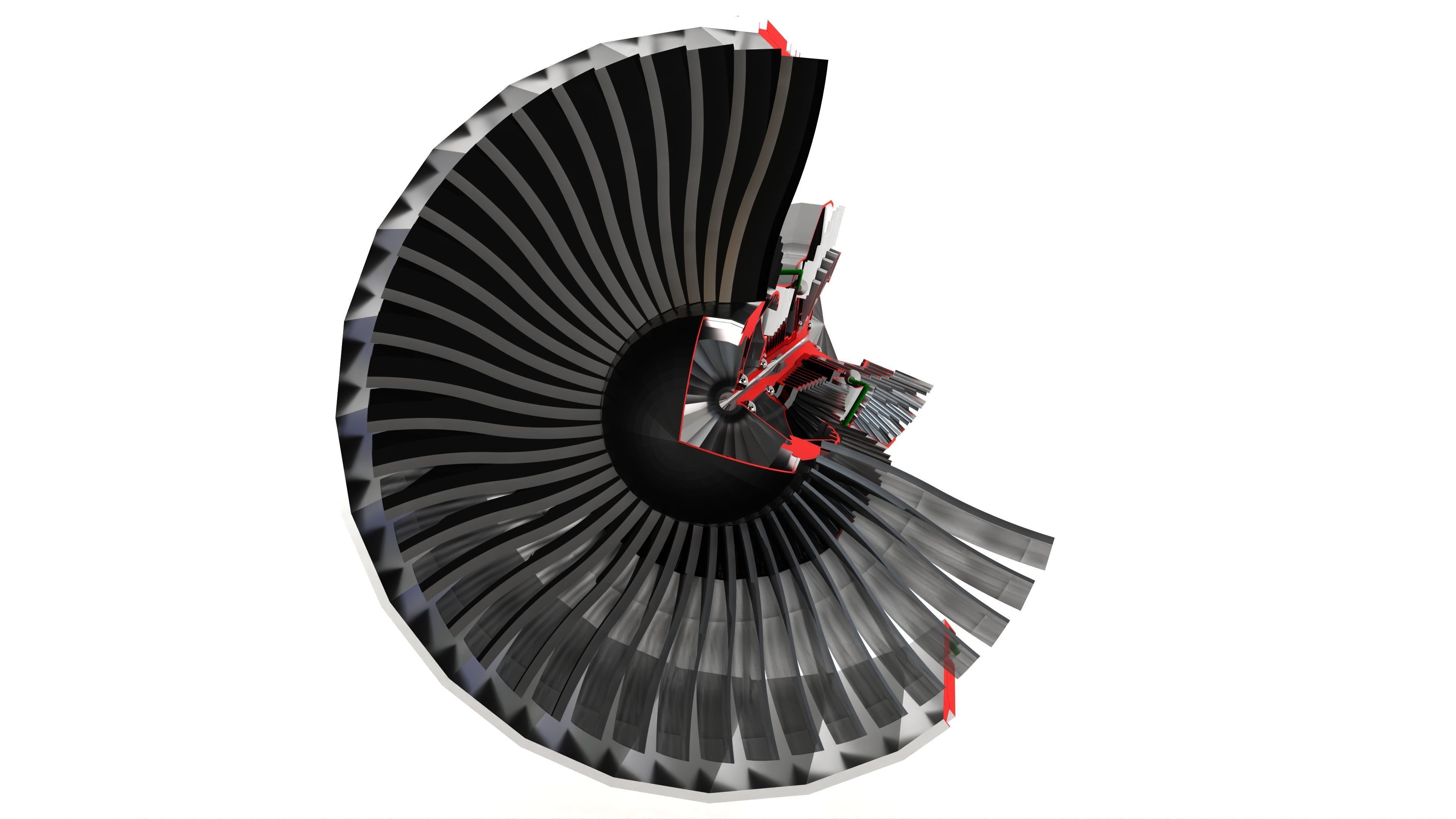
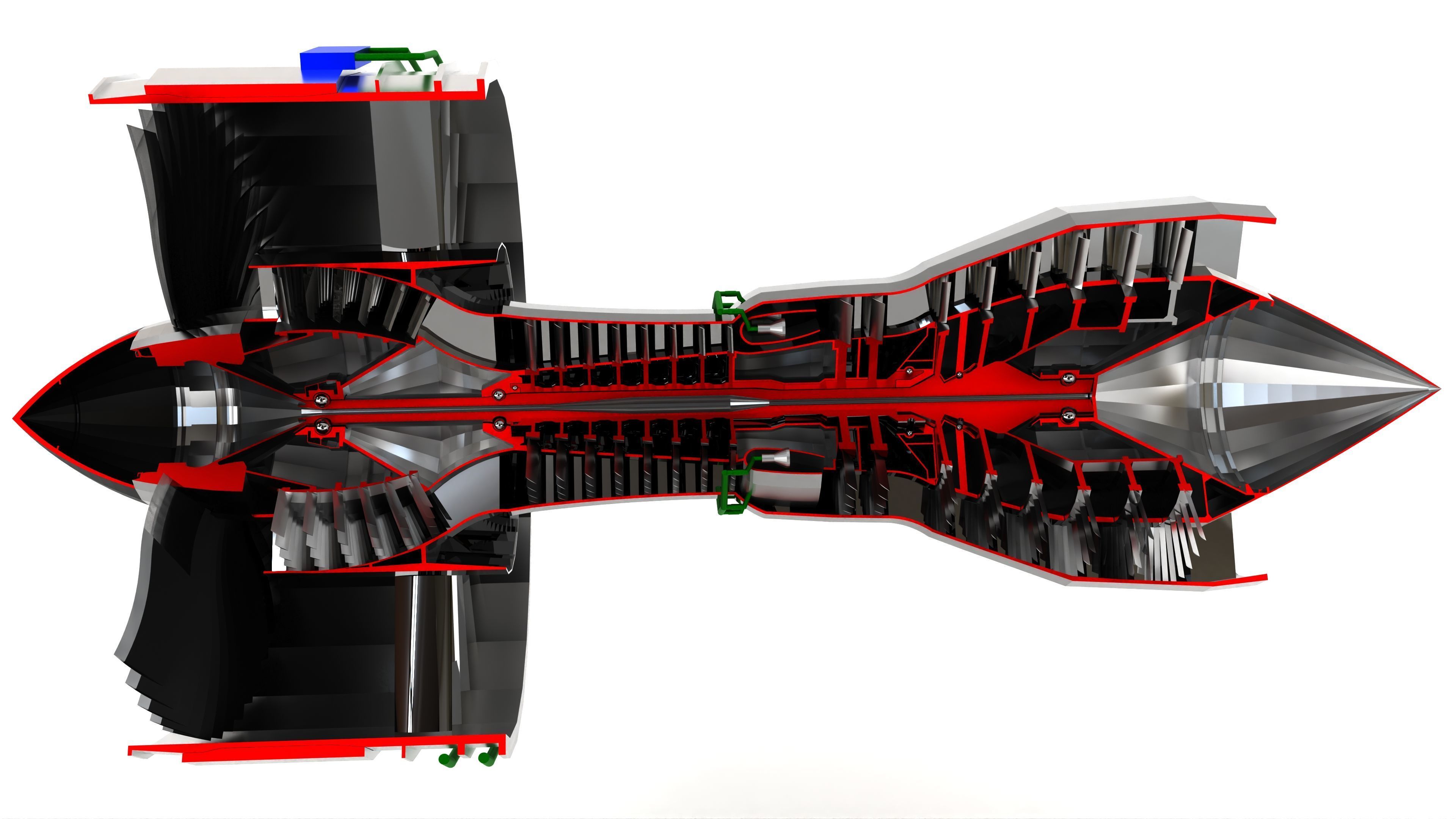
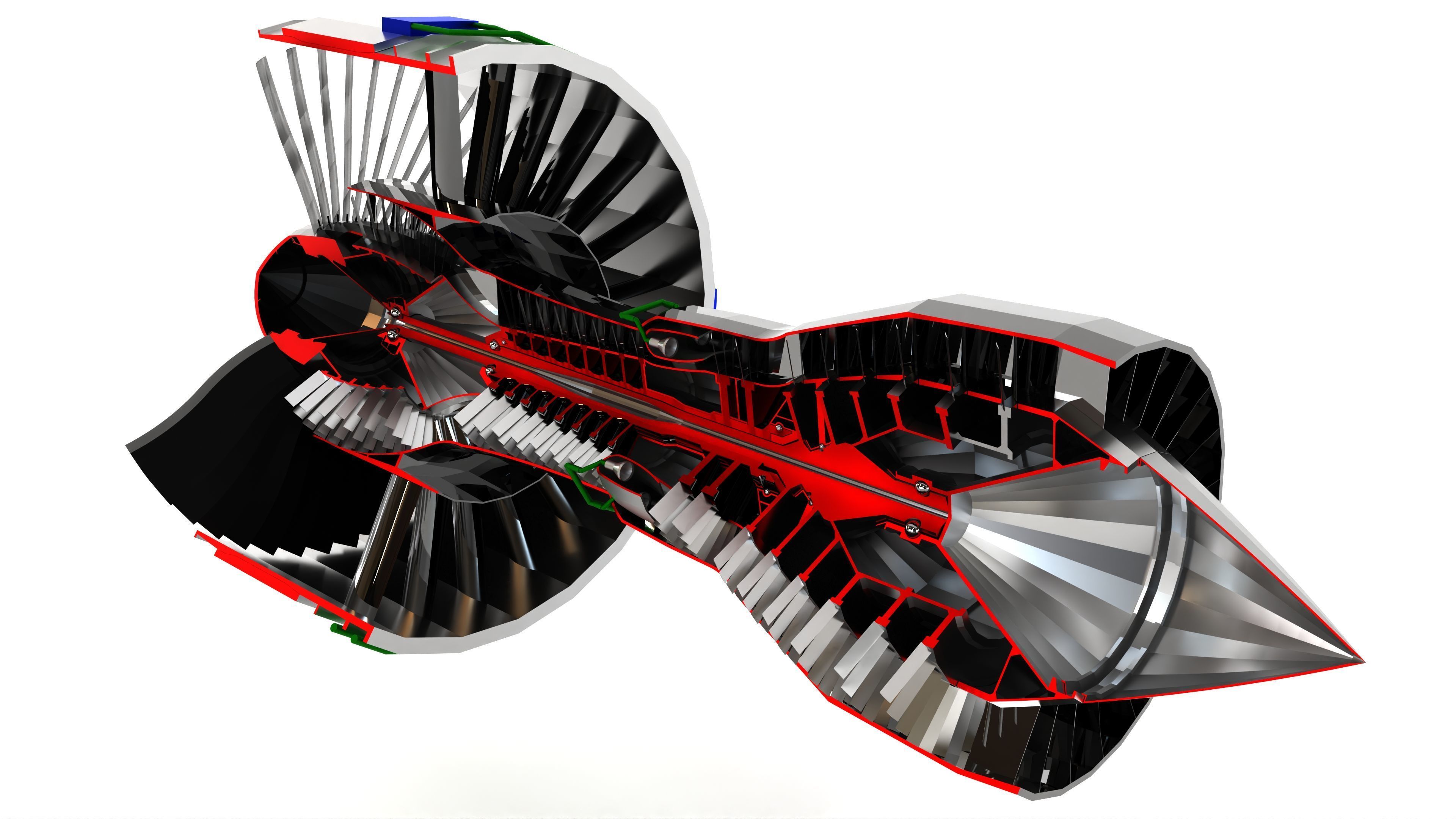
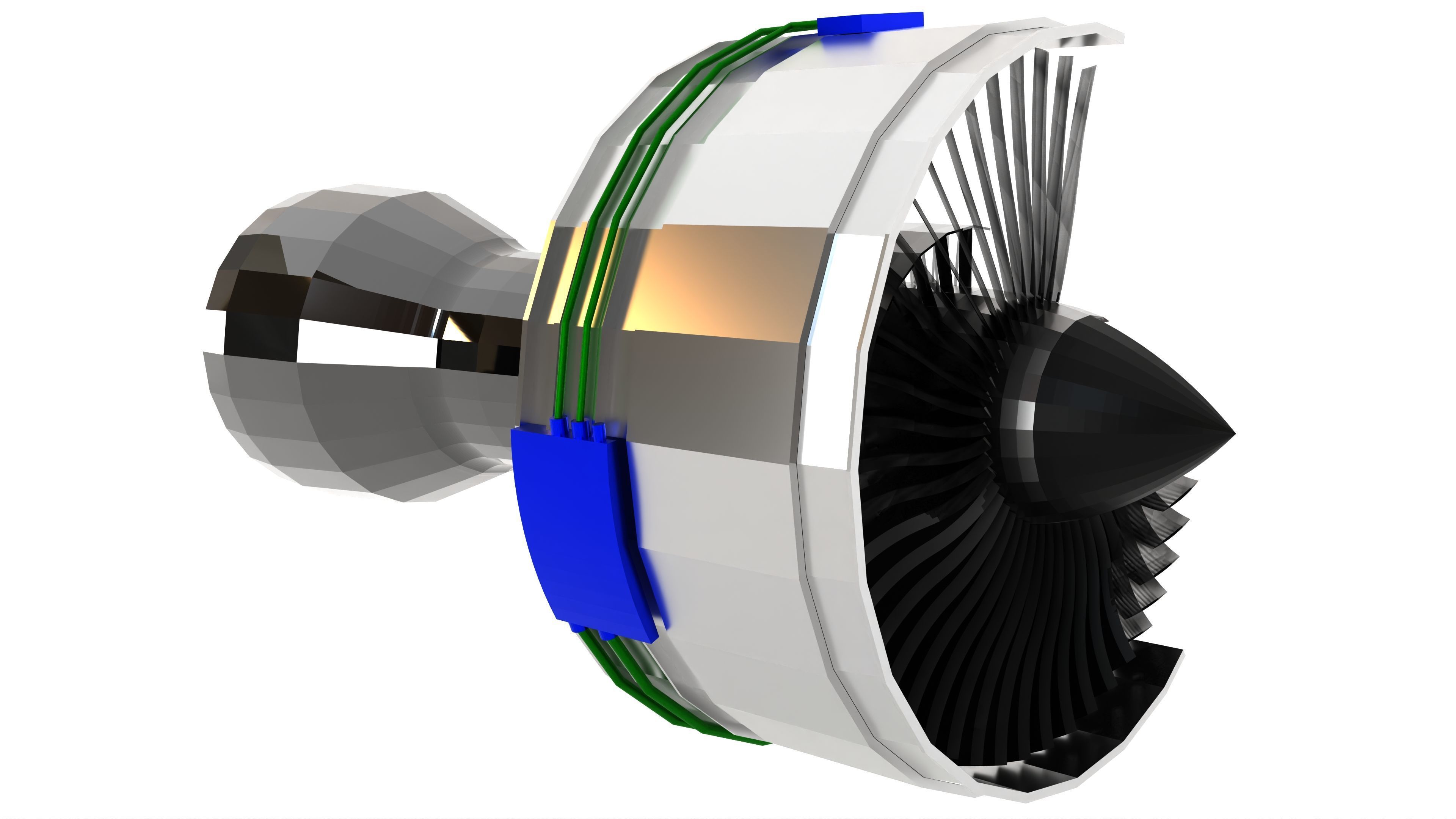
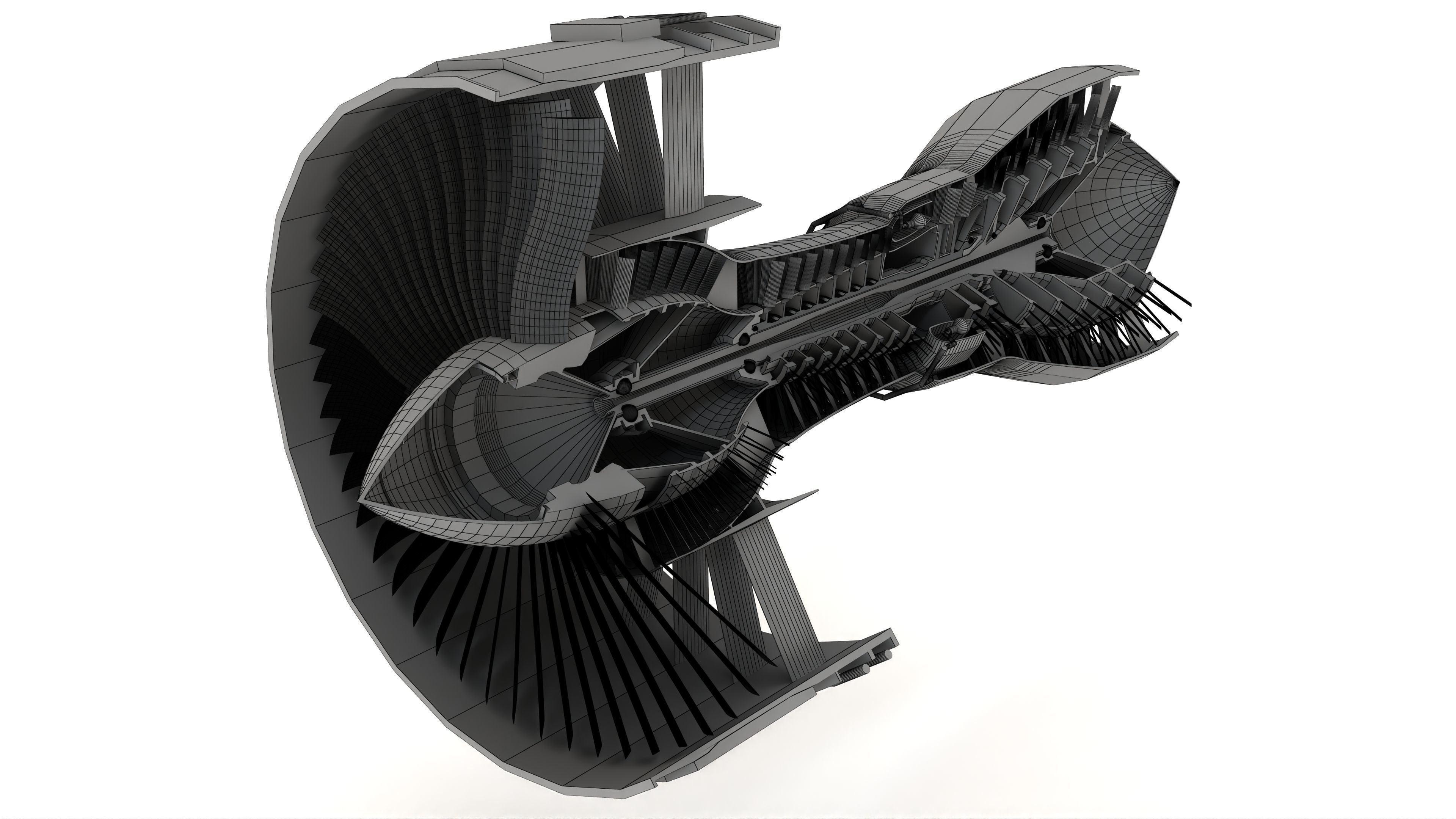
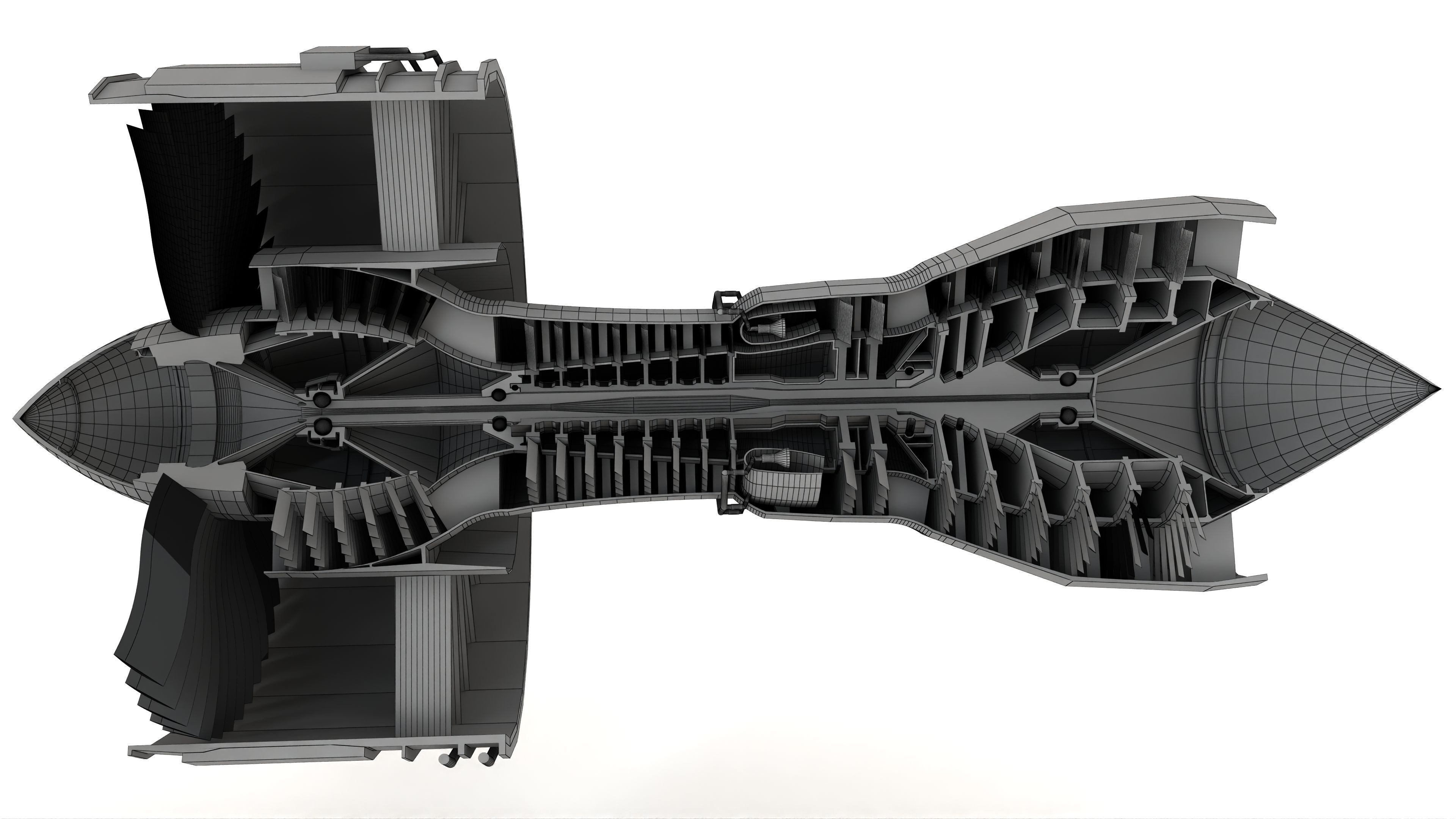
Turbofan Engine 3D model
This Turbofan Engine was modeled under 3Ds MAX 2020, the materials, Lighting and the rendering under V-Ray 7.
