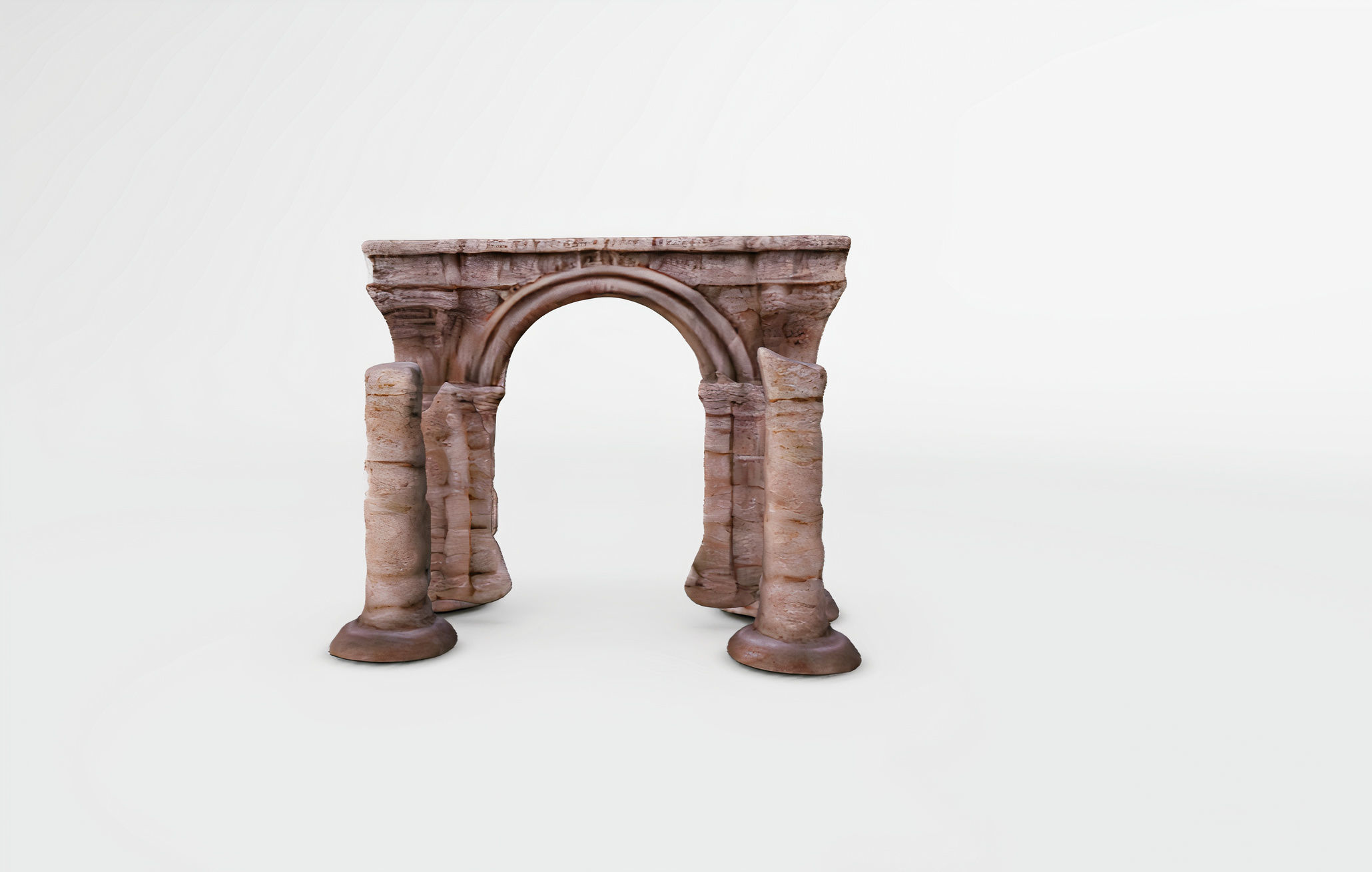
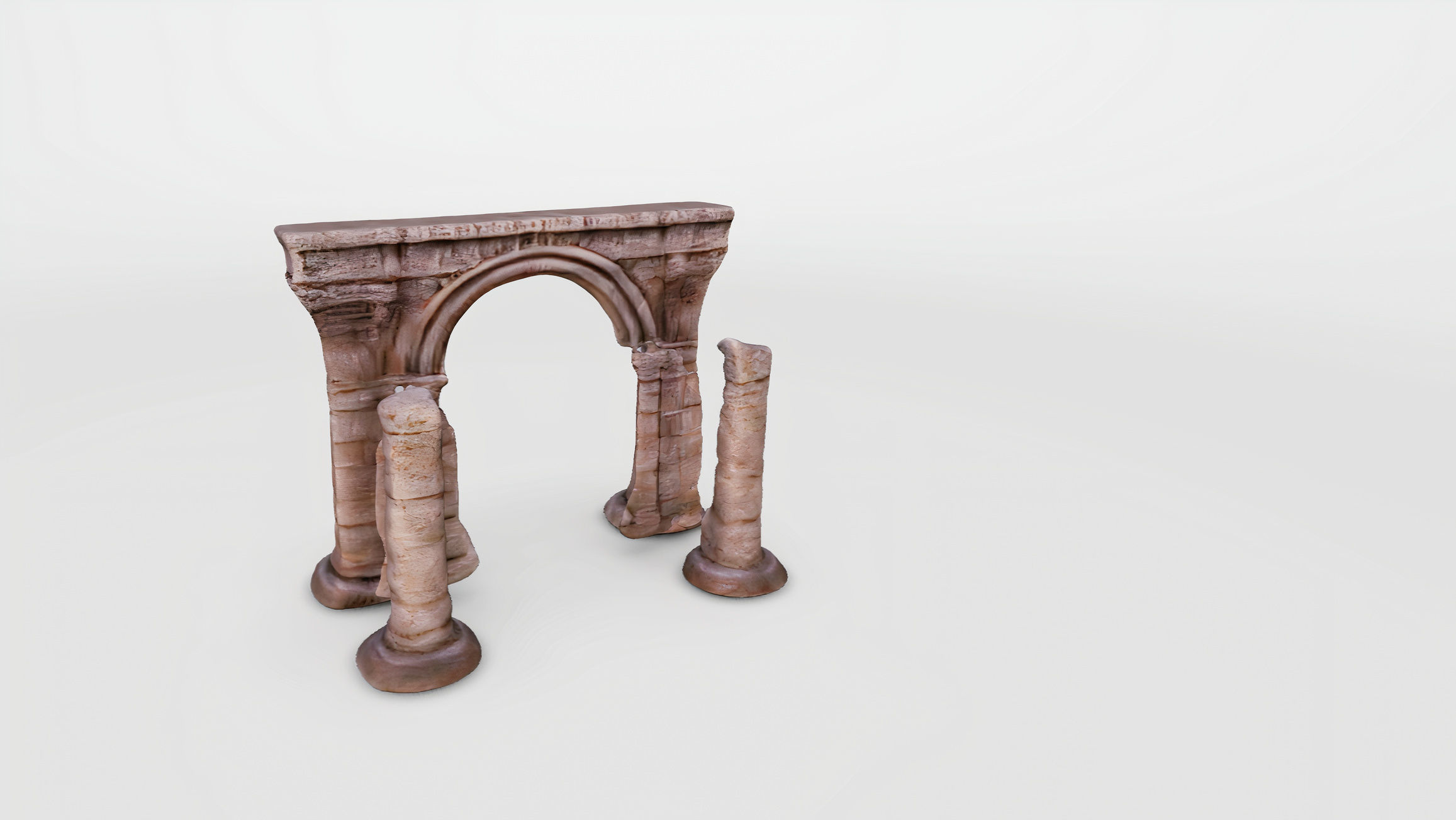
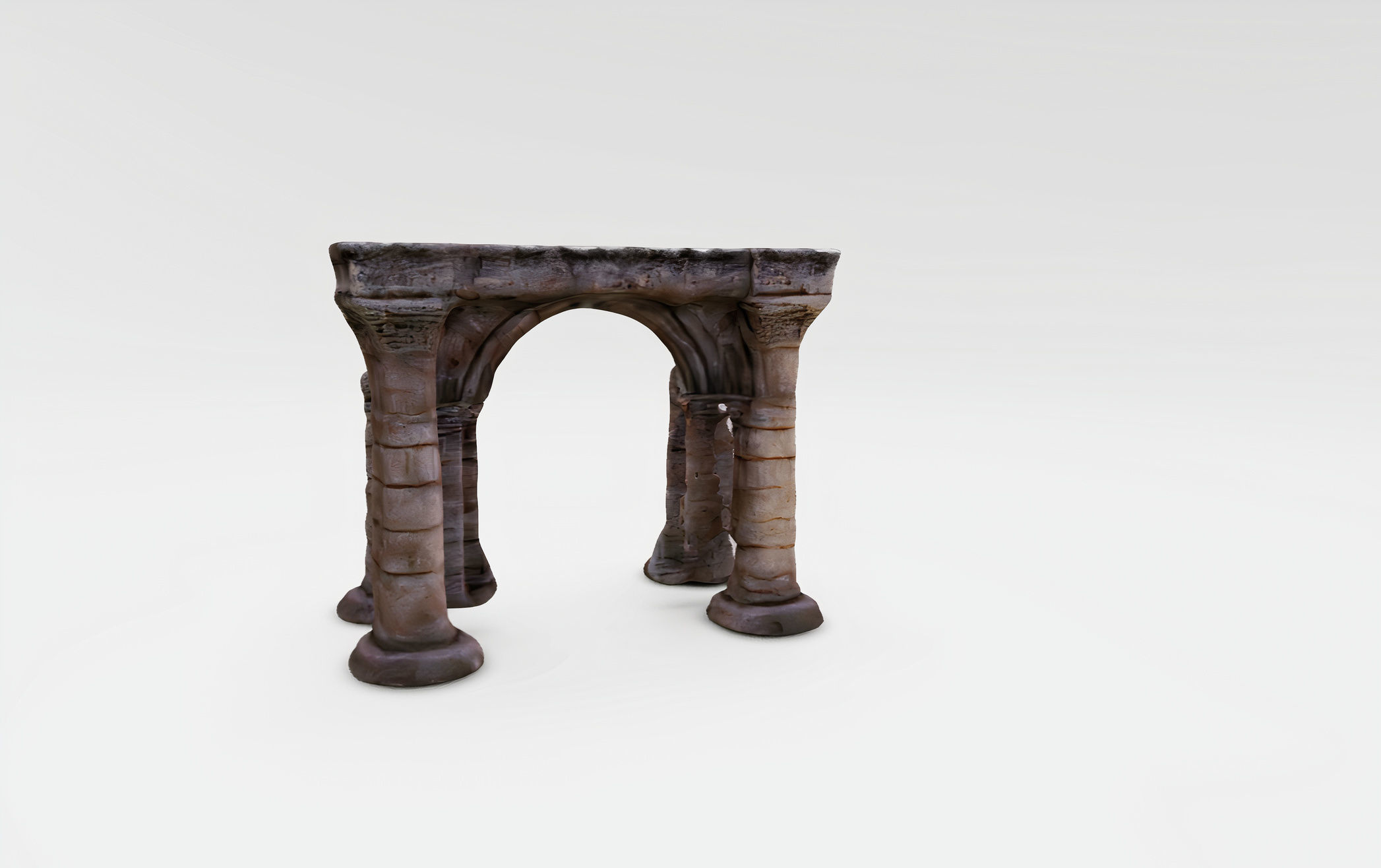
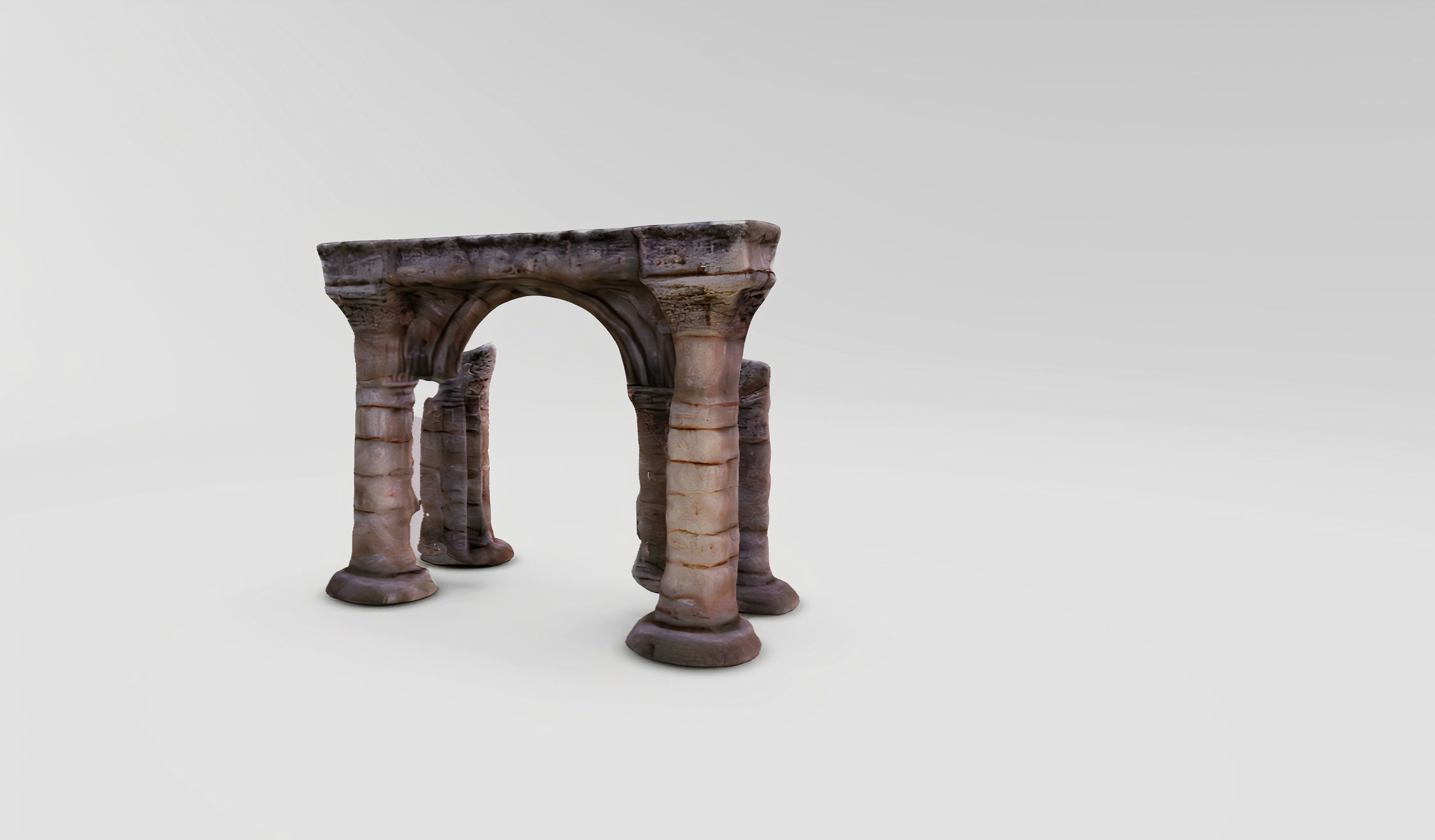
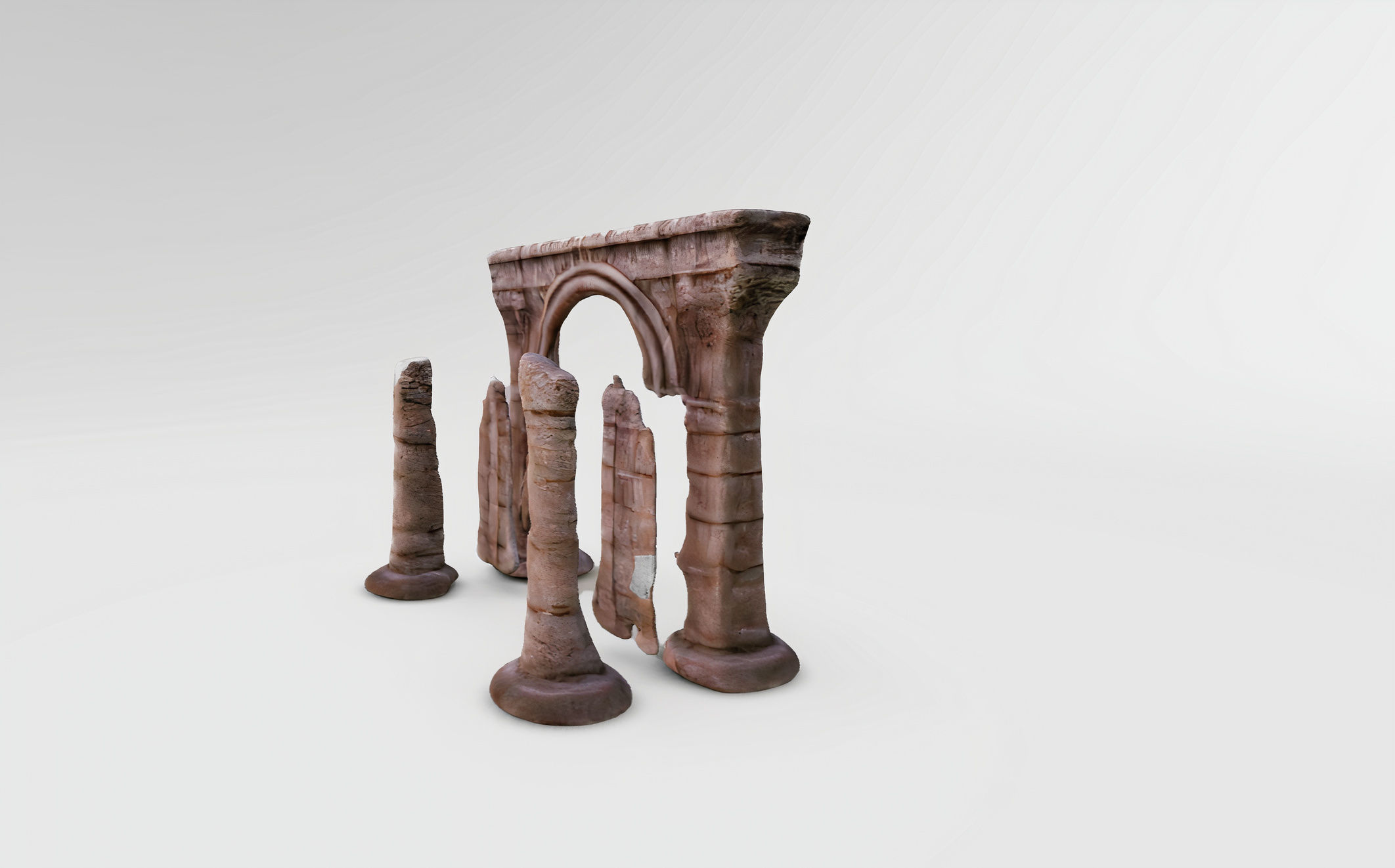
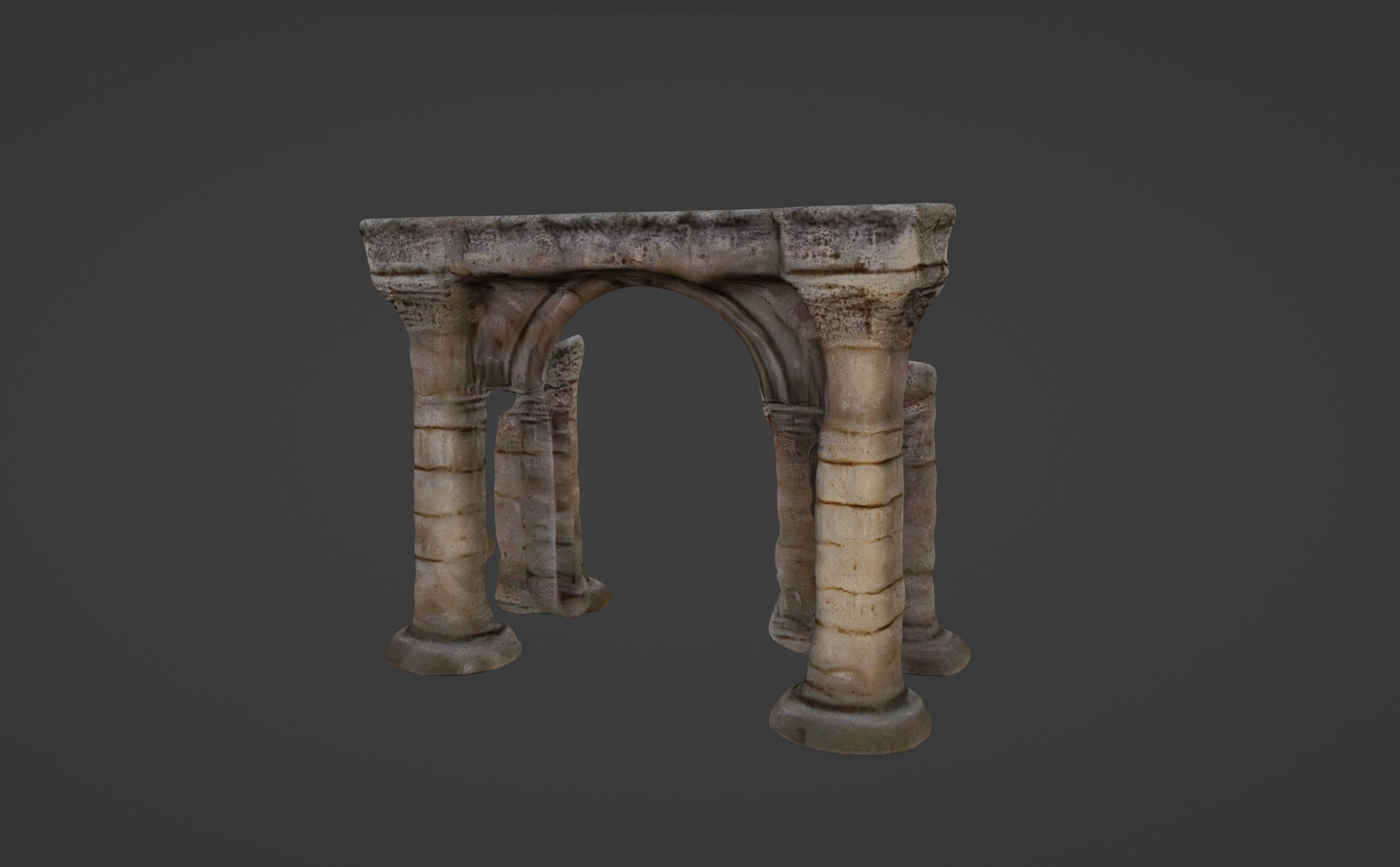
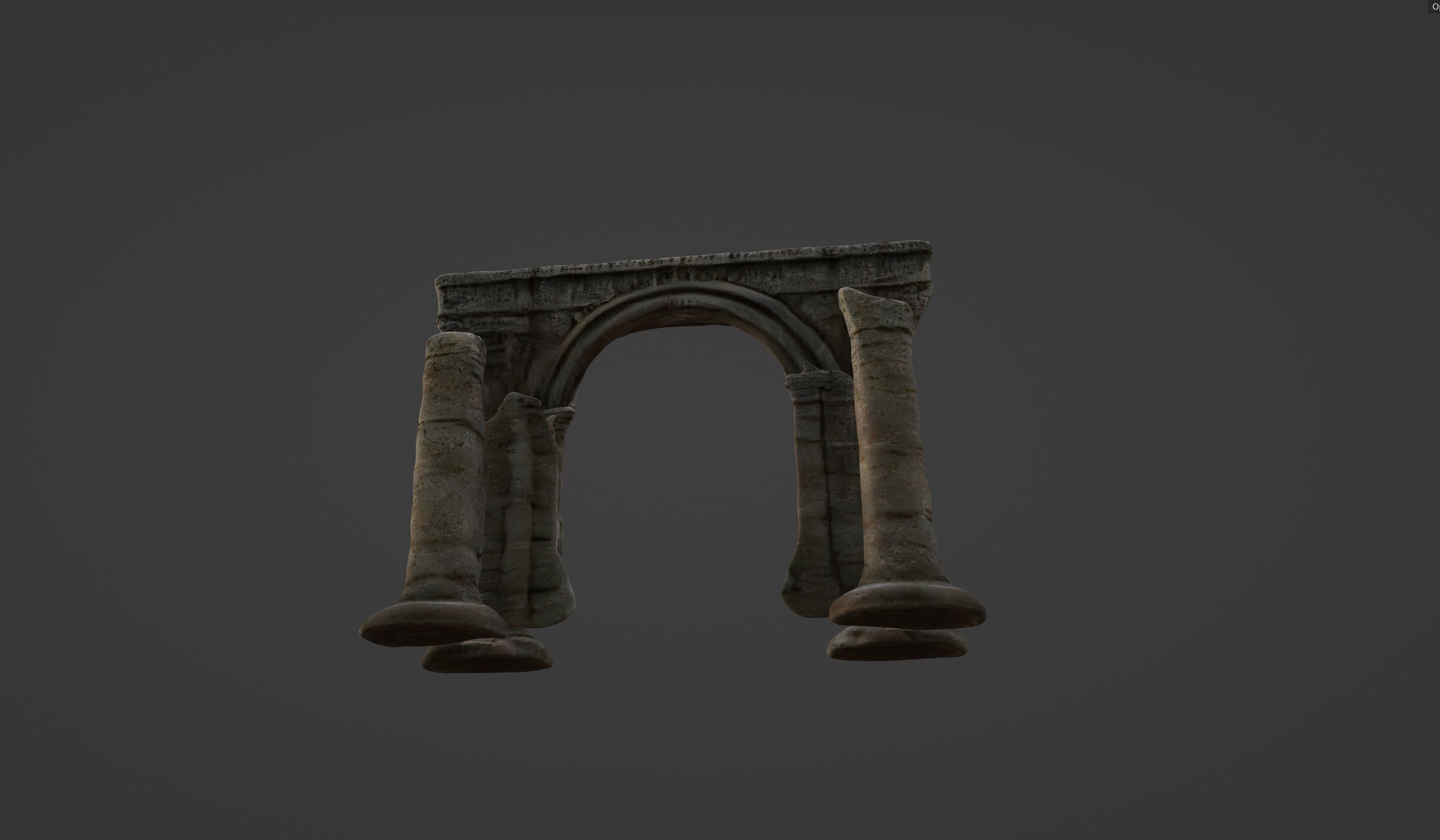
Archaic Pillars Ancient Ruins 3D model
