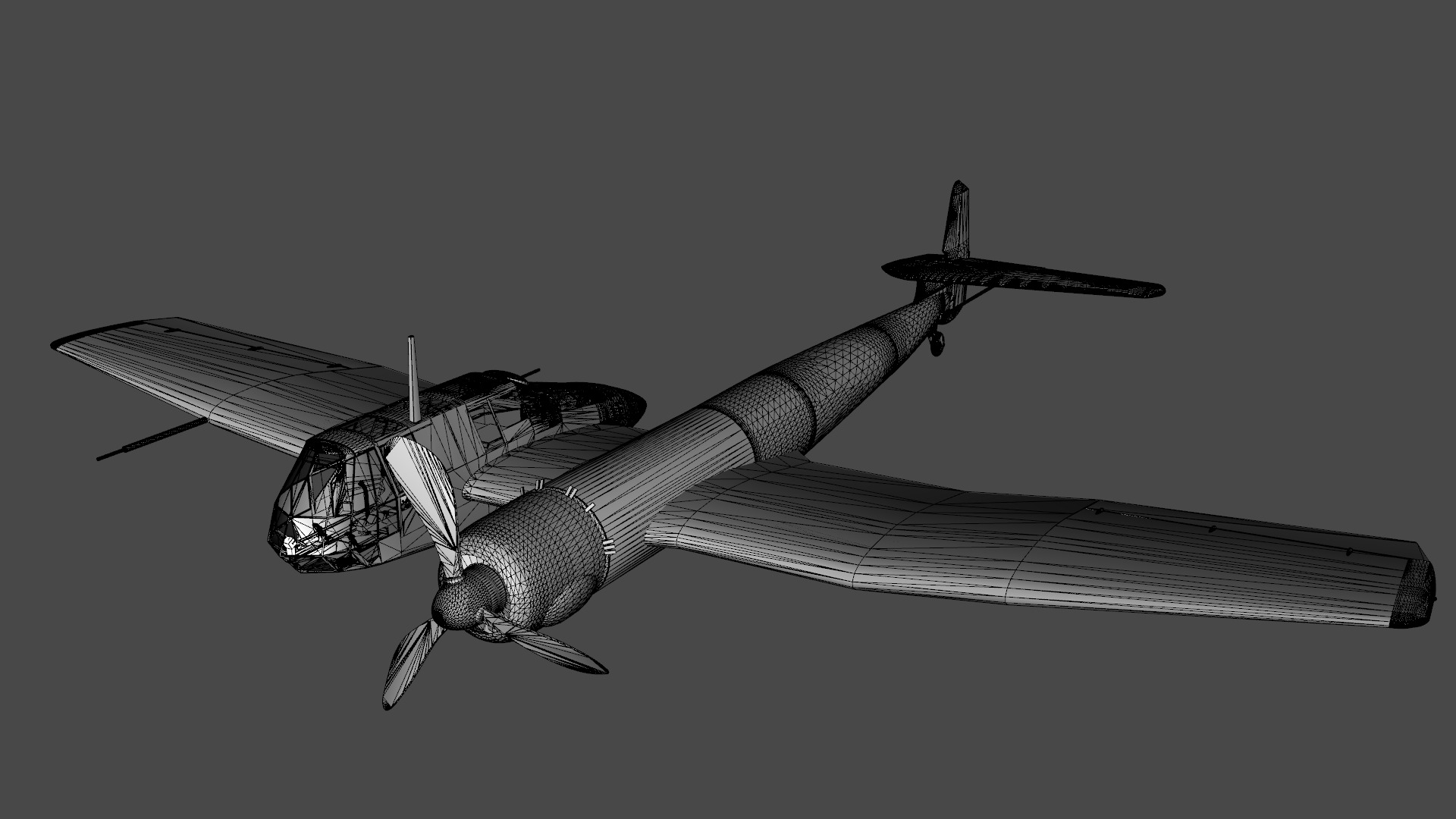
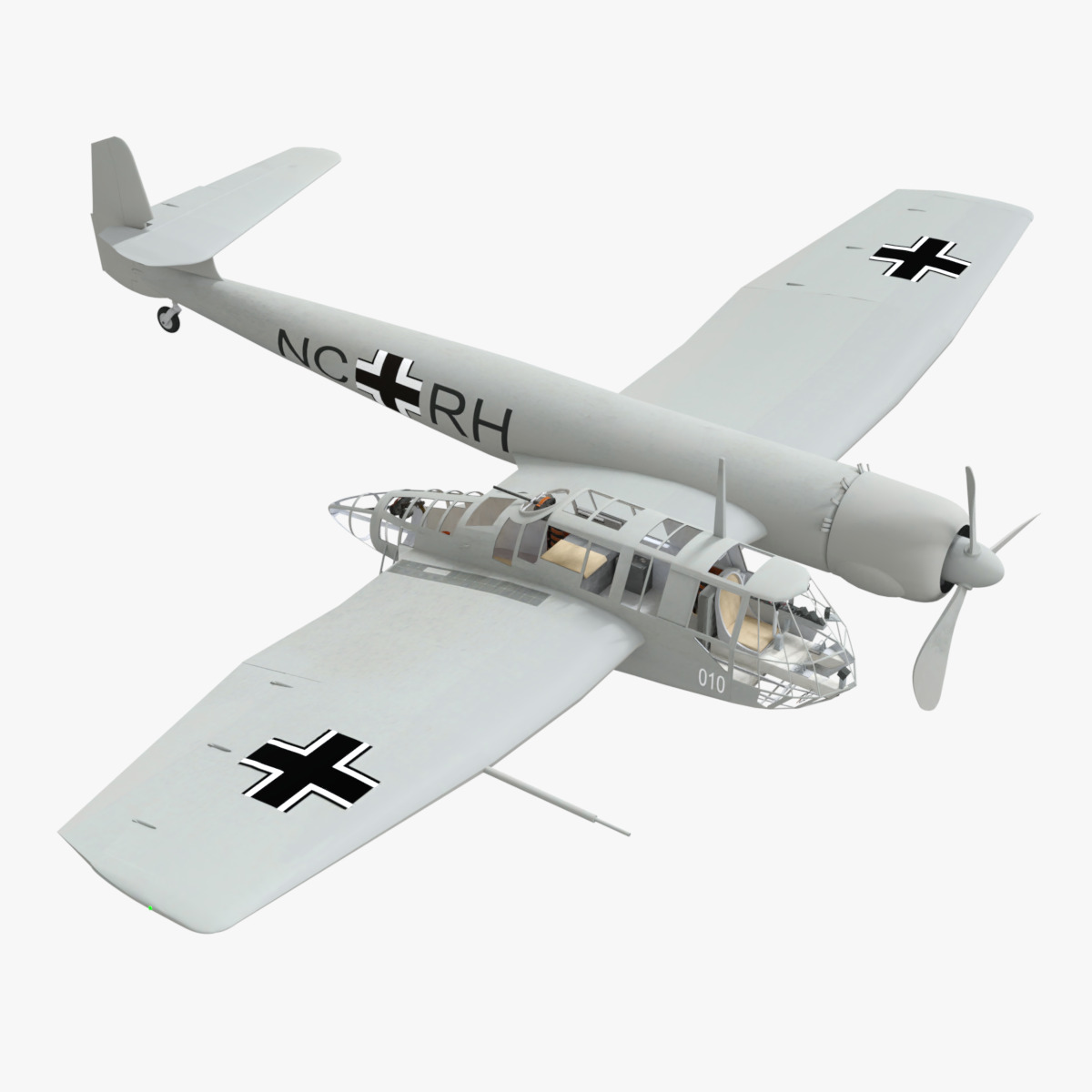
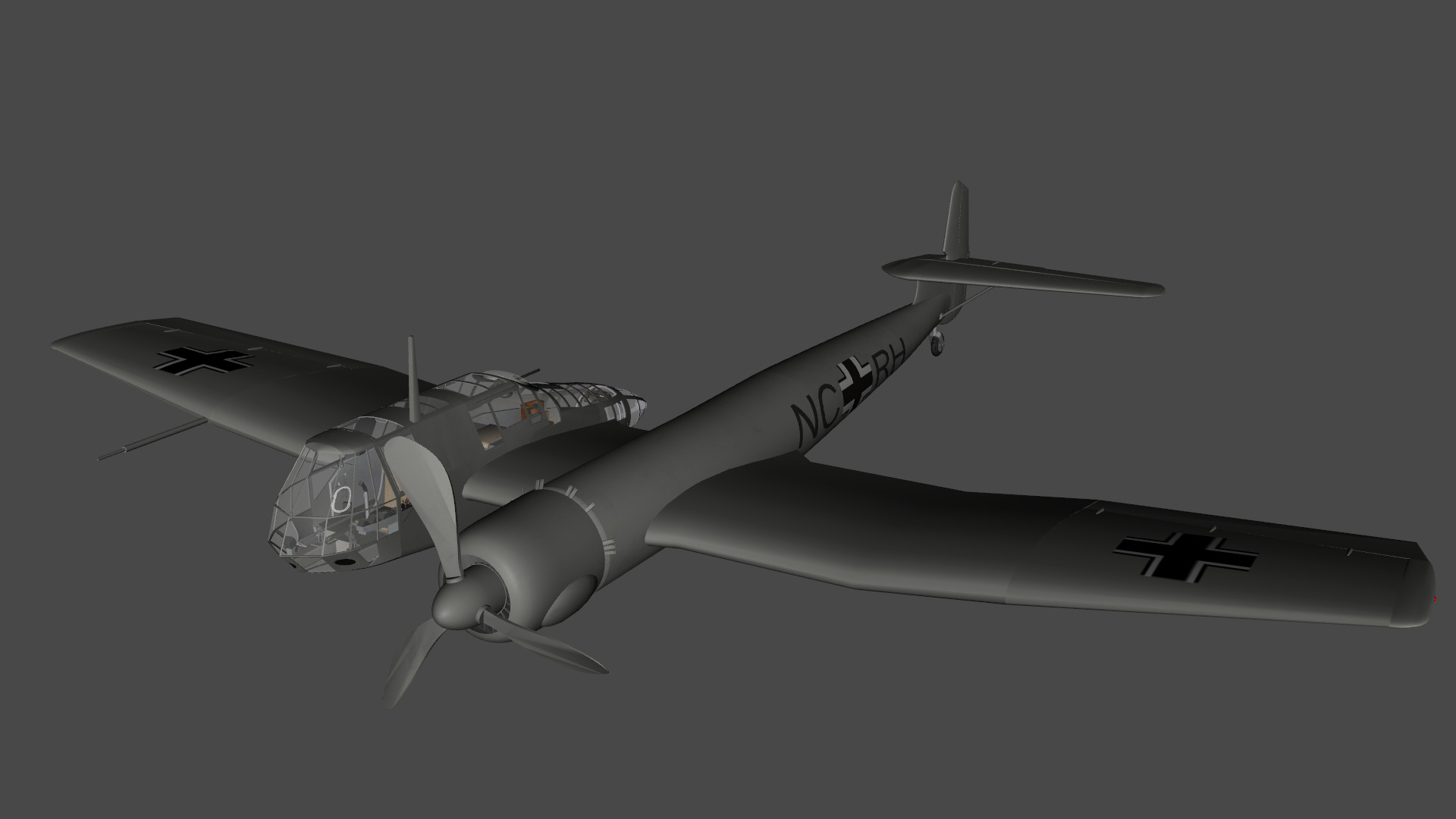
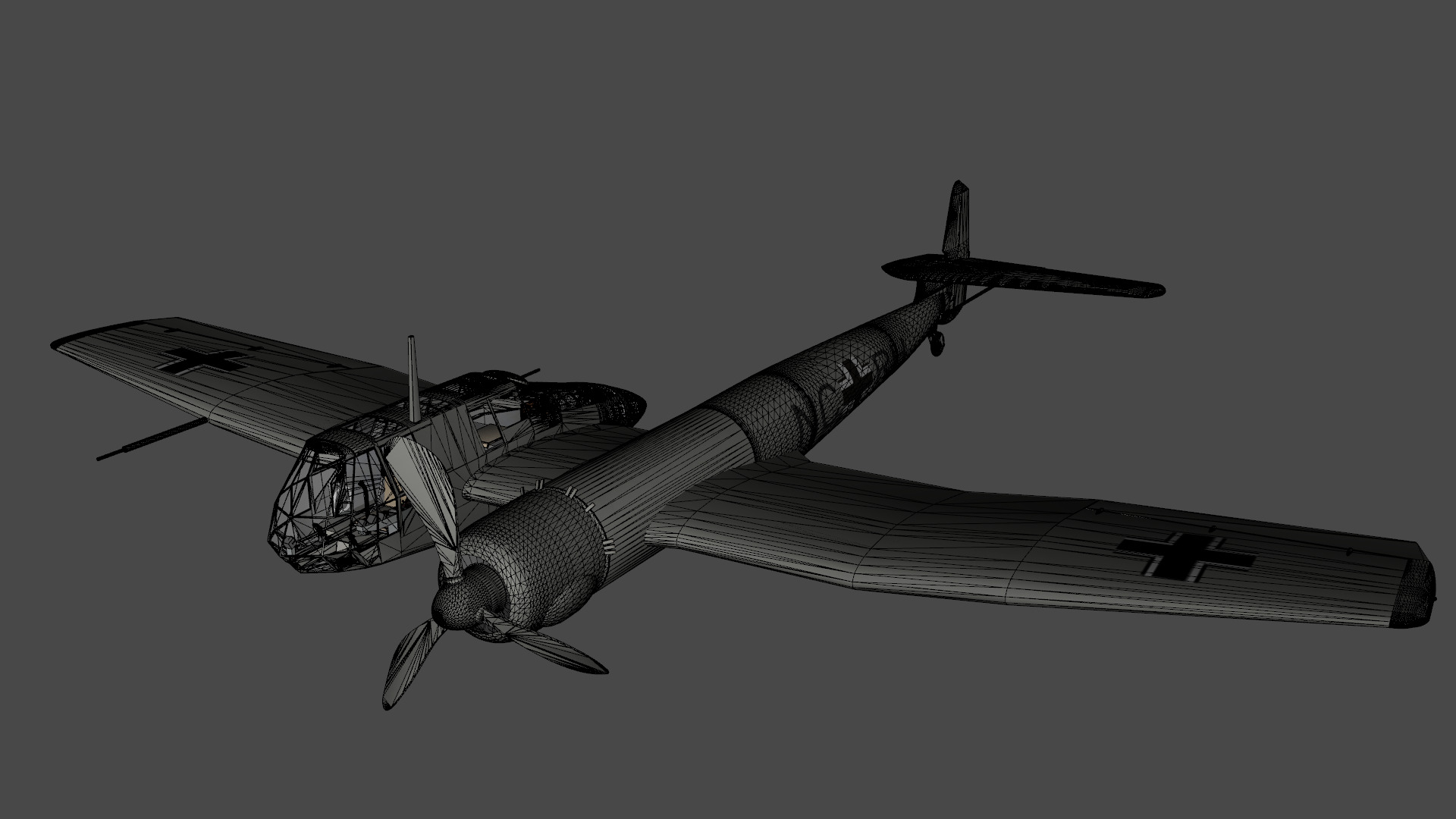
Blohm Voss BV 141 German WW2 Aircraft Low-poly 3D model
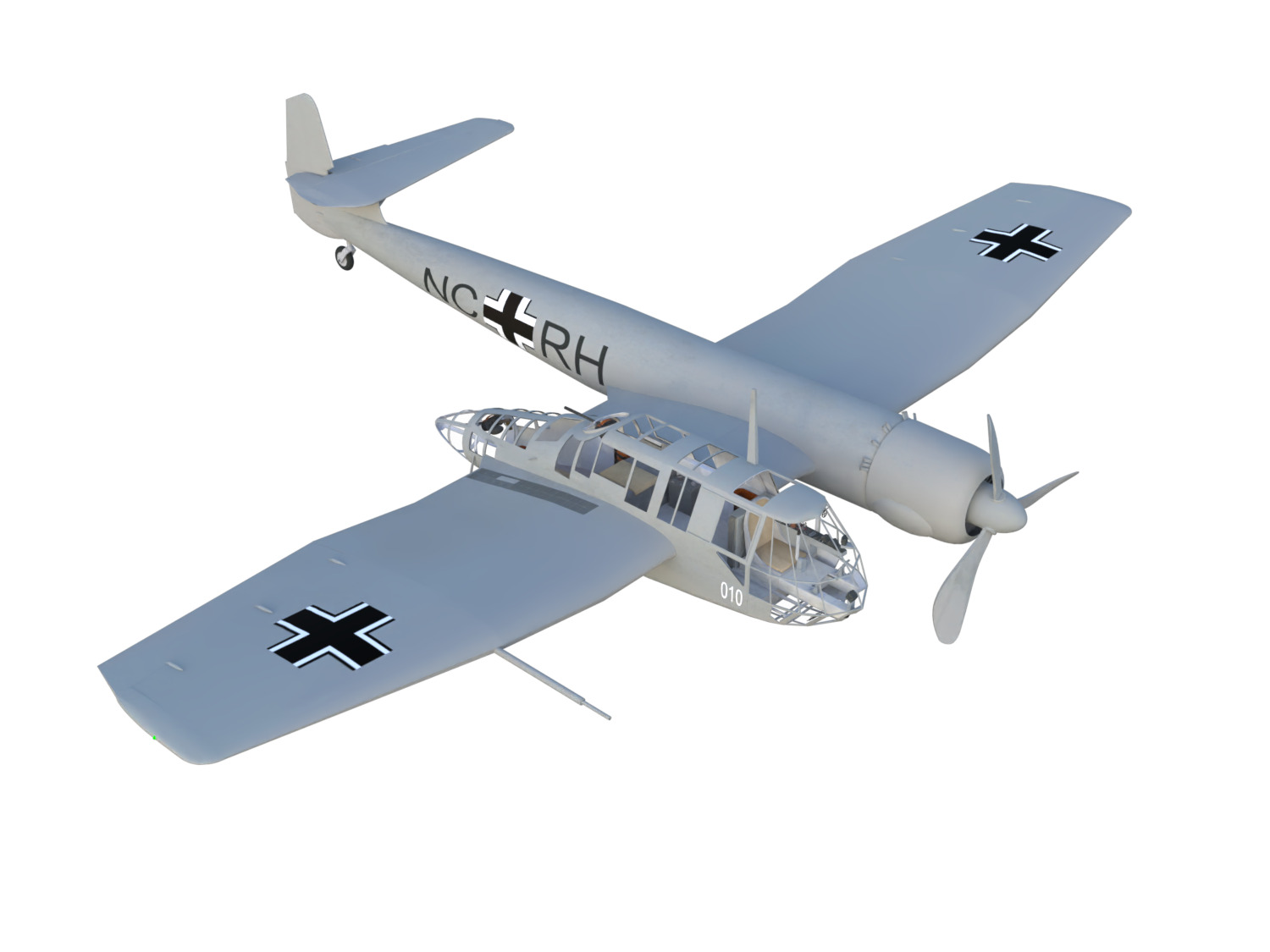
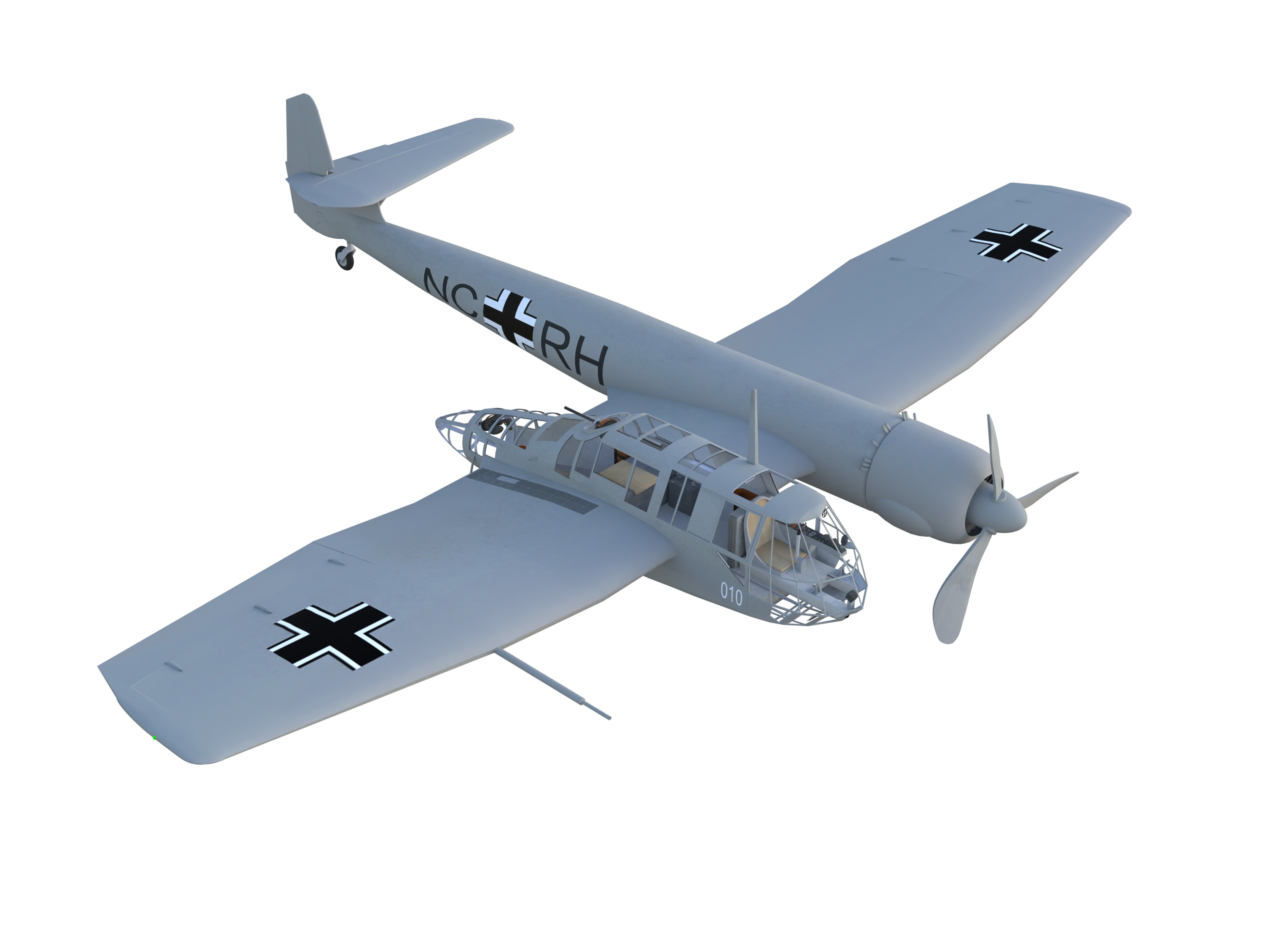