Short History of the Turbofan EngineThe turbofan engine is a modern jet propulsion system widely used in commercial and military aviation. Its development traces back to advancements in jet engine technology during the mid-20th century:
Origins in Turbojet Technology (1930s-1940s):Turbojet engines, which generate thrust by expelling hot exhaust gases at high speeds, were developed during World War II. Early turbojets, like the one in the German Me 262 and British Gloster Meteor, were effective but inefficient in fuel consumption.
Birth of the Turbofan (1950s):Engineers sought to improve efficiency and reduce noise. The turbofan emerged by incorporating a large fan at the front of a turbojet engine. The fan directs a portion of the air around the engine core, producing additional thrust (bypass thrust). This bypass air improves efficiency and reduces noise.
Early Commercial Applications (1960s):The first successful turbofan engine, the Rolls-Royce Conway, debuted in the late 1950s. It was quickly followed by engines like the Pratt & Whitney JT3D, which powered the Boeing 707 and Douglas DC-8, marking the turbofan's entry into commercial aviation.
High-Bypass Revolution (1970s-1980s):Advancements led to high-bypass turbofans, where a greater proportion of air bypasses the core. Engines like the General Electric CF6 and Rolls-Royce RB211 revolutionized long-haul aviation with enhanced fuel efficiency and quieter operation.
Modern Turbofan Innovations (1990s-Present):Today's turbofans, like the General Electric GE90 and Pratt & Whitney PW1000G, boast advanced materials, aerodynamic designs, and digital control systems. Ultra-high bypass engines focus on further reducing emissions and fuel consumption.
Future Directions:Efforts are underway to develop even more efficient turbofans using hybrid-electric systems and sustainable aviation fuels (SAF), emphasizing environmental sustainability.
The turbofan engine remains the cornerstone of modern aviation, balancing power, efficiency, and environmental considerations.