13 Aug 2013
3D Printing in Medicine: How Technology Will Save Your Life
Insight

I would not agree that the technological revolution inspired by 3D printing has already become self-evident. Recently 3D printing has been treated as the hot mainstream trend, but, believe me when I say this, there are thousands of people who are still not aware of this mind-blowing invention.
Obviously, the technology is under careful surveillance by scientists, designers, futurists, and hobbyists. No doubt, it will change our lives. 3D printing is already reshaping them. Before mid-1990s, the internet seemed like something that surpasses the boundaries of imagination, similarly to how today we read about liquid metal and rocket parts that soon will be 3D printed and it looks too far out.
Practitioners, theorists, and media cannot just stay calm and observe, so they have already launched discussions on the topic: is it really something that is going to turn a world upside down or is it just too much ado for nothing? Some so-called columnists compare 3D printing to Michelangelo's marble carvings and I think this expression is too strong, even if this hell's machine does half of a job instead of the artist. All in all, 3D printing invades more and more spheres of our casual lives. So, I guess, it is about the time to announce the fact that - folks, future is now. Not tomorrow. There is no tomorrow nowadays.
The Body Shop Kevin Hand
Since the ancient times people are looking for anything that could guarantee the eternal life. Alchemists definitely found the philosophical stone, but never shared it with mortals. Philosophers and writers went totally crazy, trying to discuss a matter of life and death.
And here...The New Age has come, when the philosophical stone turns into a 3D printer. Using living cells instead of the usual plastic material in the cartridge leads to bioprinting. Some scientists started doing it, using a regular printer, but literally just now technology opens the doors to the real achievements. If this genius idea proves to be successful, we will invite you to our personal body shop.
So, would it make the eternal life possible? CGTrader.com has thoroughly prepared a completely mind-blowing list of how 3D printing has already changed and facilitated all the branches of the medicine and what to expect in the future. Moreover, this article touches upon a controversial topic of artificial organs and the time of possible their transplantations. Keep reading!
Thousands of people do not realise that they have already become a part of 3D printing revolution. According to the report on 3D printing industry, there are more than 10,000,000 3D printed hearing aids circulating worldwide. 3D printing technology has absolutely improved their manufacturing process.
While earlier it involved a 9 step process and a huge input of time, the technology shortened it to 3 steps: scanning, modeling, and printing. Moreover, one machine is able to produce 30 hearing aids in one hour and a half. Surprise surprise, but evaluation of 3D printing technology usage for hearing aids manufacturing was started back in 1998. It is the actual revolution people have not heard about.

3D printing's contribution to orthodontics is enormously huge. Scientist Andrew Dawood, who works in Londons Wimpole Street, notices that before the 3D Printing has become the mainstream, "dentists have been using it for 10 years, to make things that really cant be made in any other way. So, we have digital dentistry here. If it is hard to imagine the process, watch a short video about 3D printing in orthodontics and it will be much more clear.
It helps to improve quality and speeds up the production. Technology enables the customer to get a transparent 3D printed teeth aligner for day-to-day use, on one's way to the dentist 3D printer is already printing out a new dental implant as well as dental crowns, bridges, stone models and a variety of orthodontic appliances. These improvements make serious sense, because I know no one, who likes these painful and long-lasting visits.
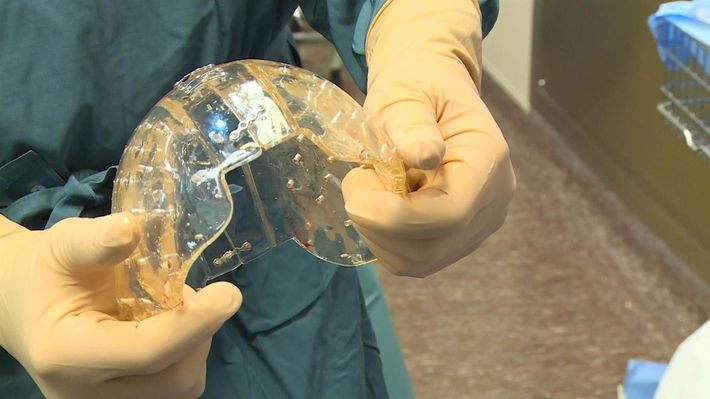
In early spring of this year, an American patient got a radical surgery performed and 75% of his skull was replaced with a 3D printed implant. This material was not only biocompatible but also a bone-like. Scott DeFelice, President and CEO of Oxford Performance Materials, announced that his company has serious plans that between 300 to 500 patients in the U.S. alone could have skull replacement surgeries each month. Last year an 83-year old woman has received the very first titanium jaw implant manufactured with 3D printer.
Moreover, recently a 3D printed biopolymer of windpipe has been surgically sewn as a splint in baby's airways. After two to three years it will be fully absorbed in the body's breathing system.
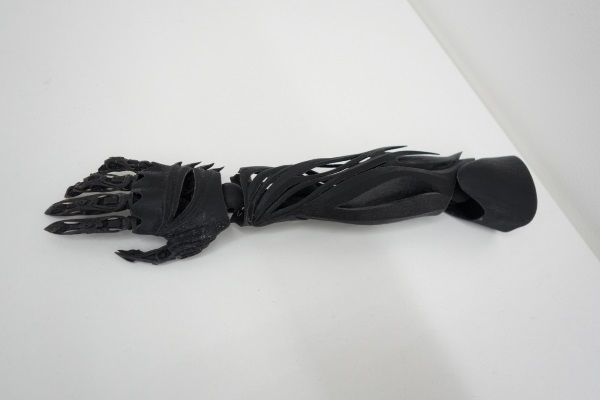

