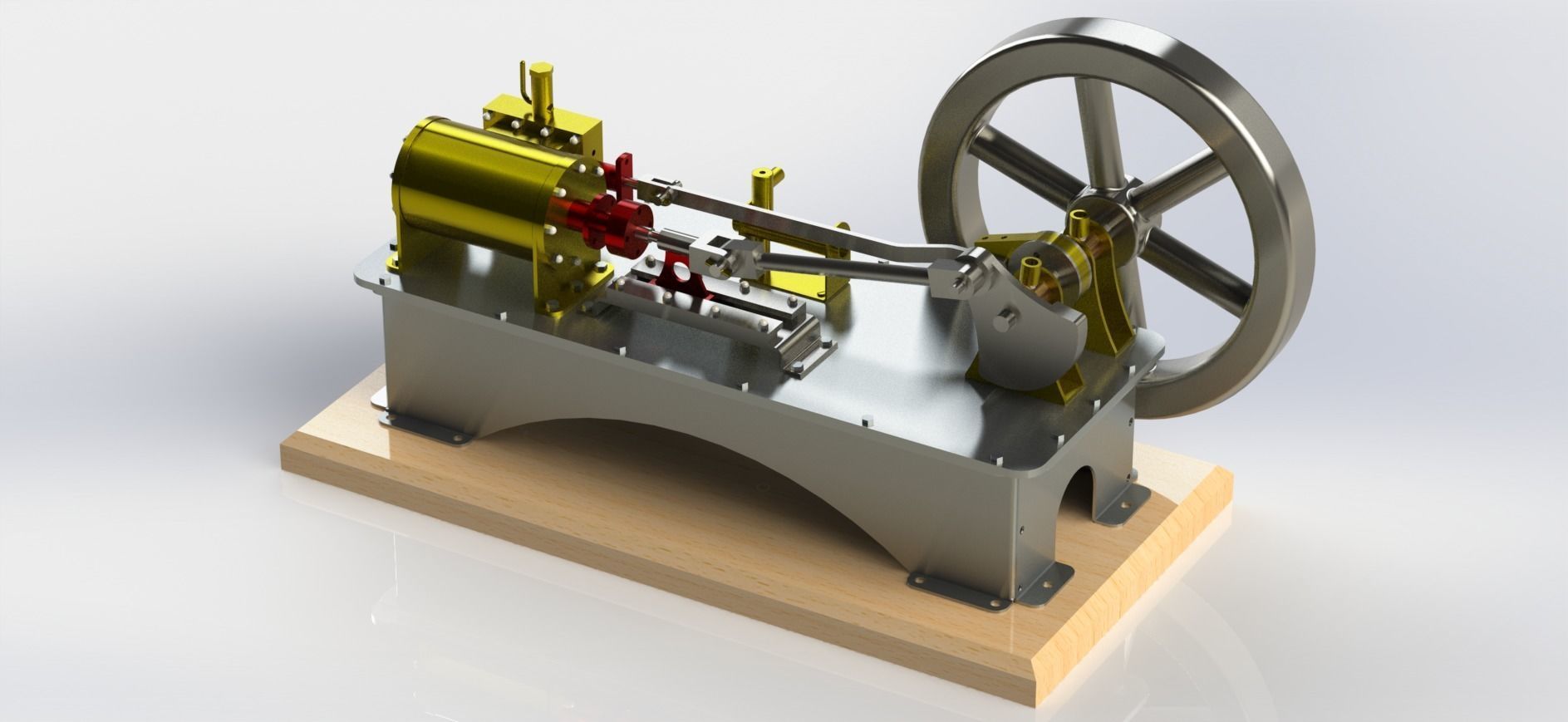
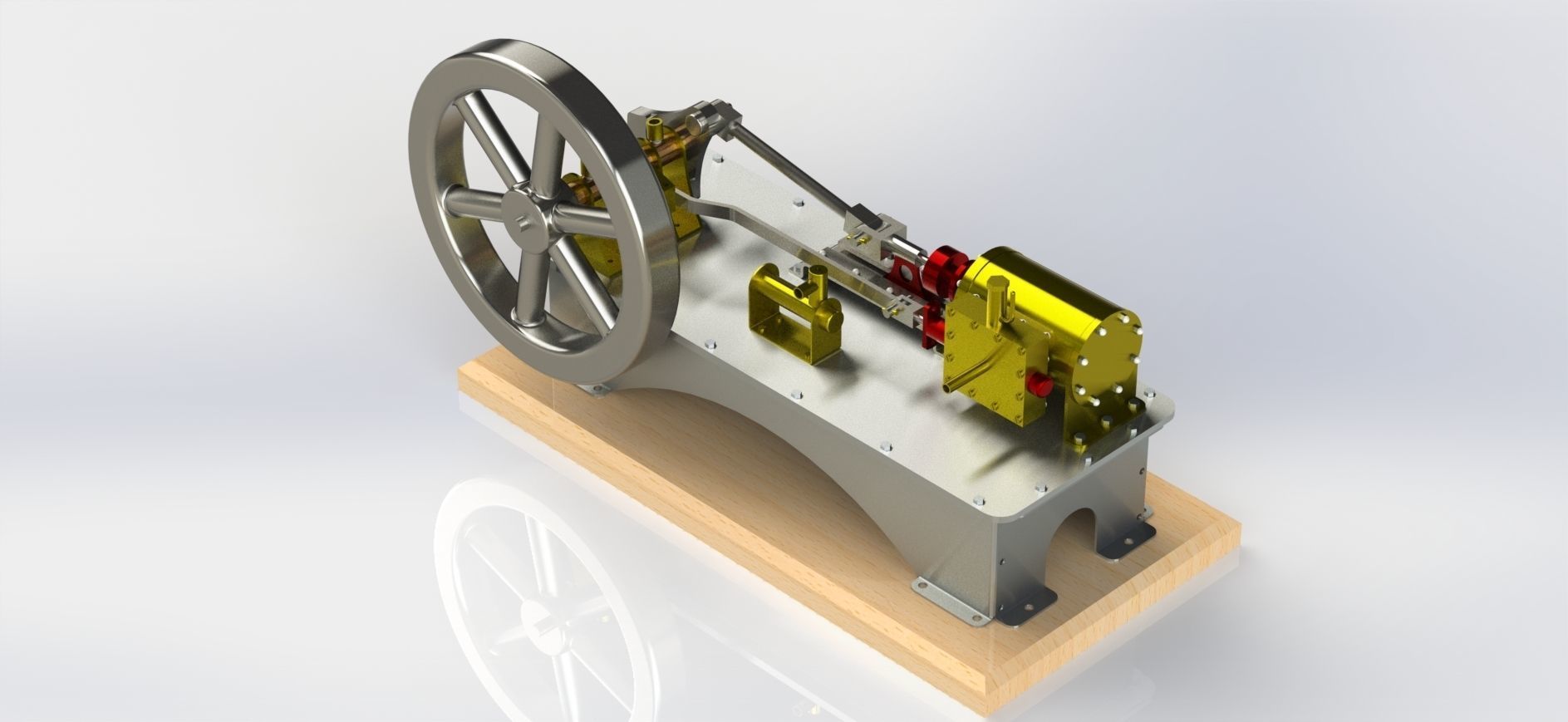
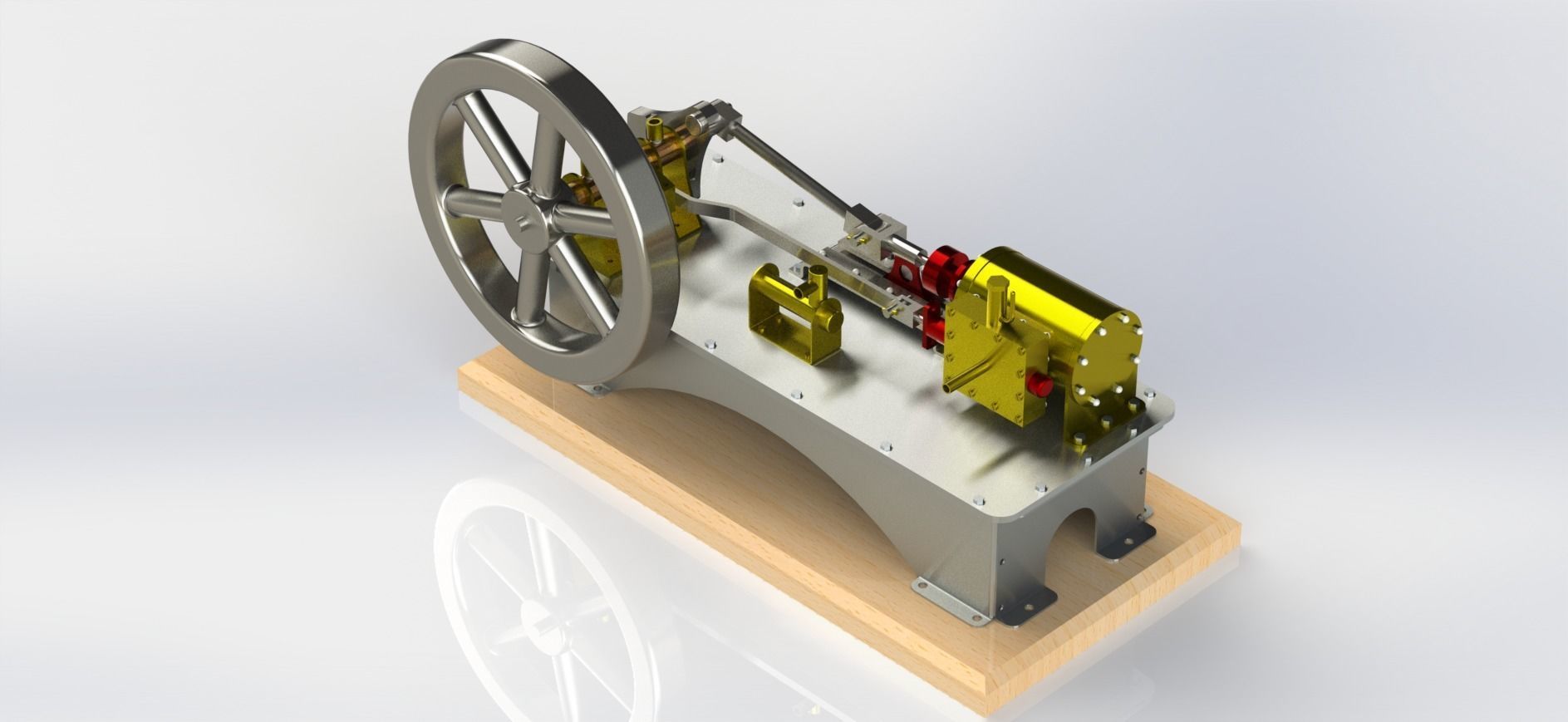
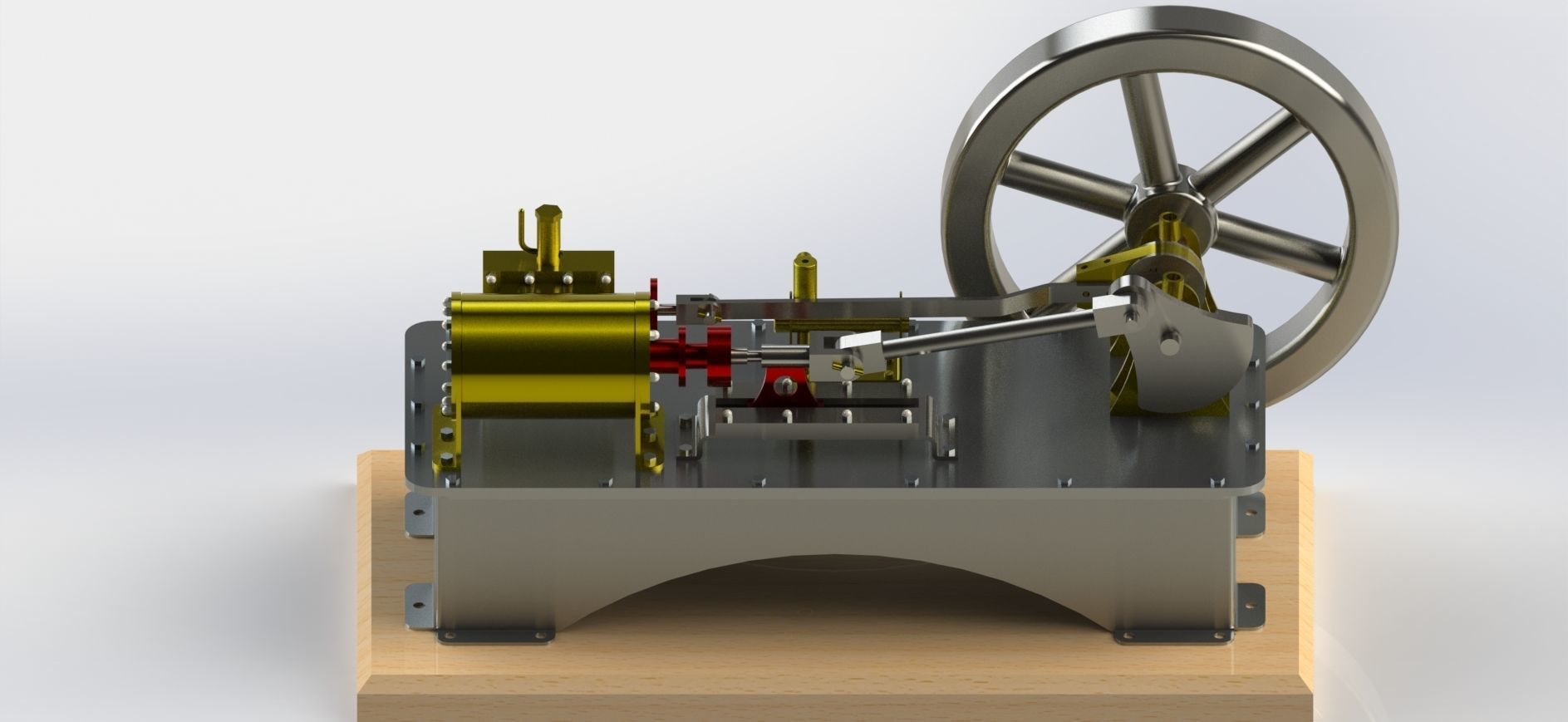
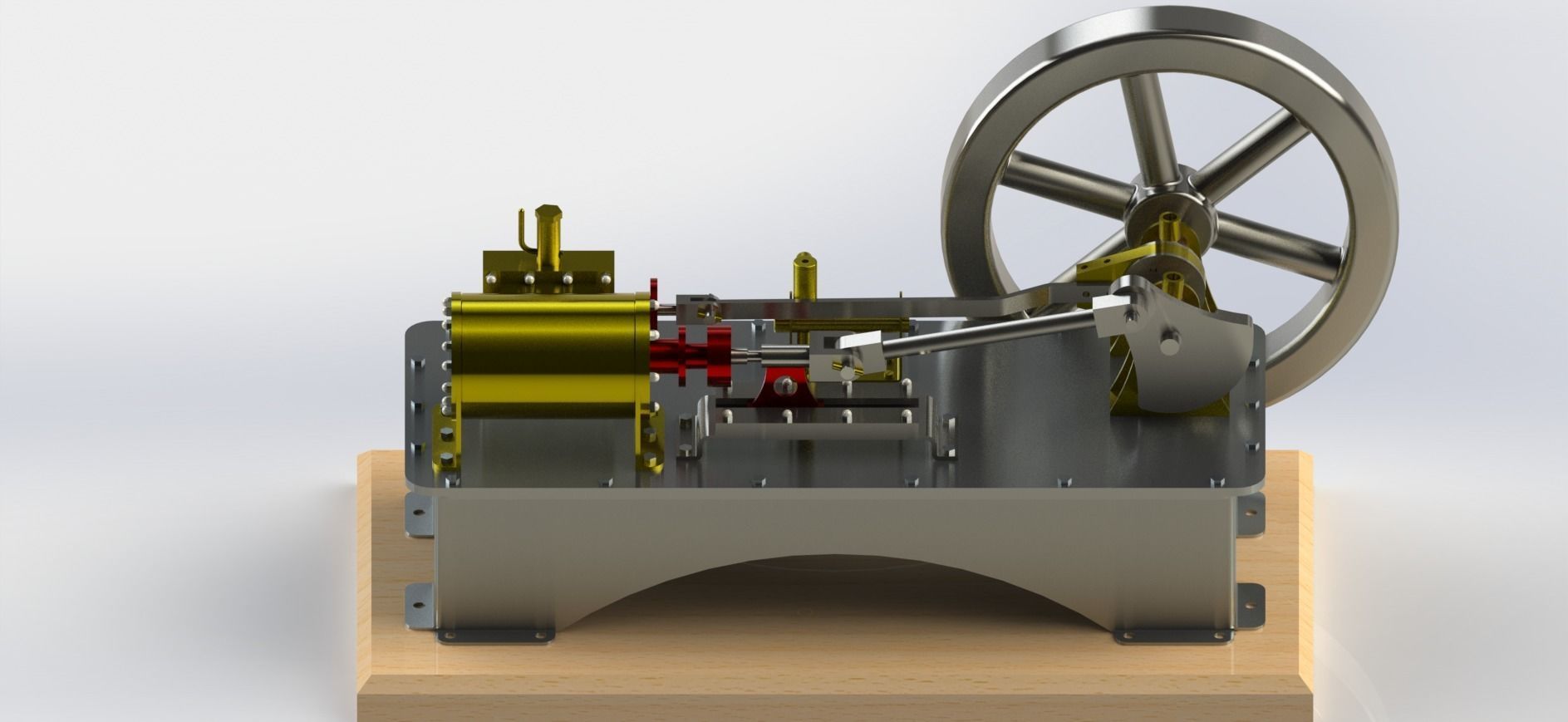
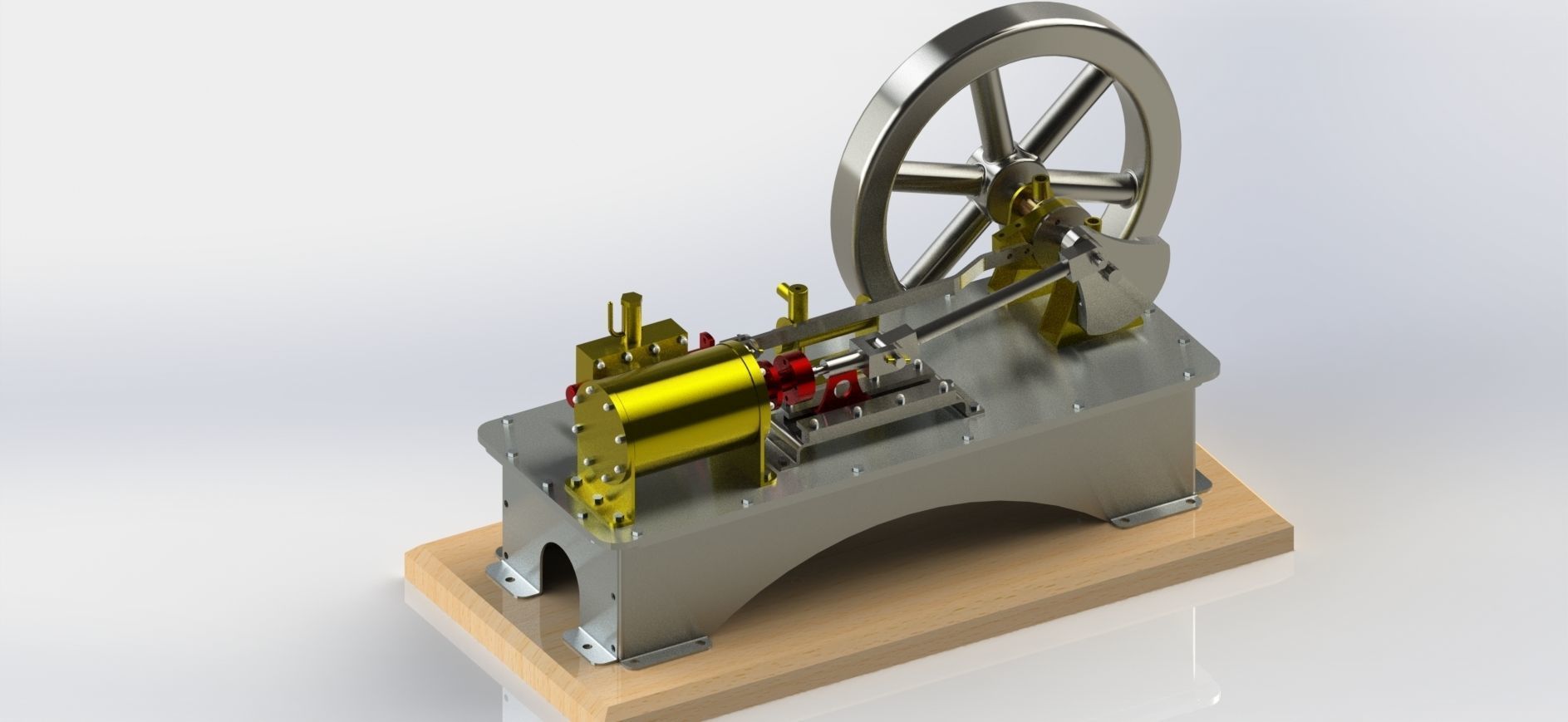
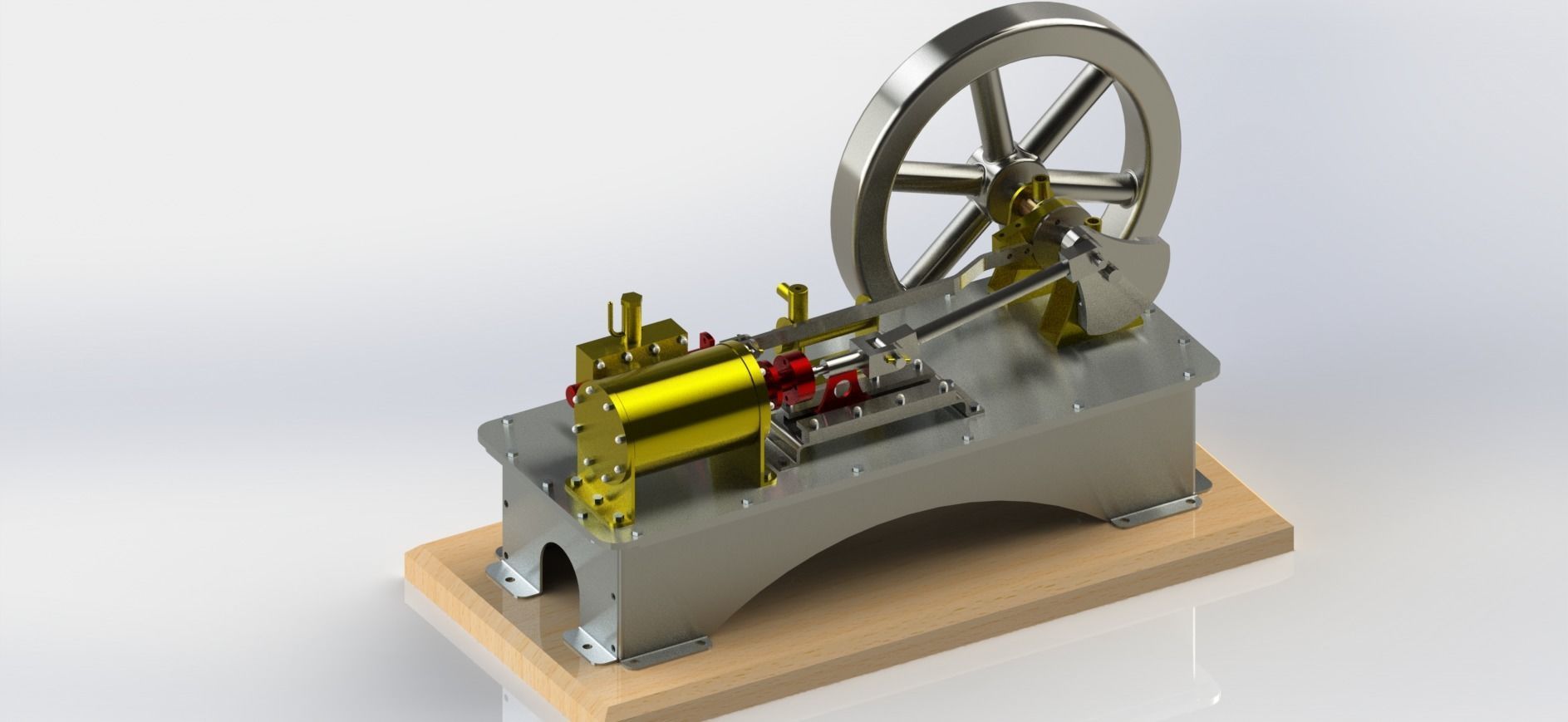
A 1-cylinder horizontal steam engine with a slide valve is a relatively simple design of a steam engine that utilizes a horizontal