Blohm & Voss BV 141 German WW2 Aircraft
Photorealistic
Low-poly
PBR/Gameready
3K High Quality Texture Map
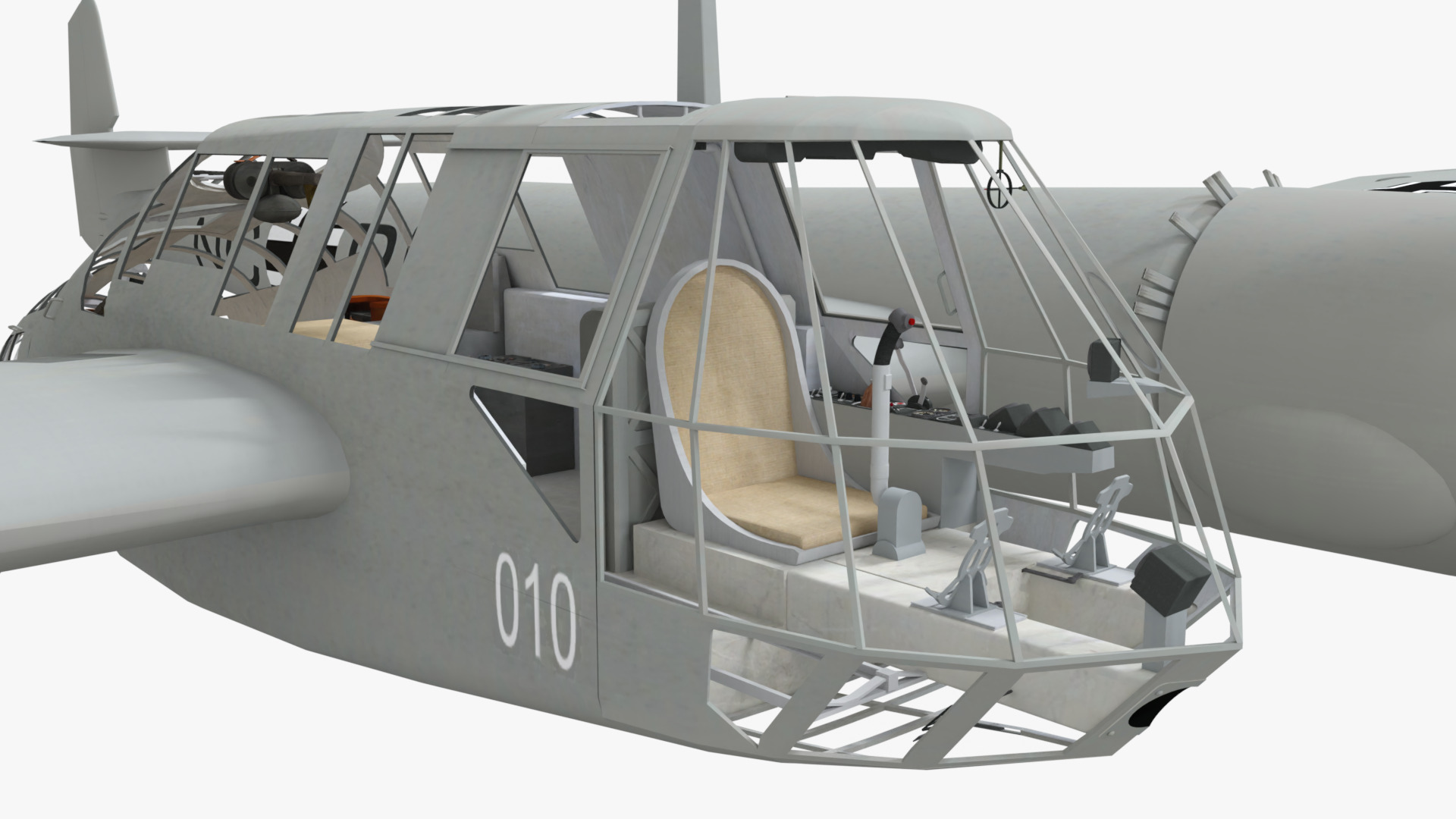
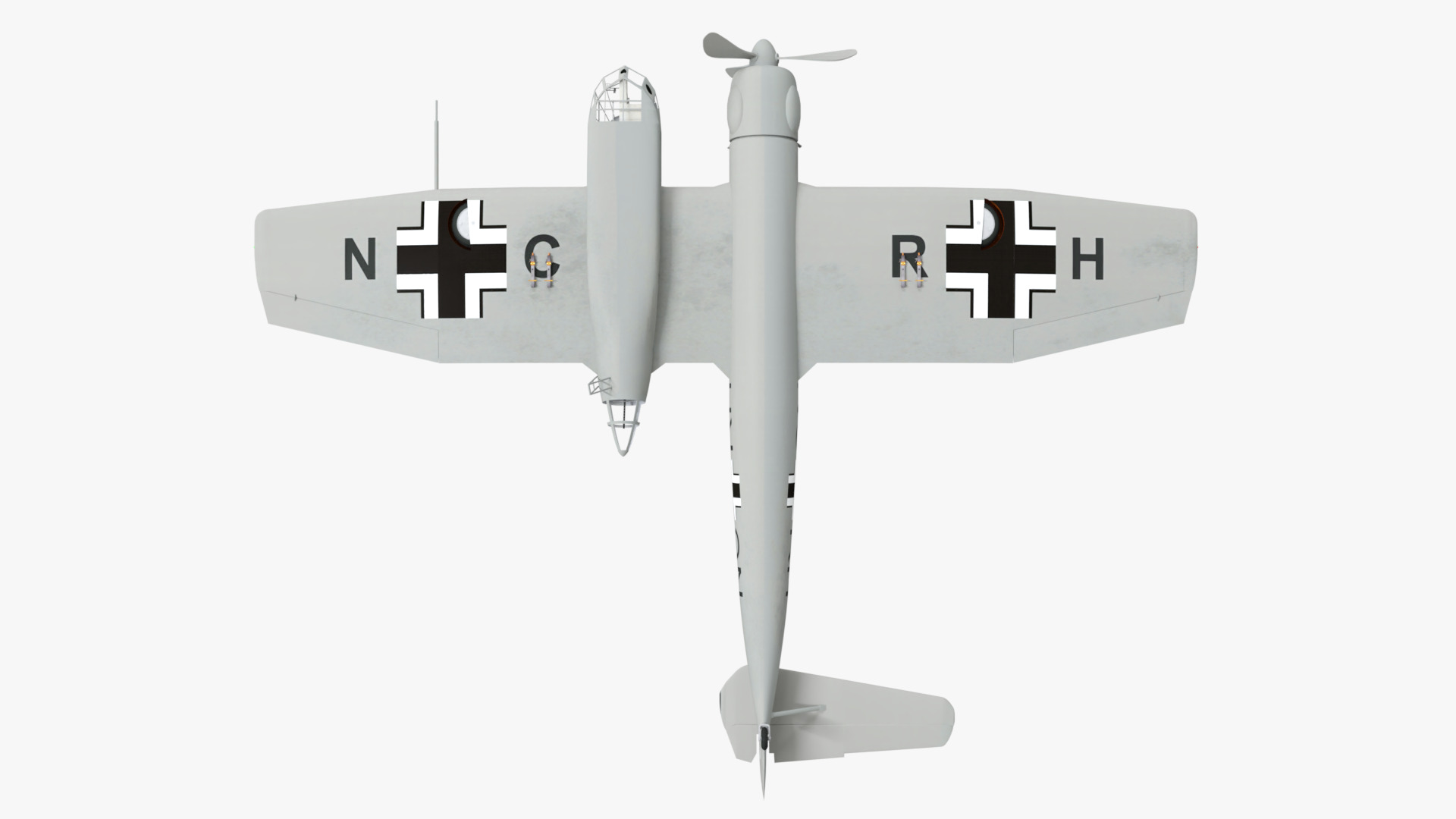
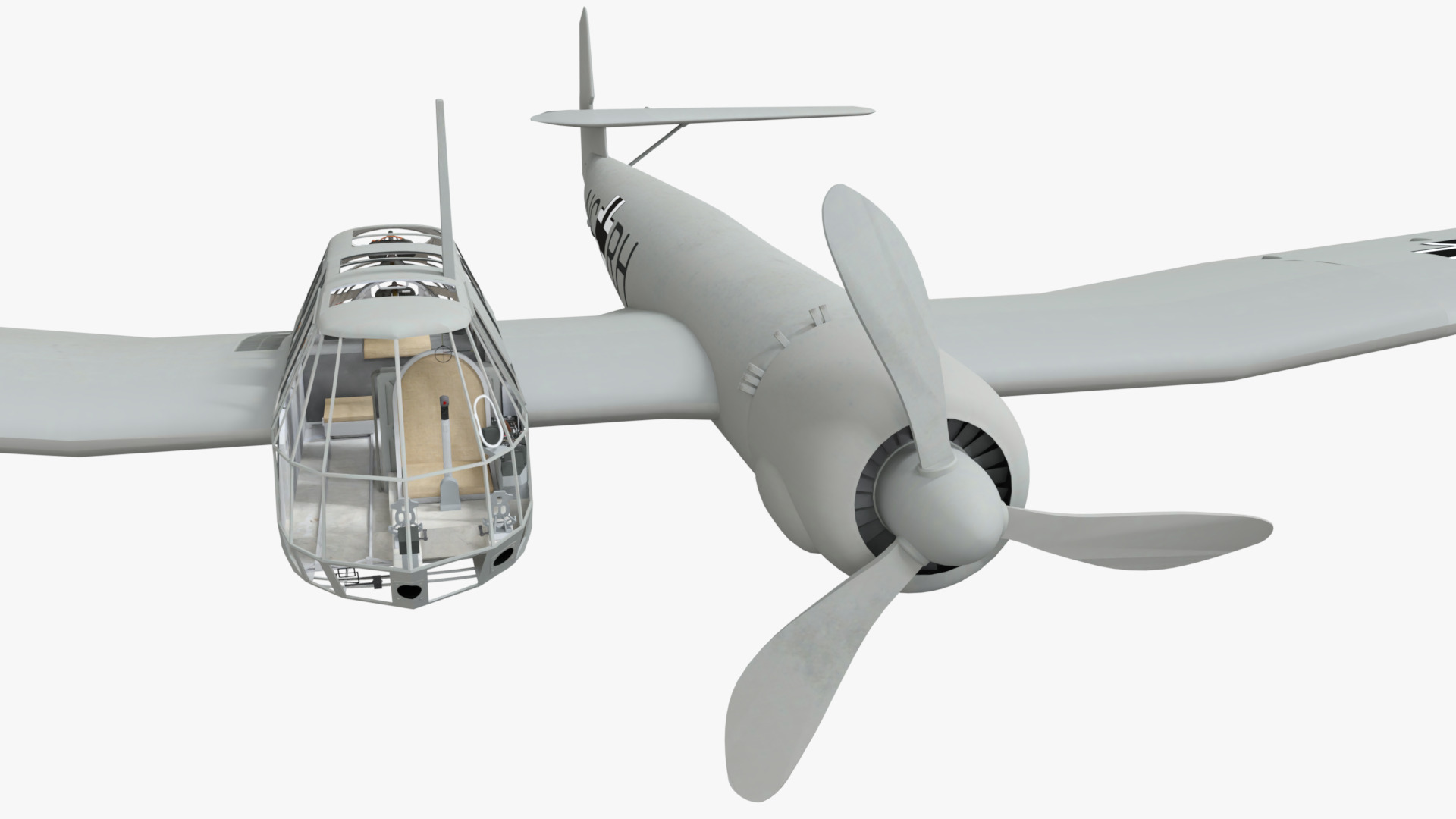
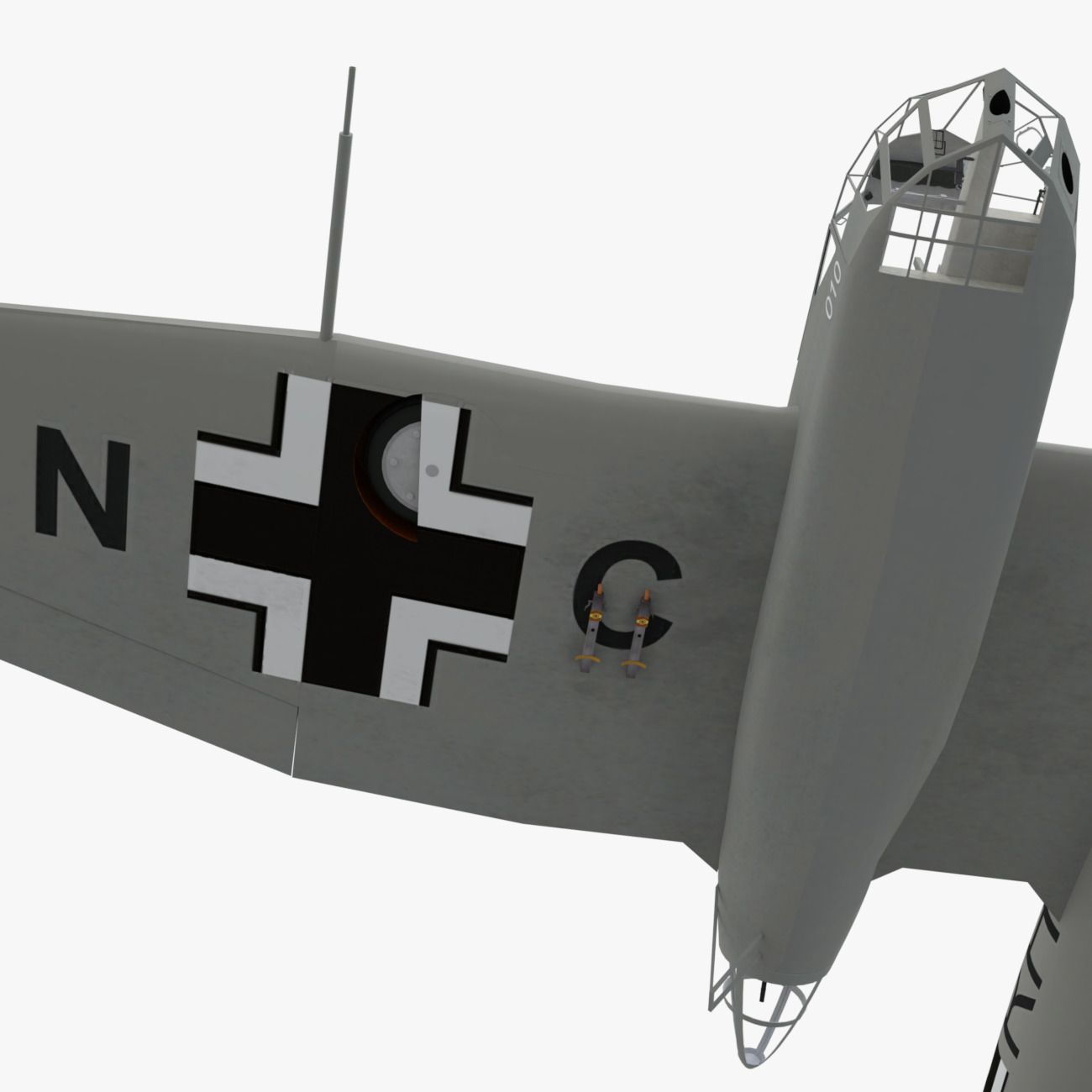