Accidents happen everyday and no one is protected from it. But IF something happens, the costs include not only the health damage, but also loads of time and money. Billions of people are in an urgent need of prosthesis, but not all of them are able to afford these surrogate body parts. Thanks to 3D printing, prosthetics becomes faster in production process, cheaper and it is the best way to solve a matter of children prosthestics: when they are growing up, it is easier and not that expensive to change a prosthesis regularly. Here I would like to highlight three particular and extremely inspiring cases.
Eric Moger was the first person to start a life once again with 3D printed face.
A famous Robohand project has proved that anything is possible. The idea was a goal to reach by Richard Van As from South Africa and he finally come up with the concept how to produce necessary hand prosthesis quickly, quite cheaply, and make it accessible to the wide society.
Meet Buttercup, the first and only bird that has 3D printed leg prosthesis ( Youtube footage).
Thanks to 3D printing and devoted designers, Buttercup has experienced the freedom of walking for the first time. Moreover, this duck is the worldwide superstar, that got an award for honours. Just creepy amazing. Get Rid of Itchy and Stinky Plaster Casts!

To tell you a secret, I have never broken any of my limbs. But honestly, I was quite jealous for my friends to have a plaster cast and let anyone to leave some images or notes on it. I was imagining that I would keep that thing long years in a closet after a removal procedure. So, 3D printing invades even this sphere with the a new slogan: light, breathable, washable and recyclable! In U.S. a single fracture happens each 5 seconds.
And here comes the Cortex dubbed Exoskeletal Cast that is still in process. Soon if you break a hand or a leg, you can still keep your style. Seriously, Jake Evill a graduate from the Architecture and Design School in New Zealand, found a way how to substitute the old plasters. A patient enters an emergency room, gets the standard X-ray and a 3D scan of the affected limb. Then the data is sent to the computer to create the individual design, based on the shape of the person's limb with some extra reinforcement around the are of the fracture.
After a while the patient gets her own nylon exoskeletal cast that is snapped into an exact place around the fractured limb. And that's the story.
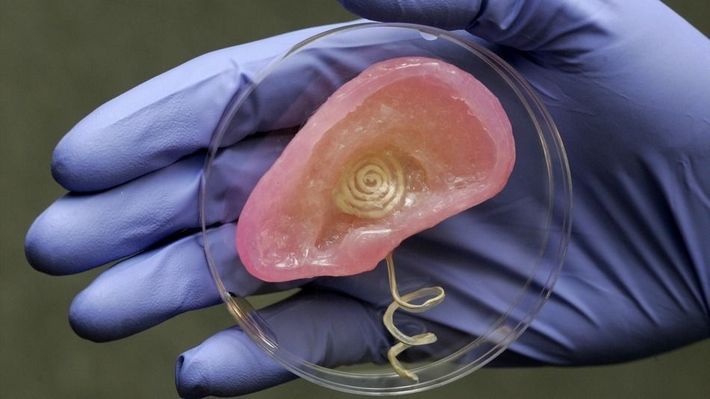
When researchers from Princeton and John Hopkins get together, expect the Big Bang. This time they met to grow an ear. Read again if you think you misread. The hearing, however, is done with electronics, but still it would help deaf people to hear the sound. World starts whispering about the cyborgs and human chimeras. On one hand it is absolutely artificial ear, but skeletal 3D structure is seeded with cartilage cells and 10 weeks later, you have a fully formed ear.
Hurray! An ear becomes stronger and is fulfilled with alive and vibrant cells. Moreover, it sounds weird, but it also has an antenna which is extremely sensitive to the microwaves. It means, that a touch of a skilled scientist would be enough to turn an ear into a satellite finder, allowing a human to hear radio, TV and other electromagnetic signals.
