1/8
Slab Revit Families significantly enhance the level of detail and accuracy in architectural and structural plans. They facilitate effective communication between architects, engineers, and contractors, leading to well-coordinated and successful construction projects.
A Slab Revit Family is a digital representation of a concrete or other material slab in the Building Information Modeling (BIM) software, Autodesk Revit. It's a crucial component in creating detailed and accurate architectural and structural plans for various reasons:
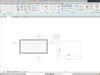
Accurate Representation: Slab families in Revit allow architects and engineers to accurately represent different types of slabs such as cast-in-place, precast, or structural slabs. These accurate representations are essential for creating precise floor plans and elevations.
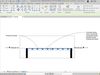
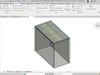
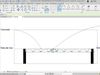
Visualization: Slab families provide a 3D visualization of the slabs within the building model. This helps architects and clients to visualize the building’s layout and understand spatial relationships between different elements.
Clash Detection: In complex building designs, various elements like beams, columns, and ducts intersect with slabs. Slab families, when properly integrated into the BIM model, enable clash detection. Architects and engineers can identify clashes early in the design phase, preventing costly errors during construction.
Quantity Takeoff: Slab families can be used to calculate the exact quantities of materials required for construction. This aids in cost estimation and project budgeting, ensuring that the right amount of materials is ordered and reducing wastage.
Structural Analysis: Slab families are essential for structural engineers. They use these families to perform structural analysis, simulate loads, and assess the slab's behavior under different conditions. This information is critical for ensuring the structural integrity of the building.
Documentation: Slab families enhance the quality of construction documentation. Detailed slabs in the BIM model provide the basis for generating accurate construction drawings. These drawings include plans, sections, and details, ensuring that contractors understand the design intent and can execute the construction precisely as planned.
Material and Cost Information: Slab families can store information about the material properties, cost, and other specifications. This data is invaluable for project management, helping to track costs, manage budgets, and make informed decisions about material choices.
Phasing and Scheduling: In large projects, construction often occurs in phases. Slab families can be linked to construction schedules, enabling project managers to plan the construction sequence effectively. This is crucial for maintaining project timelines.
Facility Management: After construction, the detailed information about slabs stored in the BIM model is immensely useful for facility management. It aids in maintenance planning, renovations, and future expansions, ensuring that the building remains functional and efficient over its lifecycle.
REVIEWS & COMMENTS
accuracy, and usability.