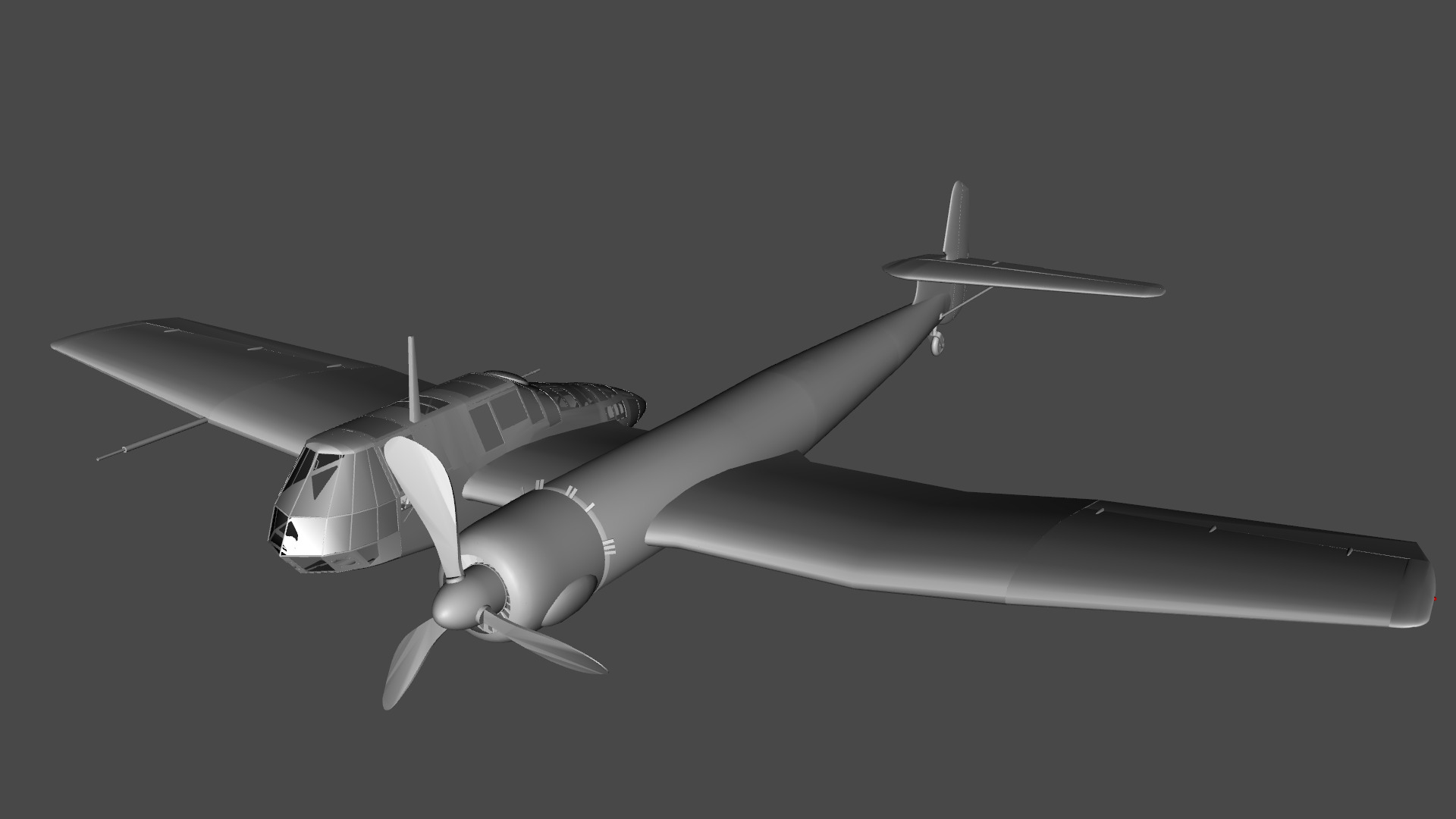
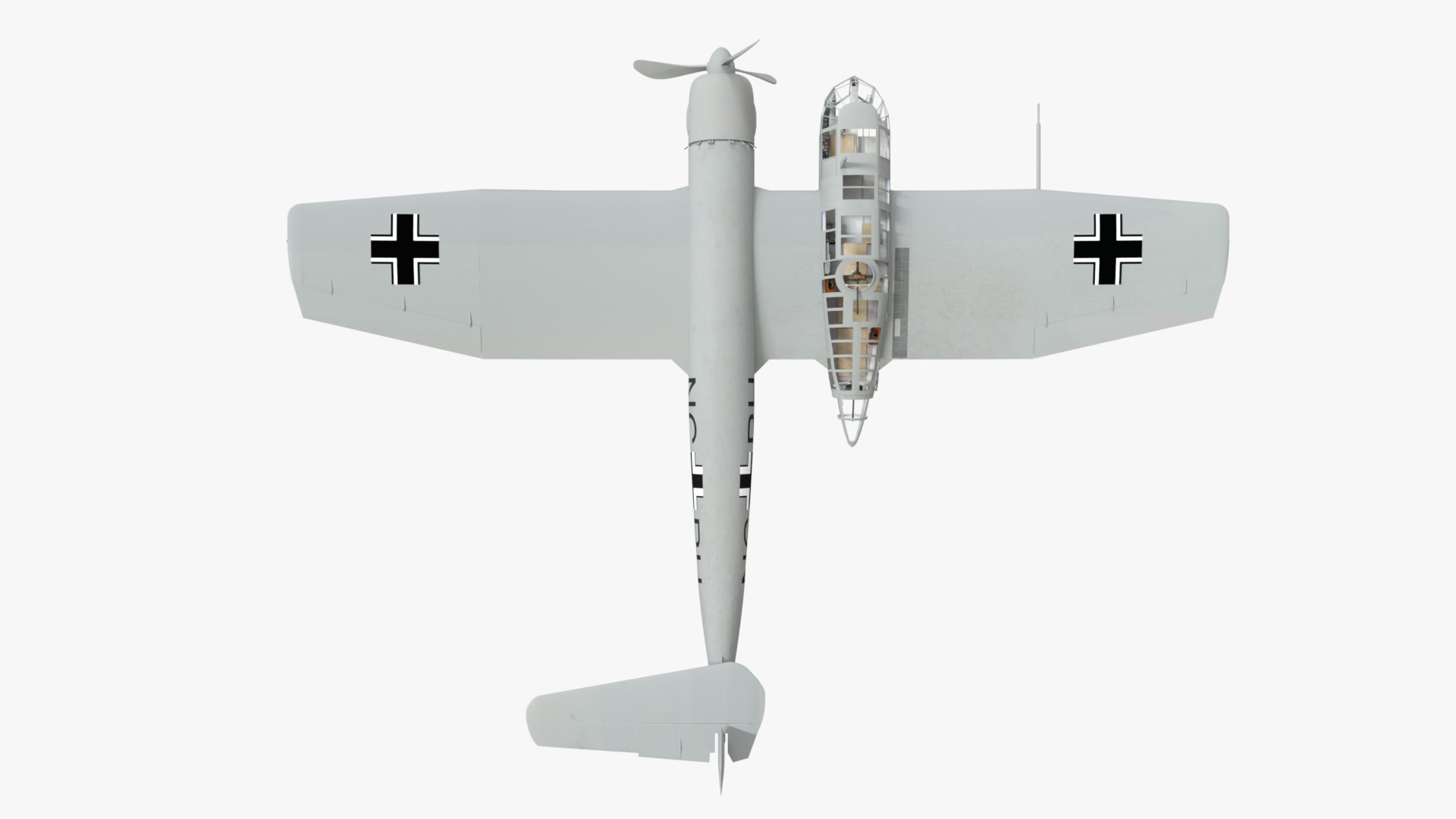
The Blohm & Voss BV 141 (originally the Ha 141)[4] was an unorthodox tactical reconnaissance aircraft developed by the German aircraft manufacturer Blohm & Voss. It was notable for its uncommon structural asymmetry.