The body must supply it with nutrients (blood vessels) if you want to finally stick the ear on someone's head. So, once the blood vessels are in place, skin will be doable. It sounds like a sci-fi scenario, but the further we go, the more fantastical everything looks like.
Firstly, it is important to note that embryonic stem cells are the unique ones. They are derived from early stage embryos and are capable of transforming into any tissue in the body: brain tissue, muscle or a bone. Thus, the fact is that the scientists are not only thinking about the possible ways to create the artificial organs, but they are also step by step moving towards it.
3D printing enabled the group of Heriot-Watt University scientists to produce clusters of embryonic stem cells. The scientists used the method of valve-based printing in order to keep these cells in high level of viability, to stay accurate to produce spheroids of uniform size and to maintain their pluripotency that addresses to differentiation into any other cell type.
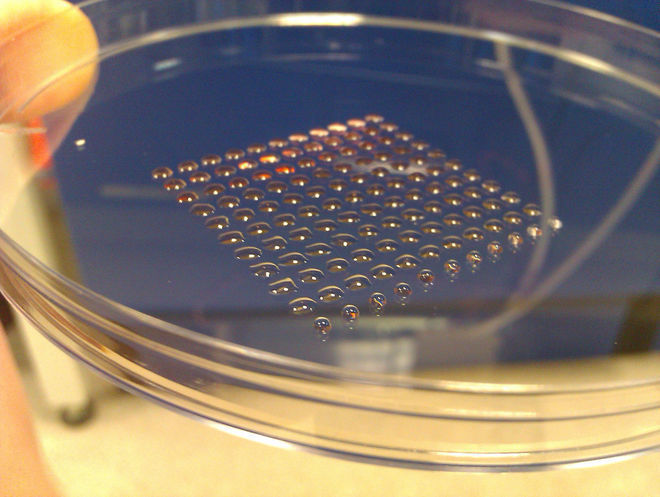
In the picture above you can see aggregated embryonic stem cells after 24 hours (left) and after 48 hours (right). Artificial organs are still in the near future, but this achievement is extremely significant for drug testing purposes while using artificial human tissue or even printing cells directly inside the body.
Everyone knows that wear of knee joints is a big and painful problem. So, the human body's own cartilage is still the best material for lining knee joints. Researchers at St. Vincent's Hospital in Melbourne, managed to harvest cartilage from stem cells that are taken from tissue under the kneecap.
With the help of 3D printing, researchers created a 3D scaffold to grown cartilage cells on, so pea-sized spheres of cartilage were grown over 28 days. Unfortunately, this kind of tissue still lacks of its own blood supply, so in a case of cancer or car accident, it would not repair itself.

The highest goal of the technology is to save lives. From 3D printed food and plastic wrenches, technology moves straight to artificial blood cell printing and represents the important step in the development of artificial organ transplants since the current generation of artificial organs lack the vascular network needed to function properly. Scientists from Germans' Fraunhofer Institute use the particular technique that involves artificial biological molecules printed out with a 3D inkjet printer, then they form the shape of blood vessels.
This technology is still quite imprecise for the fine structures of capillary vessels, so the scientists use the laser to zap the molecules and to form the material. Real blood vessels have two layers as well as the artificial ones, so they can form complex branching structures.
There are a bunch of labs, working on blood vessels to produce. One of them found sugar as the best component for the structure to avoid any seams. Moreover, 3D printed blood vessels could also serve as organic bypasses for people with clogged arteries or as replacement capillaries for smokers. Hey, smokers, do not gloat too much and do not increase the number of daily cigarettes to smoke.

