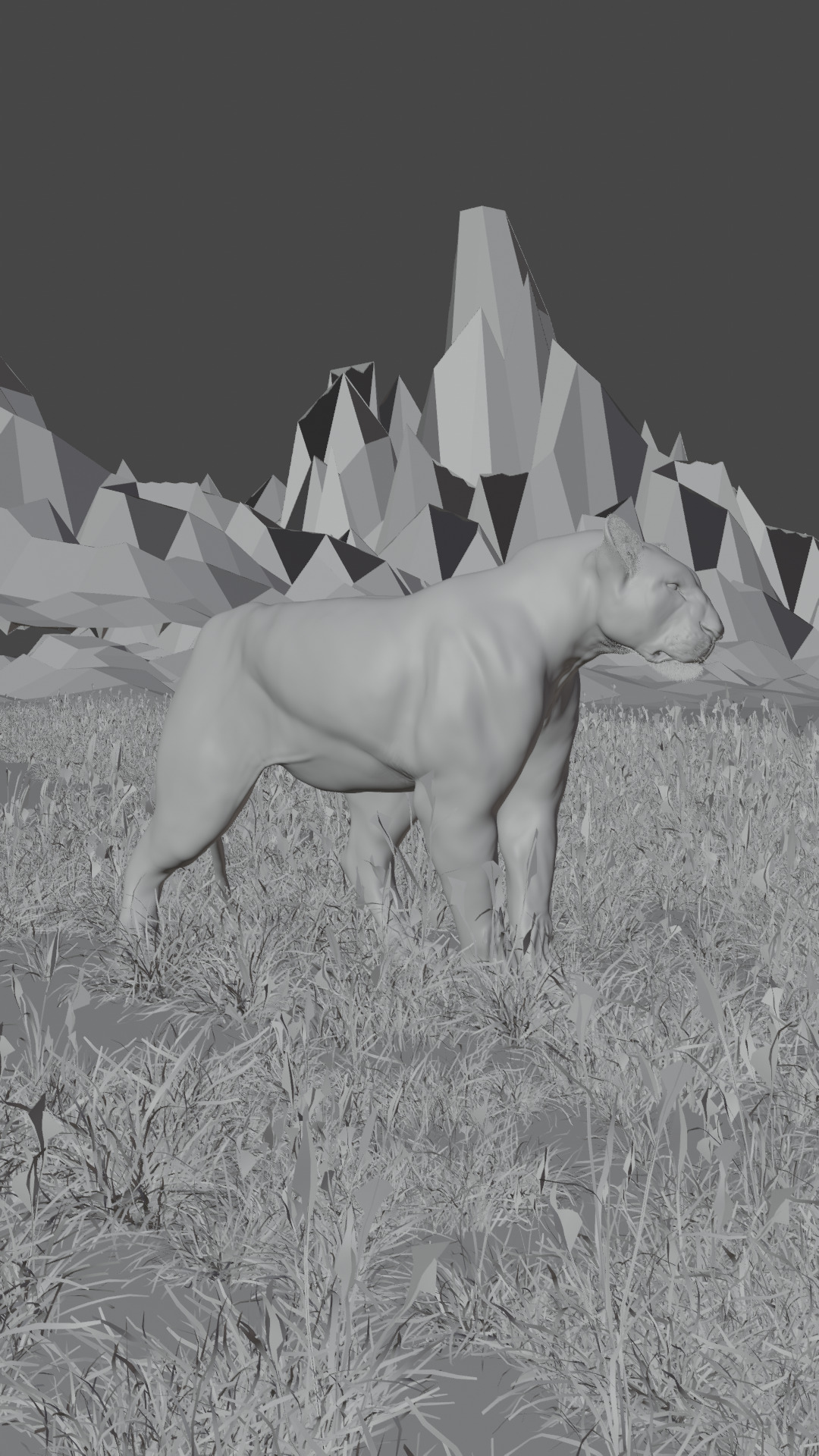
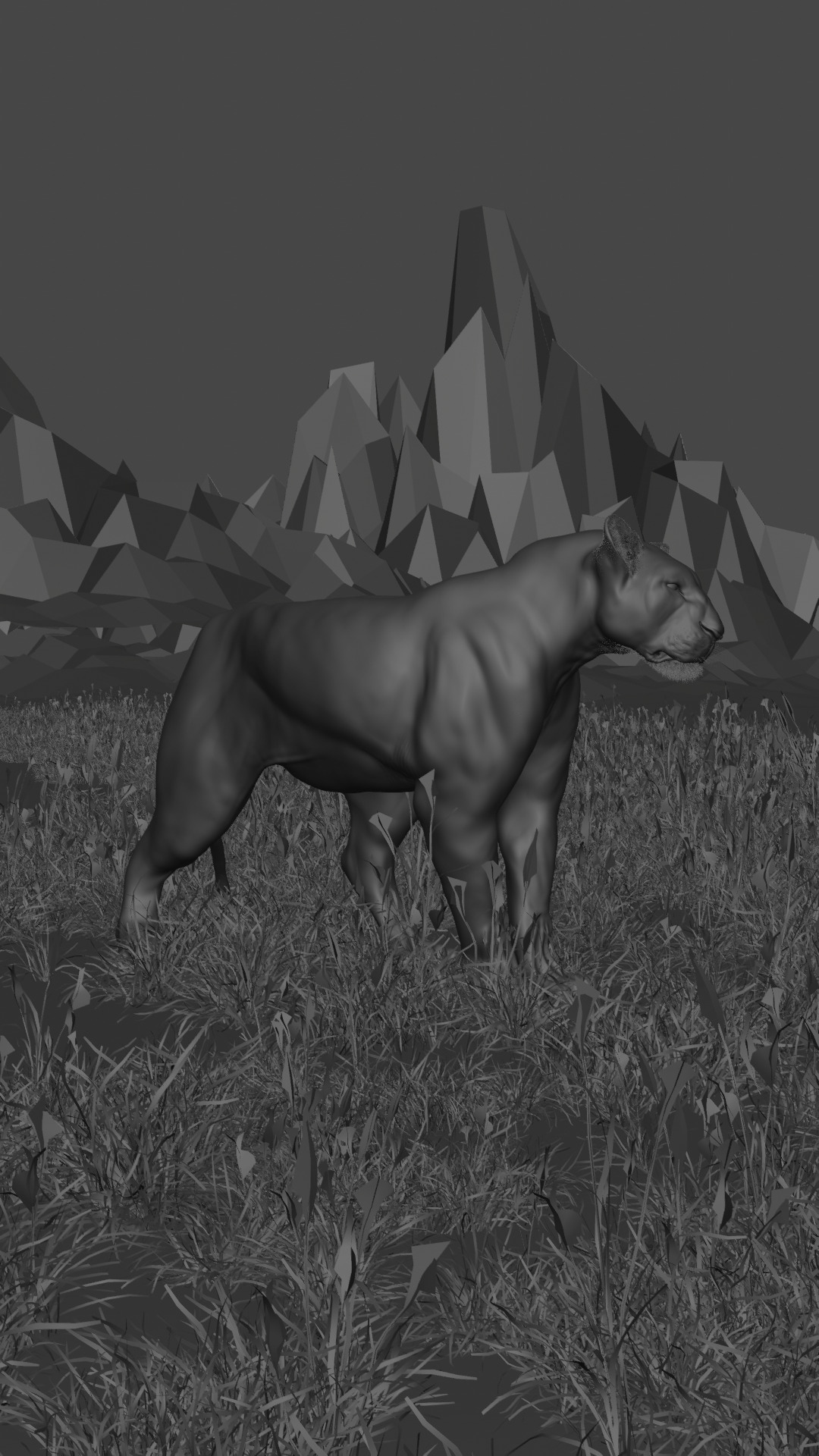
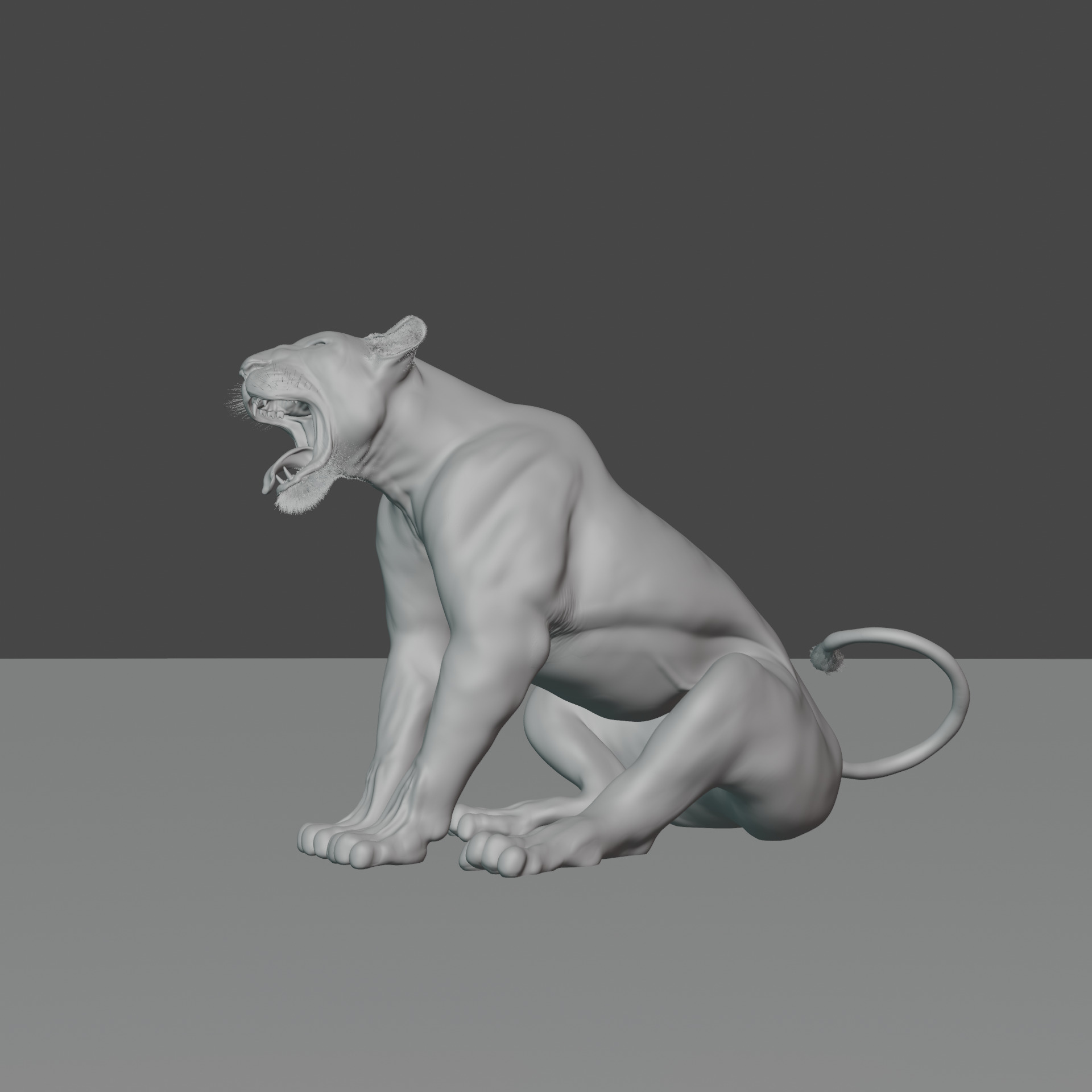
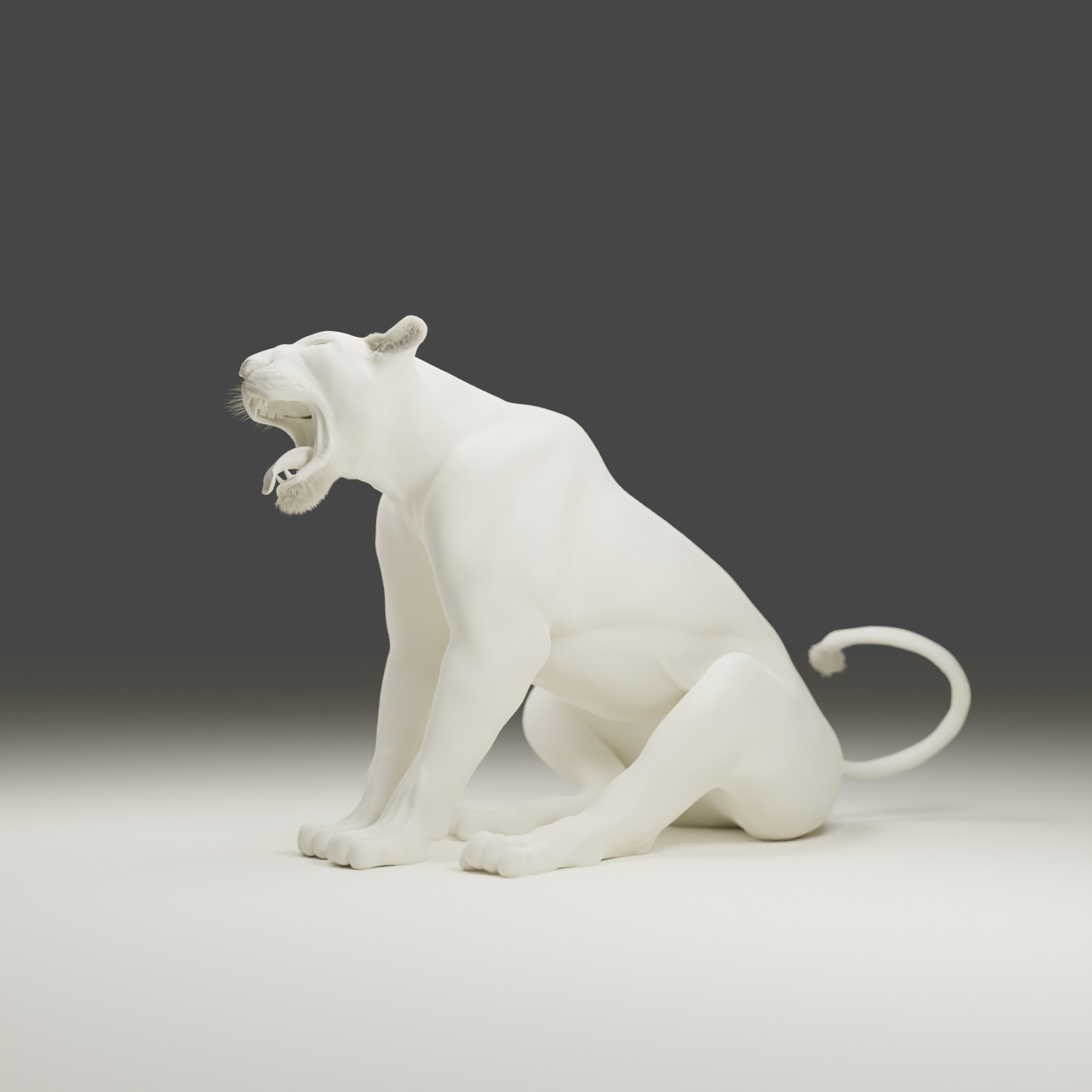
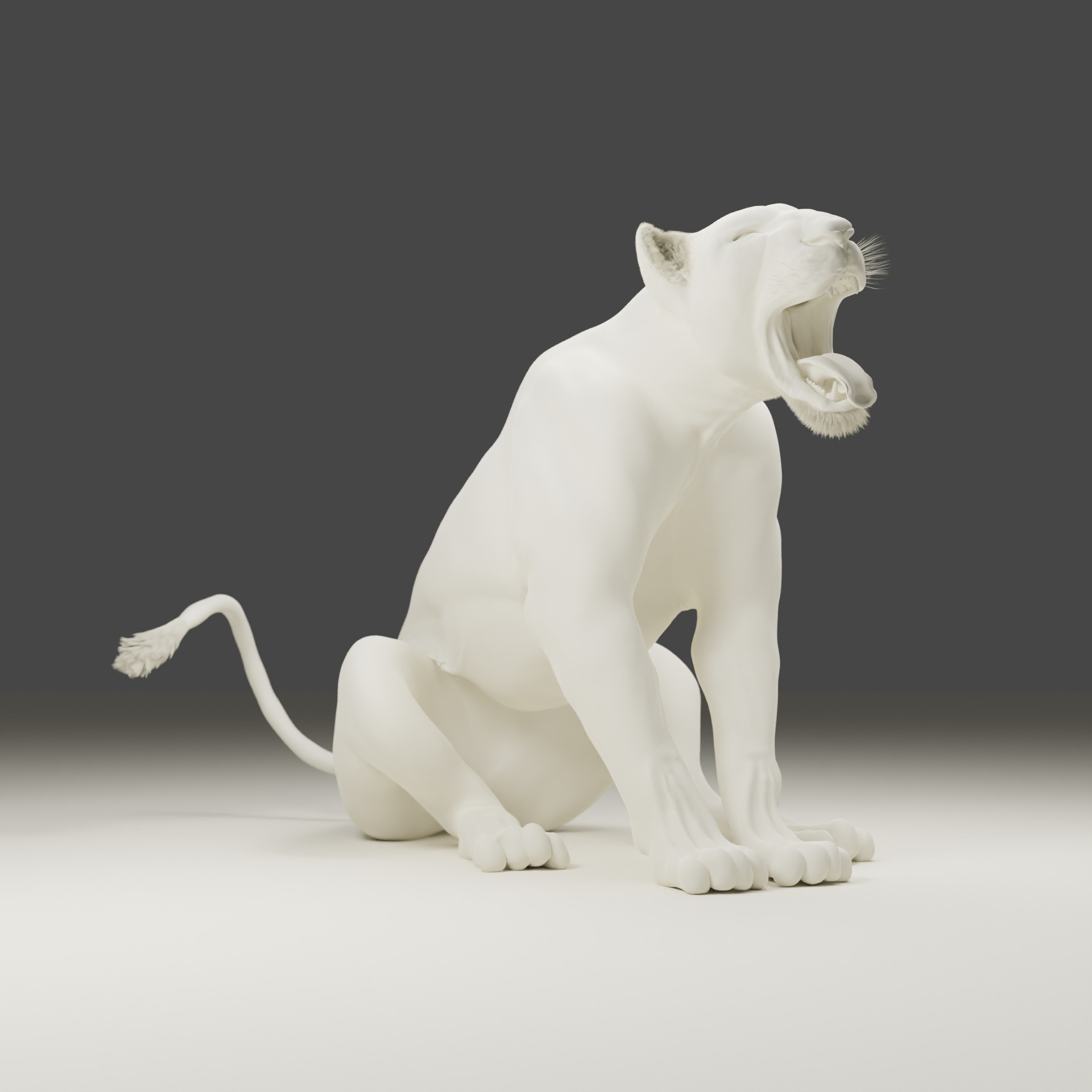
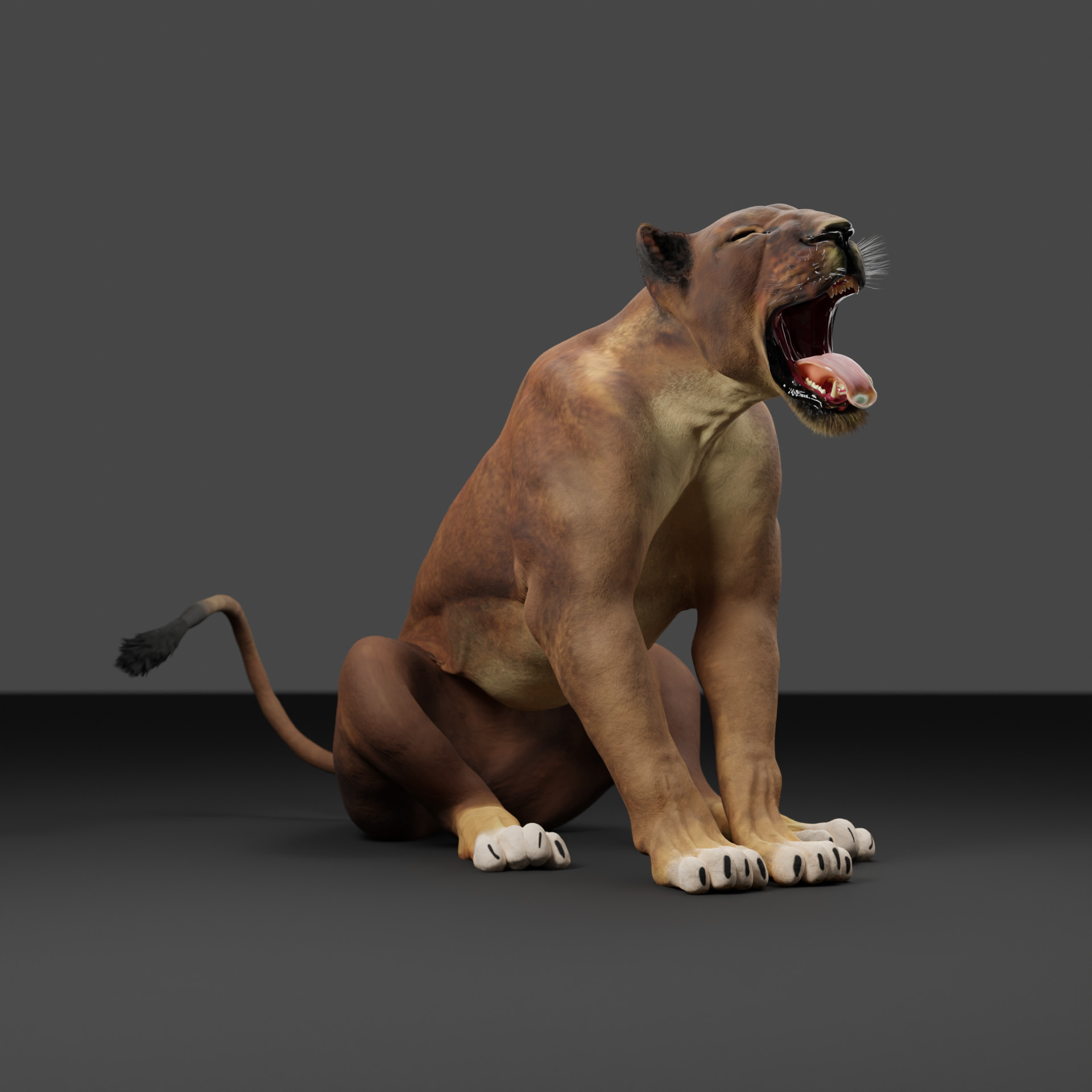
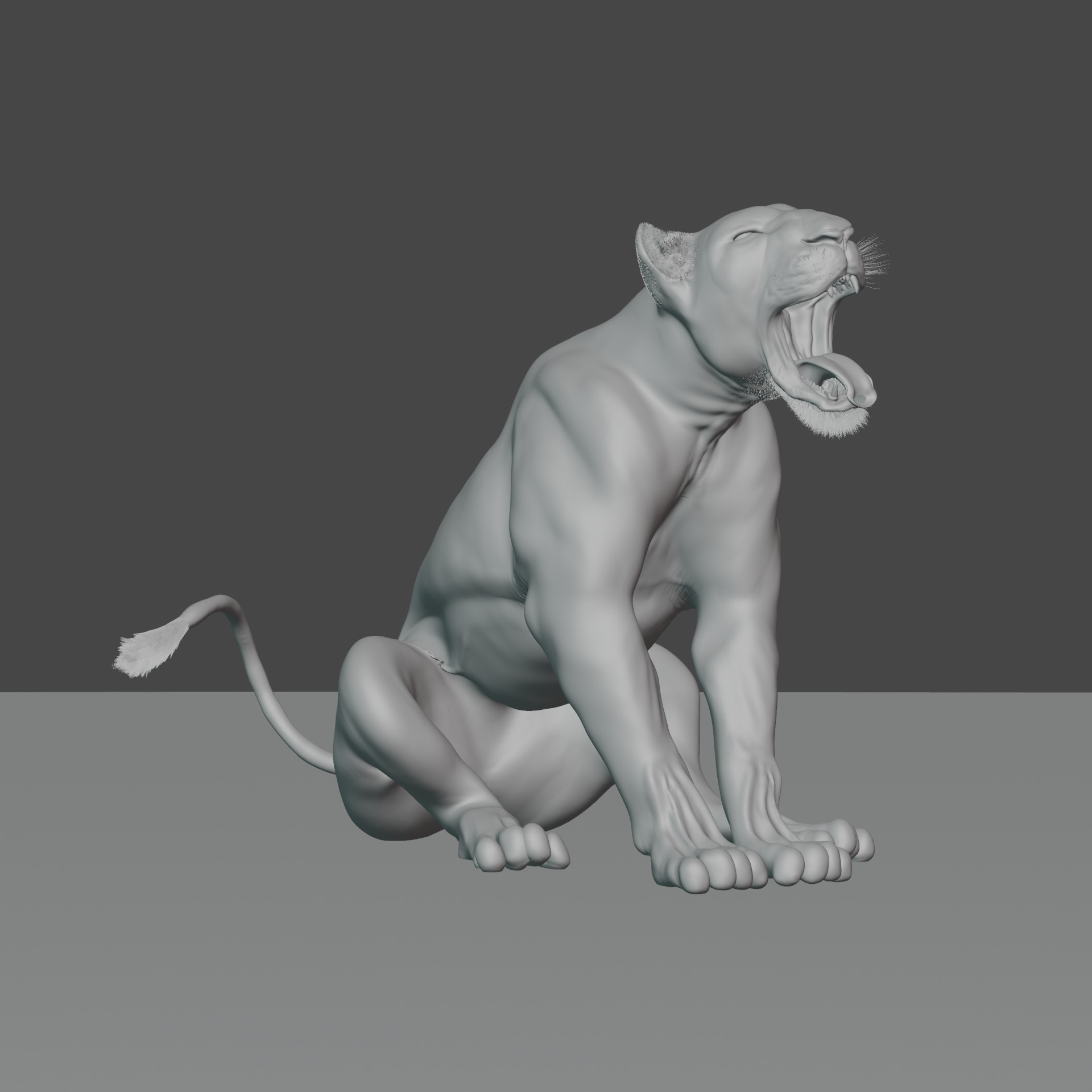