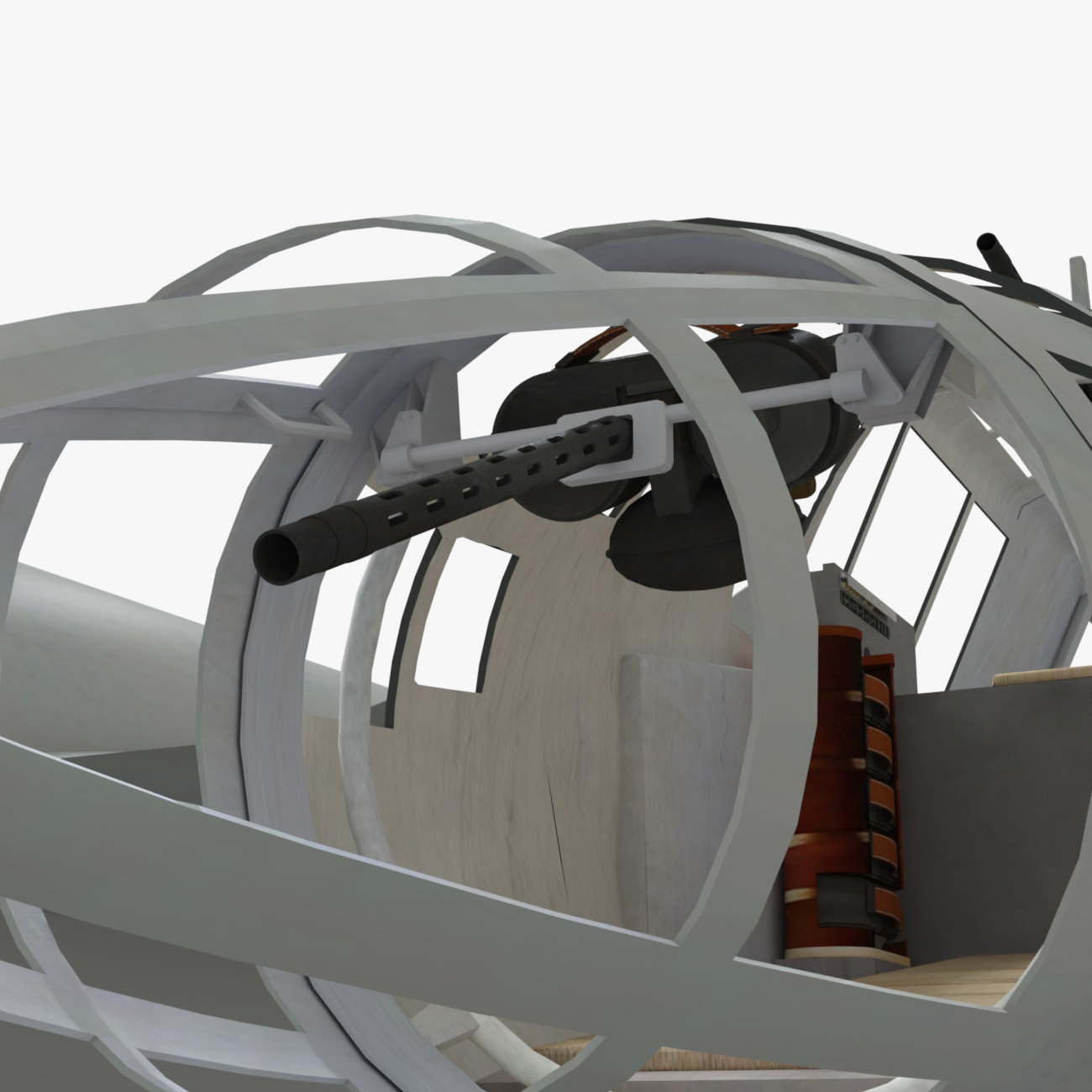
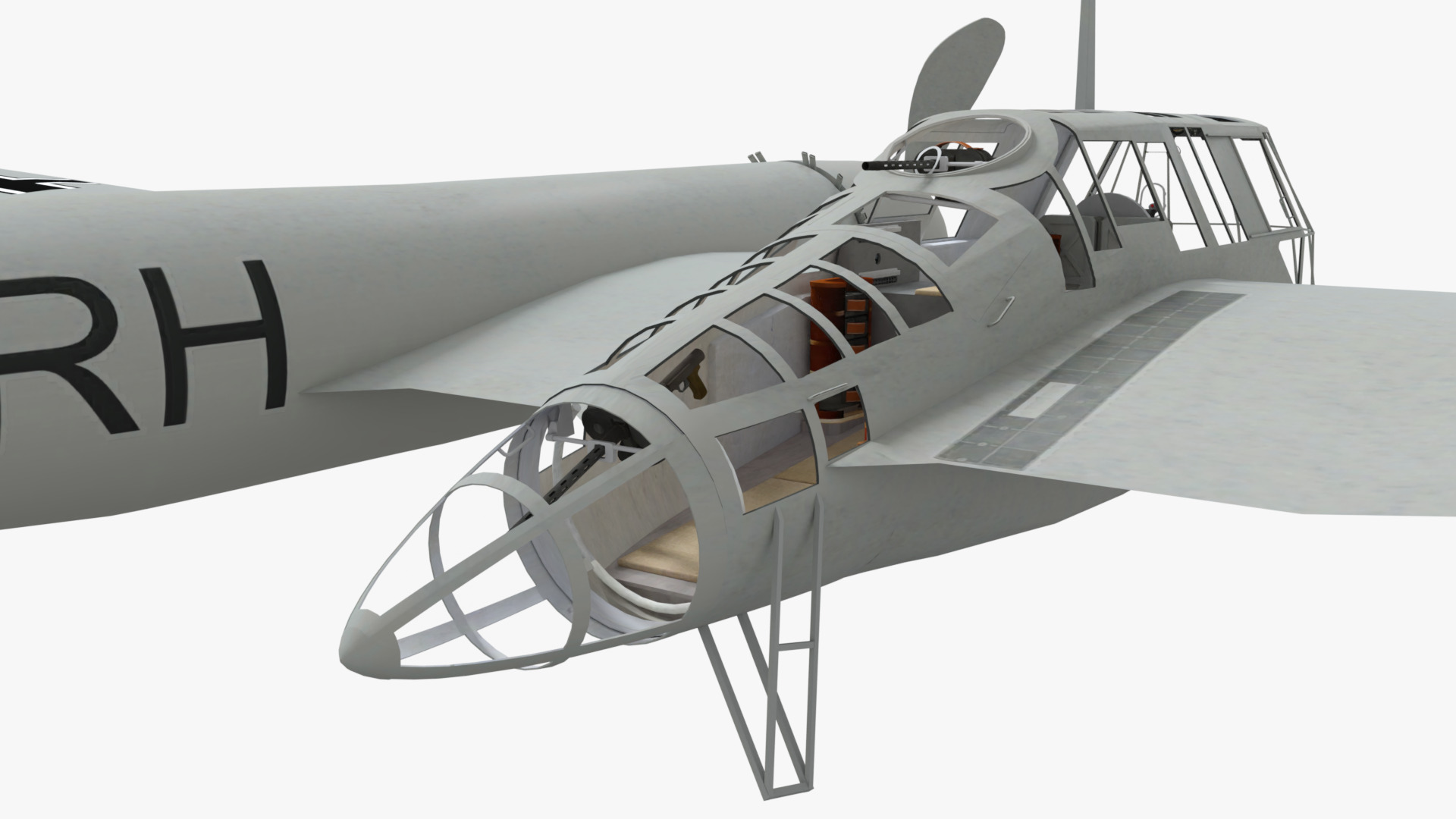
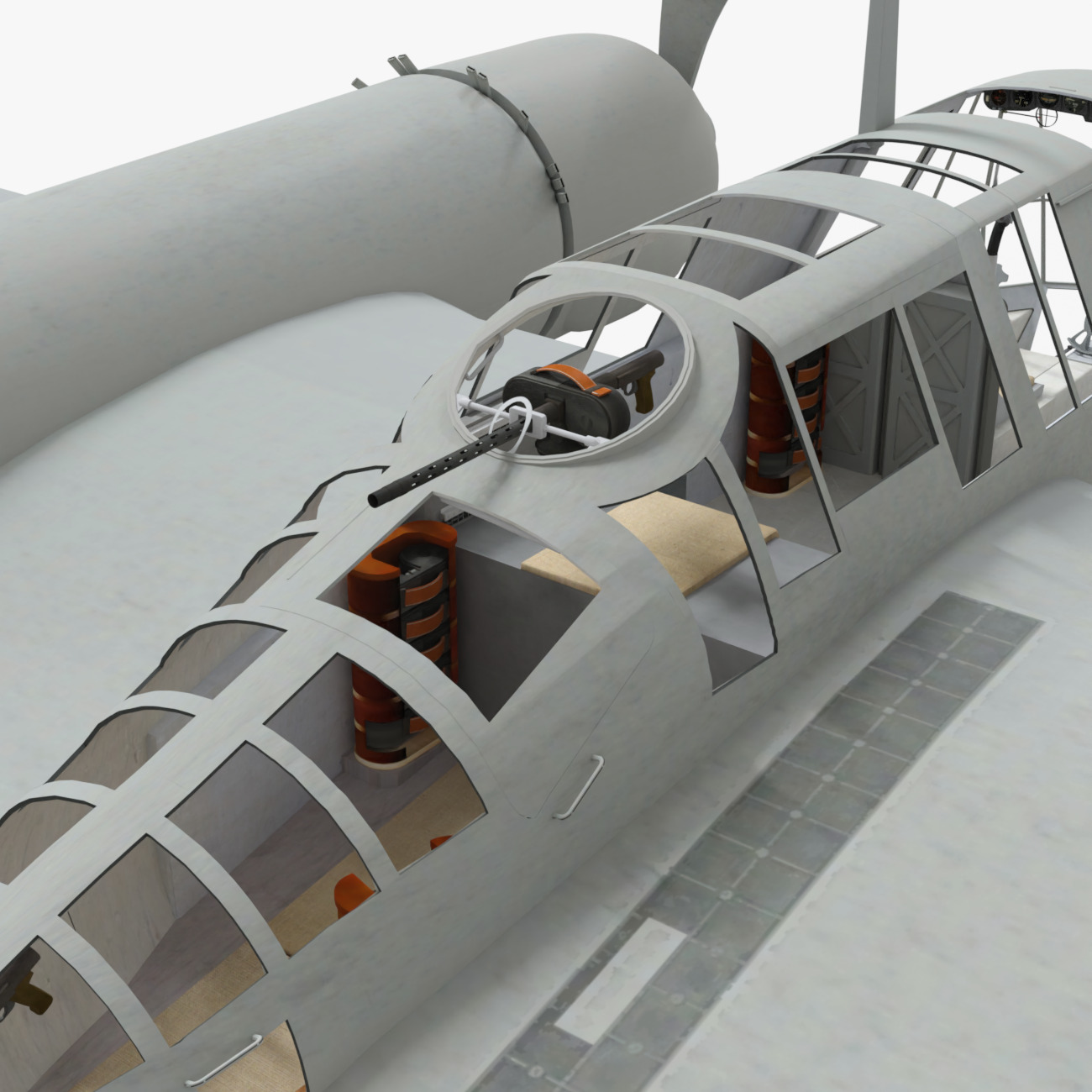
Development commenced during 1937 in response to a Reichsluftfahrtministerium (RLM/German Aviation Ministry) specification seeking a new single-engine reconnaissance aircraft. While not invited to participate, the firm's design team opted to use a radical configuration for the BV 141 that placed the crew inside of a Plexiglas-glazed gondola that was positioned starboard of the engine and tail boom. Although the RLM declined to finance its development in favour of other options, Blohm & Voss chose to spend its own money to produce a prototype, which performed its maiden flight on 25 February 1938.
During flight testing, the aircraft proved itself to possess relatively good performance. Despite this, the RLM cancelled production plans for the BV 141A in April 1940 due to its perceived lack of power. A more powerful version of the aircraft, the BV 141B, commenced testing in 1941. However, development was protracted and a planned operational deployment on the Eastern Front was cancelled in 1942. The aircraft was never ordered into full-scale production for multiple reasons; these included the unavailability of the preferred engine and strong competition from another tactical reconnaissance aircraft, the twin-engined Focke-Wulf Fw 189 Uhu. Several examples were captured and studied by the Allied powers.