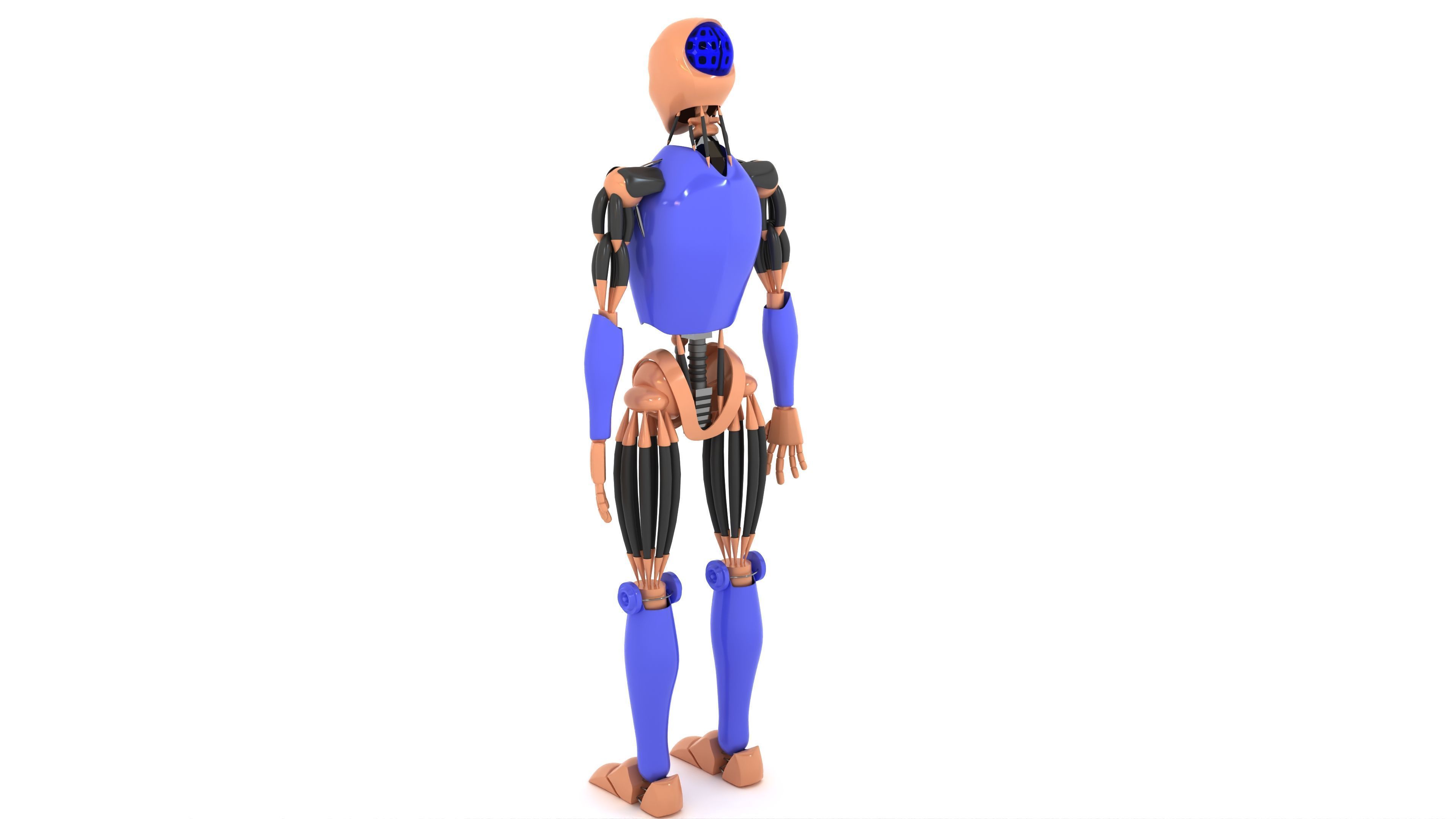
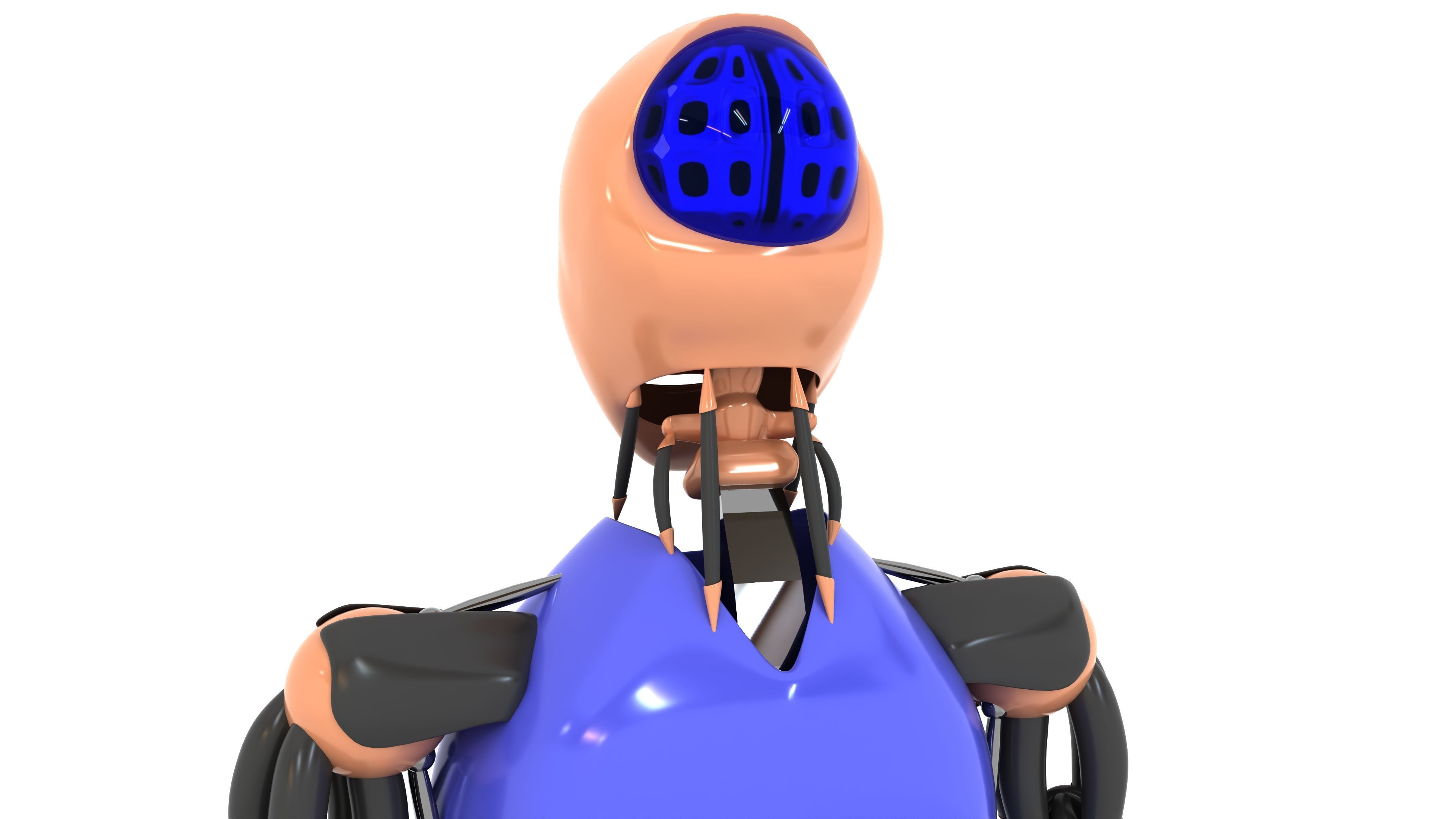
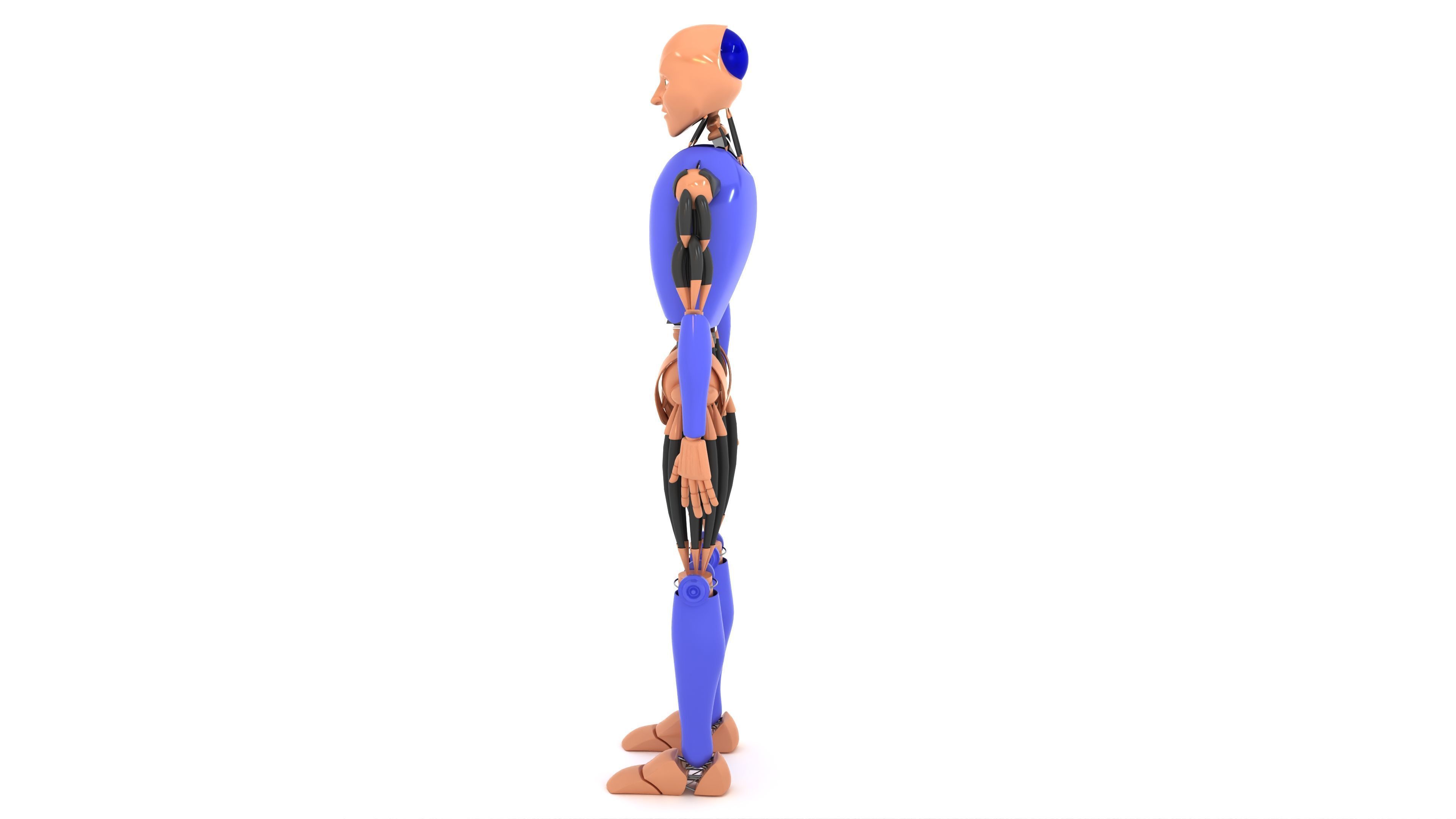
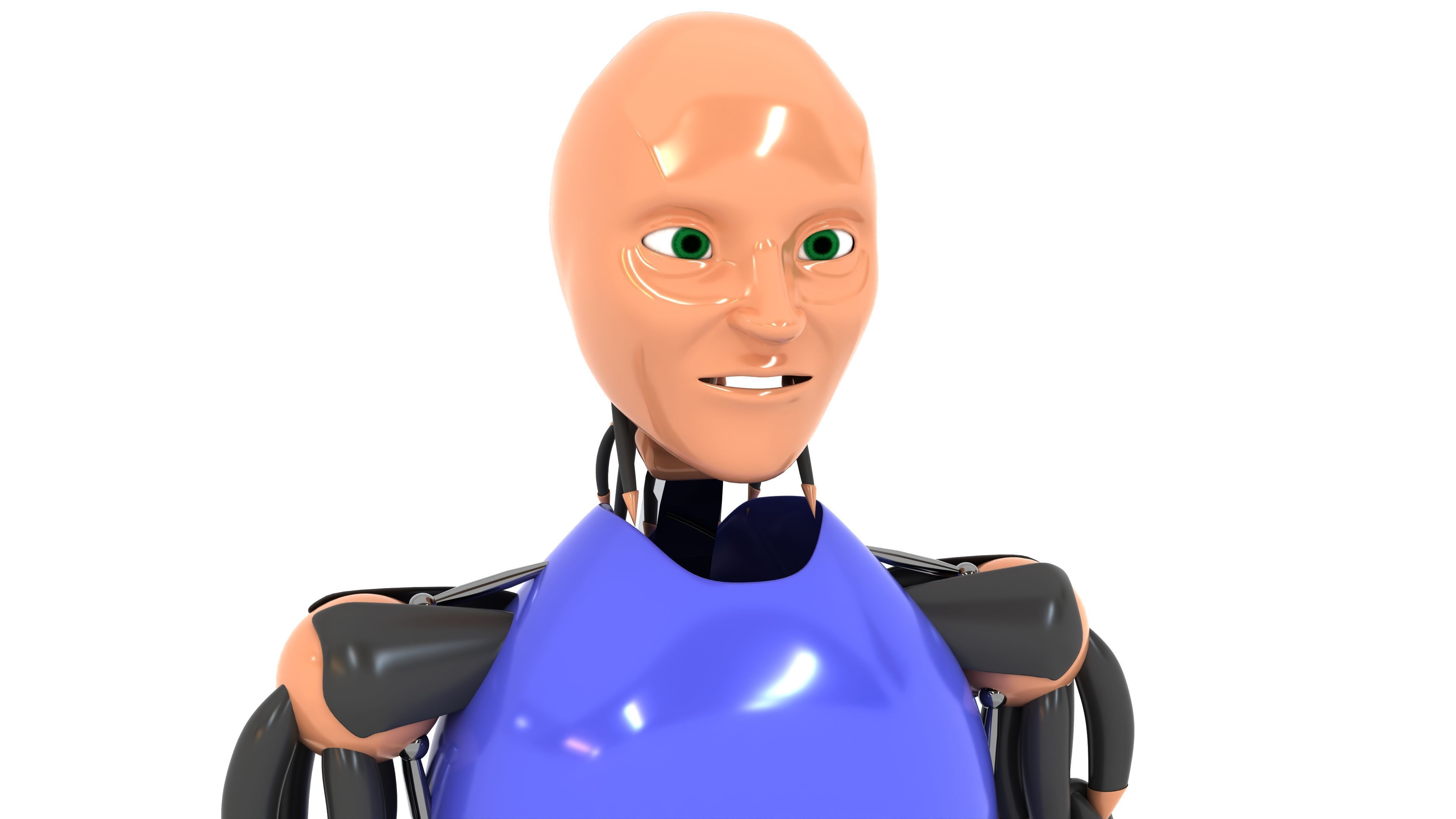
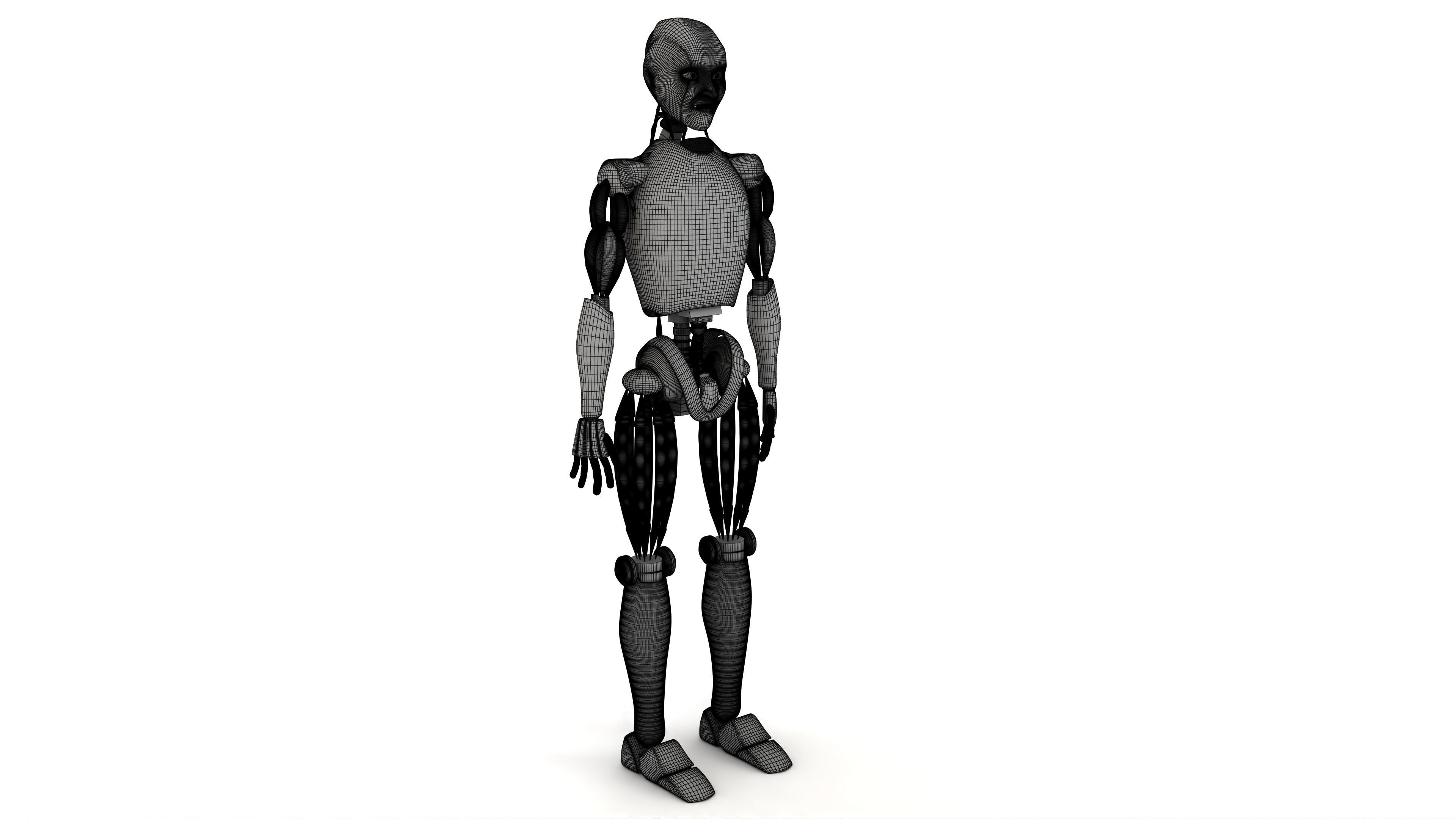
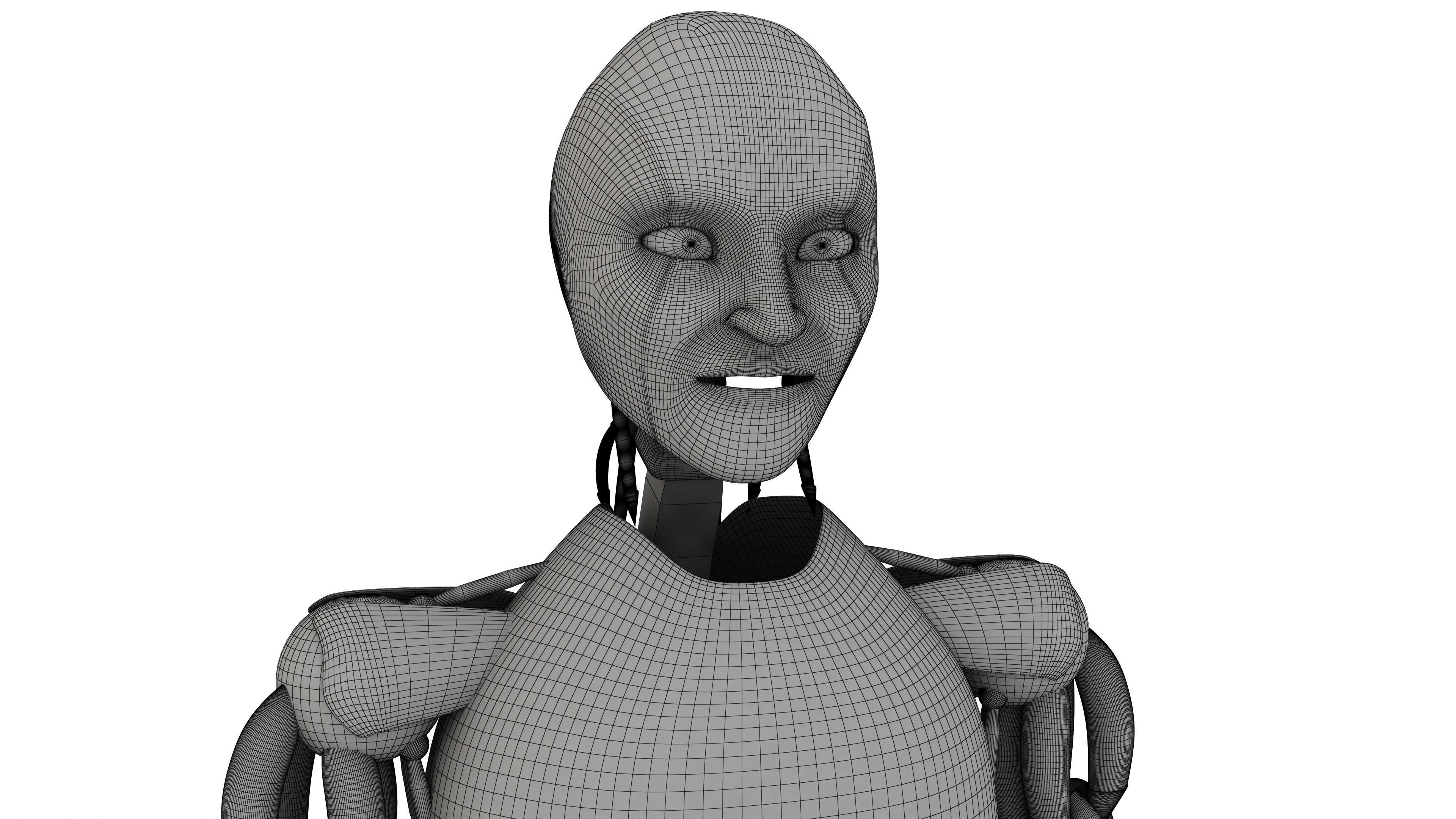
Humanoid Robot 3D model
This Humanoid Robot was modeled under 3Ds MAX 2020, the materials, Lighting and the rendering under V-Ray 7.
A Short History of Humanoid RobotsHumanoid robots have a rich history, evolving from early mechanical automata to advanced AI-driven machines.