Lioness - 3D Model 3D model
A lioness is a female lion, scientifically known as Panthera leo. Here are some key facts about lionesses:Physical Characteristics:
Size: Smaller and lighter than male lions, weighing between 260–400 pounds (120–180 kg). Length: Around 4.5 to 5.5 feet (1.4–1.7 m) long, excluding the tail. Appearance: They lack the thick mane that male lions have, giving them a more streamlined look which aids in hunting.
Habitat:
Found mainly in sub-Saharan Africa with a small population in the Gir Forest of India (Asiatic lions). Prefer savannas, grasslands, and open woodlands.
Behavior:
Social Structure: Lionesses live in prides, which are social groups typically consisting of related females, their cubs, and a few male lions. Role in the Pride: They are the primary hunters and work together to catch prey like zebras, wildebeests, and antelopes. Communication: Use roars, grunts, growls, and body language to communicate within the pride.
Reproduction:
Lionesses give birth to 1–4 cubs after a gestation period of about 110 days. They often nurse each other's cubs, showing strong cooperative behavior.
Diet:
Carnivorous: Hunt large mammals but will also scavenge when necessary. Hunting Technique: Use stealth, teamwork, and speed to ambush prey.
Lifespan:
In the wild: Around 10–15 years. In captivity: Can live up to 20 years due to better care and absence of threats.
Interesting Facts:
Lionesses are faster than male lions, reaching speeds of up to 50 mph (80 km/h) for short bursts. They often hunt at night or during cooler times of the day to conserve energy.