cylinder and a slide valve mechanism for controlling the flow of steam into and out of the cylinder. This design is commonly found in historical steam engines and can be a fascinating engineering project or educational tool. Here are the key components and how it works:
Components:
Cylinder: The main chamber where the steam's pressure is utilized to move a piston.
Piston: A cylindrical object that fits inside the cylinder and moves back and forth due to the pressure of steam.
Crankshaft: A rotating shaft connected to the piston that converts reciprocating motion into rotary motion.
Connecting Rod: A rod that connects the piston to the crankshaft, transmitting the piston's motion to the crankshaft.
Flywheel: A heavy, circular wheel attached to the crankshaft. It stores kinetic energy and helps smooth out the engine's rotational motion.
Slide Valve: The slide valve is a crucial component that controls the flow of steam into and out of the cylinder. It moves back and forth to direct steam to the appropriate side of the piston.
Eccentric Cam: An eccentric cam is often used to drive the slide valve. It's mounted on the crankshaft and provides the necessary reciprocating motion for the slide valve.
Working:
Steam Inlet: Steam from a boiler is directed into the cylinder through a port on one side of the cylinder.
Piston Movement (Power Stroke): Steam enters one side of the cylinder, pushing the piston away from the steam inlet. This is known as the power stroke. As the piston moves, it turns the crankshaft.
Slide Valve Movement: The slide valve is actuated by the eccentric cam on the crankshaft. It moves in synchronization with the piston, covering and uncovering ports to control the steam flow.
Exhaust Stroke: After the power stroke, the slide valve redirects steam to the other side of the piston, and the used steam from the previous stroke is expelled from the cylinder through an exhaust port.
Piston Return: The momentum of the flywheel and the connecting rod's action return the piston to its original position, ready for the next cycle.
Steam Switch: The process repeats, alternating between the two sides of the piston, driving continuous rotational motion of the crankshaft.
This type of engine showcases the fundamental principles of steam power and is a classic example of how reciprocating motion is converted into rotary motion. It was commonly used in various industrial applications and continues to be of historical and educational interest.