The 3D model displayed appears to be a digital representation of ancient architectural ruins, specifically a series of columns and an arch. This model could serve educational purposes, architectural visualization, or as an asset in digital media such as video games or virtual reality experiences. The various file formats indicate that the model is highly versatile and can be used across different platforms and software.
.fbx (Filmbox): A popular file format used to provide interoperability between digital content creation applications. It is widely supported across various 3D software and is commonly used for game development due to its ability to store complex information such as animations.
.obj (Wavefront Object): A geometry definition file format first developed by Wavefront Technologies. It is widely supported and acts as a neutral interchange format for static 3D models without proprietary software restrictions. It is a good choice for sharing models when textures and materials are not a concern.
.glb (GL Transmission Format, Binary): A compact binary file format for 3D models and scenes. It's efficient for the web and virtual reality applications because it supports motion and is optimized for minimal file size and fast loading.
.usdz (Universal Scene Description Zip): Developed by Apple in collaboration with Pixar, this format is used for sharing 3D content natively in iOS and macOS environments with a focus on augmented reality experiences.
.blend (Blender): This is the native file format of Blender, a free and open-source 3D creation suite. It stores all aspects of 3D models, including animations, textures, and even the user interface layout. Ideal for Blender artists who want to work with the raw project file.
.stl (Stereolithography): A file format native to the stereolithography CAD software created by 3D Systems. It is widely used for 3D printing and computer-aided manufacturing due to its simplicity, focusing solely on the geometry of the model in terms of vertices and faces, without support for textures or animations.
Each format offers different advantages depending on the intended use of the model, ranging from detailed animation and texturing capabilities to straightforward geometric representation for physical production.