Skin graft transplantation is nothing new in the medicine. It has become casual but extremely painful procedure, while a part of healthy skin is removed to cover the damaged place of a body. As 3D printing technology has enabled scientists to play even with the most futuristic ideas, they come up with one: to produce the artificial skin. Researchers at the University of Toronto have developed a method of loading skin cells and various polymers into 3D printer to artificially create thick layers of skin.
Moreover, the scientists from the Institute of Regenerative Medicine at Wake Forest University in Winston-Salem, North Carolina aim to print skin directly onto burn wounds. Professor James Yoo and his team were highly inspired to keep developing a portable bioprinting system by the injuries brought from the battlefields in Iraq and Afghanistan, where around 30 % of injuries involve the skin.

18 people die everyday in the U.S. waiting for a transplant. I am not brave enough to count the continents that are left behind. Each small step in the field of medicine, using 3D printing, brings the scientists a bit closer to the main goal: to begin growing organs. A surgeon Anthony Atala has demonstrated an early-stage experiment at a 2011 TED Talk, where he printed a prototype human kidney.
This primitive organ produces urine-like substance only. Actually, Wake Forest Institute For Regeneration works on more than 30 different replacement tissues and organs, including bladder, cartilage, trachea and heart healing therapies to cure the disease. Using the same technology Atala's young patient 10 years ago has received an engineered bladder. It actually was the first lab-grown organ to be implanted into a human. Find out, how Anthony Atala has printed human kidney on stage.
The world's first artificial liver is already on its' way. Heriot-Watt University team and dr. Will Shu are intensively experimenting towards it. Firstly, they seek to use these artificial liver for drug testing in order to avoid drastic cuts of animal lives and get life-saving medicine to the clinic faster. This process aims to develop miniature human liver tissues - where finally 'livers-on-a-chip' can be highly improved using technology that will print cells in 3D onto testing surfaces.

San Diego-based Organovo team has already managed to create mini-livers that are half a millimeter deep and and 4 millimeters wide. The researchers used a gel to build three types of liver cells and arranged them into the same kind of 3D cell architecture found in a human liver. Company's ultimate goal is to create human-sized structures suitable for transplant. Moreover, the big hurdle is being able to print larger branched networks of blood vessels to nourish such an organ.
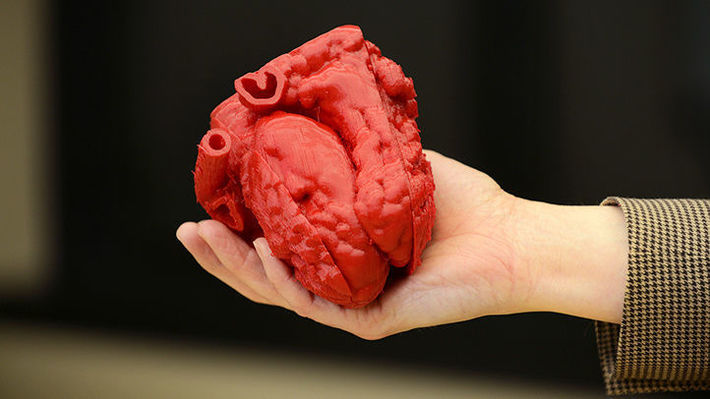
No, I am not going to announce that, guys, you know, recently scientists have 3D printed a heart out. This crucial moment is still in the future. Most of the researchers predict it in the next decade. By now the technology is being used to produce heart replicas that are extremely helpful in the area of surgery. Doctors possess data from individual patients and convey it to 3D printer that is able to replicate the organs of particular individuals, reflecting their personal intricacies and deformities. So, the device synthesizes images from CT scans or ultrasounds, translating that information into thin layers of plastic that are stacked until they form a 3D object.
When a surgeon holds a heart of a particular patient, he is able to make connections that were not possible to make just staring at the computer screen. Moreover, doctors may prepare for the really serious cardiological operations, 3D printing a replica that differs in thickness of layers. So, it is able to imitate a valve, a surrounding tissue and the bone. This way helps a lot, while saving time of the operations and providing assurance.
Seemingly, the plots of the greatest sci-fi books and movies are already taking a place on the Earth. Firstly, a mobile phone has become a must-have item and nowadays it even reveals some facts about the person, who uses it. A decade ago we had a second mind-blowing challenge to accept the internet in our daily use. Now we cannot imagine our lives without. If it disappears, millions of offices could close down for a while.
Here comes 3D printing with the shocking news that the world can be 3D printable and in 10 years 3D printed artificial organs will surprise no one. Oh well, I am already looking towards the revolution of the fourth dimension.
Interested in selling 3D models? Request a free e-guide below and learn all the tricks to make money off your talent:
Comments