Ancient and Early Automata: The concept of humanoid machines dates back to ancient civilizations. Greek myths mentioned Talos, a giant mechanical man, while Chinese and Arab inventors built water clocks with automata resembling humans.
Renaissance Engineering: In the 15th century, Leonardo da Vinci designed a mechanical knight capable of basic movements, marking the first recorded design of a humanoid robot.
Industrial Age: The 18th and 19th centuries saw the rise of complex mechanical automata created for entertainment, such as Jacques de Vaucanson’s flute-playing automaton.
20th Century Robotics:
1920s: The term robot was popularized by Karel Čapek's play R.U.R. (Rossum’s Universal Robots), describing artificial humanoid workers.1940s-50s: Early robotics pioneers like Isaac Asimov introduced the concept of robot ethics (the Three Laws of Robotics).1970s: The first functional humanoid robots, such as WABOT-1 in Japan, emerged.Modern Advancements:
2000s: Honda’s ASIMO and Sony’s QRIO showcased human-like movement and interaction capabilities.2010s: Robots like Sophia (by Hanson Robotics) advanced in AI, facial expressions, and conversational skills.Present: Humanoid robots are used in healthcare, customer service, and research, with ongoing advancements in AI and physical dexterity.Humanoid robots symbolize the fusion of engineering, AI, and creativity, striving to replicate and support human life.A Short History of Humanoid RobotsHumanoid robots have a rich history, evolving from early mechanical automata to advanced AI-driven machines.
Ancient and Early Automata: The concept of humanoid machines dates back to ancient civilizations. Greek myths mentioned Talos, a giant mechanical man, while Chinese and Arab inventors built water clocks with automata resembling humans.
Renaissance Engineering: In the 15th century, Leonardo da Vinci designed a mechanical knight capable of basic movements, marking the first recorded design of a humanoid robot.
Industrial Age: The 18th and 19th centuries saw the rise of complex mechanical automata created for entertainment, such as Jacques de Vaucanson’s flute-playing automaton.
20th Century Robotics:
1920s: The term robot was popularized by Karel Čapek's play R.U.R. (Rossum’s Universal Robots), describing artificial humanoid workers.1940s-50s: Early robotics pioneers like Isaac Asimov introduced the concept of robot ethics (the Three Laws of Robotics).1970s: The first functional humanoid robots, such as WABOT-1 in Japan, emerged.Modern Advancements:
2000s: Honda’s ASIMO and Sony’s QRIO showcased human-like movement and interaction capabilities.2010s: Robots like Sophia (by Hanson Robotics) advanced in AI, facial expressions, and conversational skills.Present: Humanoid robots are used in healthcare, customer service, and research, with ongoing advancements in AI and physical dexterity.Humanoid robots symbolize the fusion of engineering, AI, and creativity, striving to replicate and support human life.