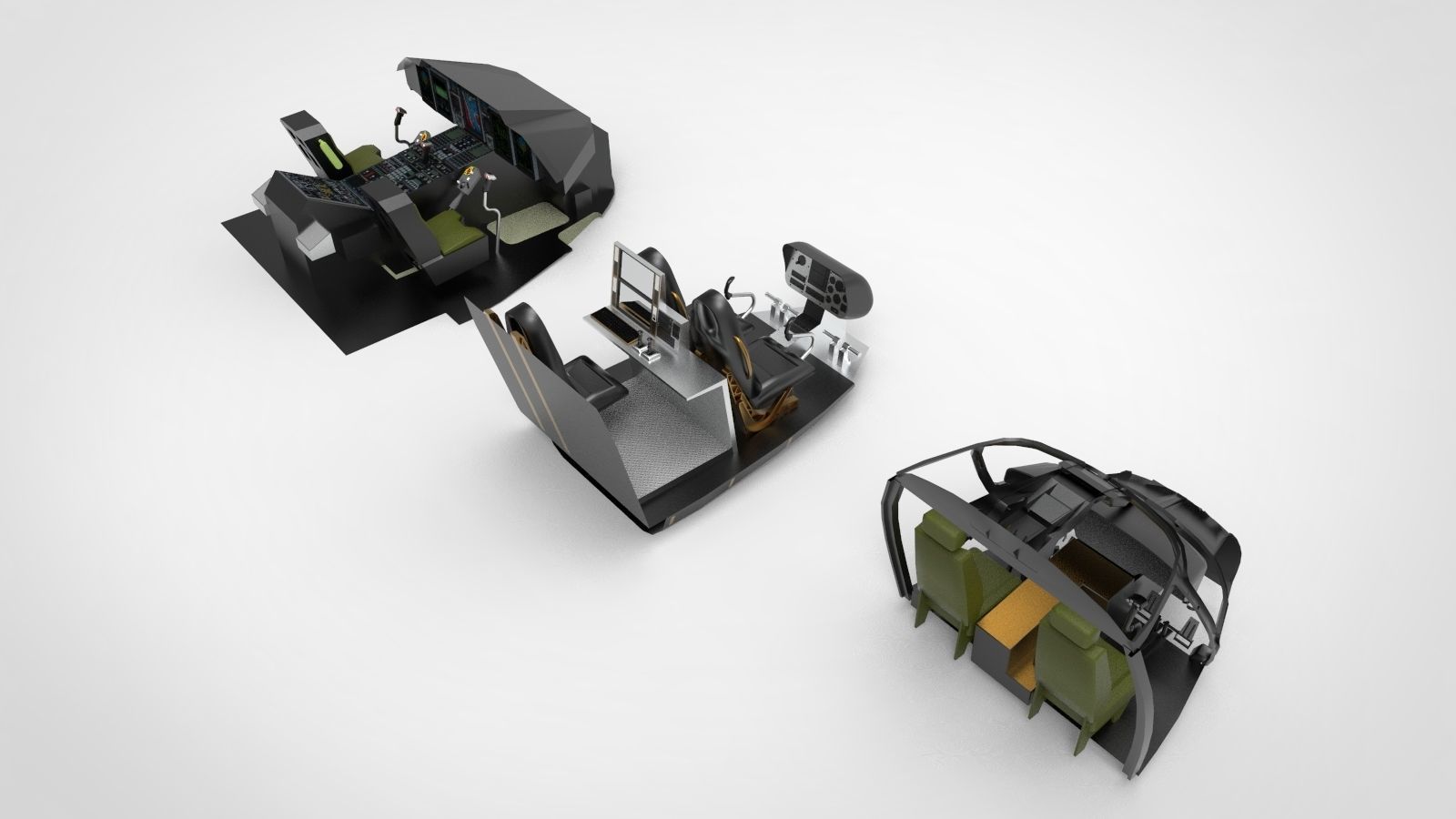
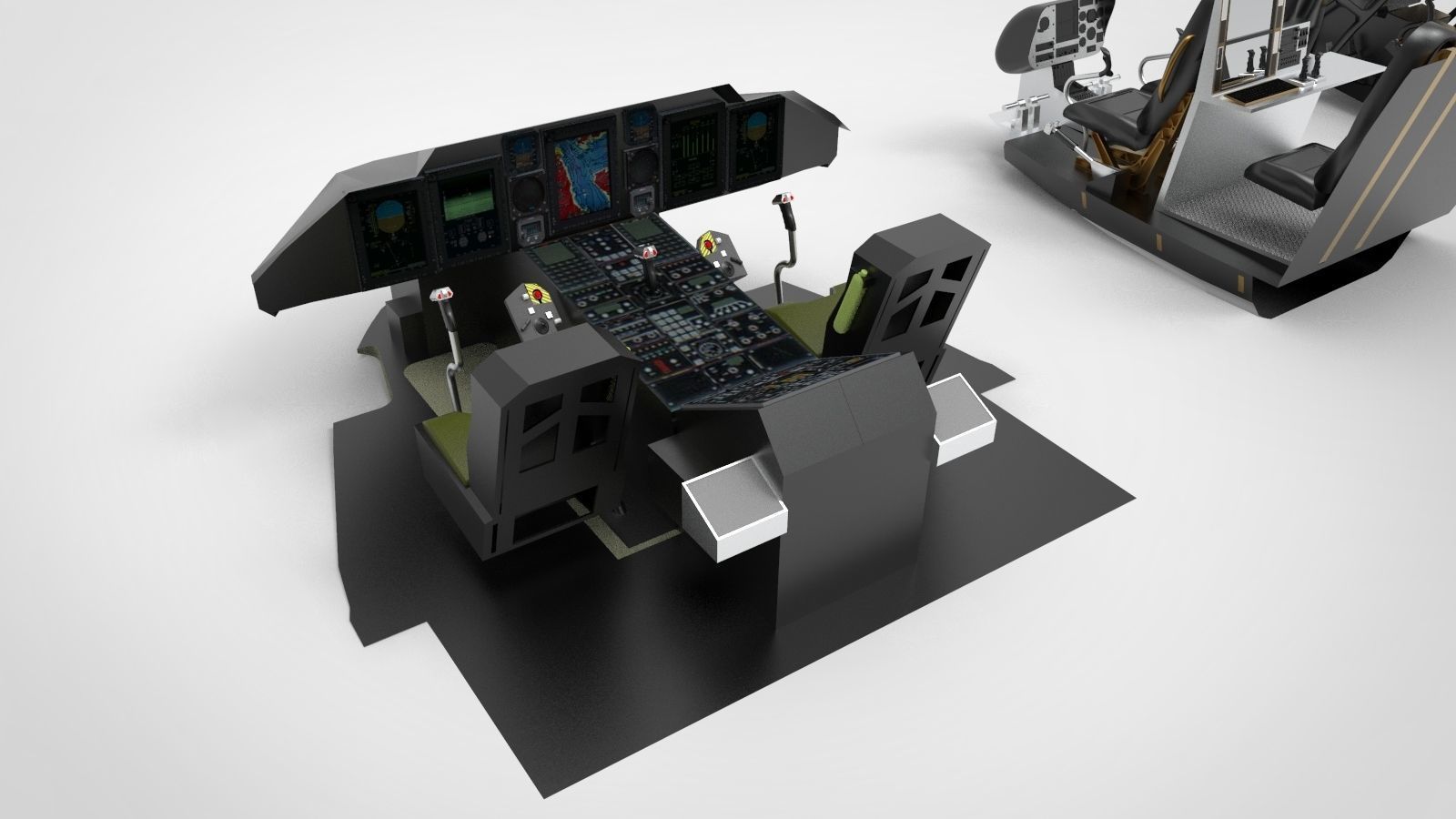
cockpit helicopter 3 type 3D model
Helicopters come with various types of cockpits, each designed to cater to specific operational requirements. Here are brief descriptions of three common types:
Conventional Cockpit: A conventional cockpit features a traditional layout with analogue instruments and manual flight controls. It provides a straightforward interface for the pilot, offering direct physical control over the helicopter's flight systems. This type of cockpit is commonly found in older or smaller helicopters, providing a simple and familiar operating environment.
Glass Cockpit: A glass cockpit, also known as a digital cockpit, employs advanced digital displays and integrated avionics systems. It replaces traditional analogue instruments with digital screens, offering a comprehensive and customizable presentation of flight data, navigation information, and aircraft systems. Glass cockpits enhance situational awareness, reduce pilot workload, and facilitate easier interpretation of critical flight information.
Integrated Cockpit: An integrated cockpit incorporates a combination of digital displays, advanced avionics, and fly-by-wire flight control systems. It offers a highly sophisticated interface that integrates all major flight functions into a single cohesive system. Integrated cockpits enhance pilot efficiency, safety, and mission capabilities by providing seamless interaction between flight controls, navigation systems, sensors, and mission-specific equipment.
Each type of cockpit provides distinct advantages and is tailored to the specific requirements of the helicopter's mission, technological advancements, and operator preferences. The choice of cockpit type depends on factors such as aircraft model, operational needs, and the desired level of automation and situational awareness.